Difference between revisions of "BMP terminology"
m |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
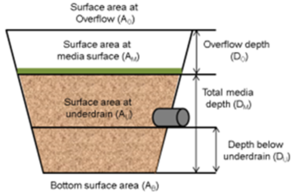
[[File:BMP terminology 2.png|300px|thumb|alt=image showing BMP terms|<font size=3>Schematic illustrating some of the terms and dimensions used in the Stormwater Manual.</font size>]] | [[File:BMP terminology 2.png|300px|thumb|alt=image showing BMP terms|<font size=3>Schematic illustrating some of the terms and dimensions used in the Stormwater Manual.</font size>]] | ||
| − | *Bottom surface area (A<sub>B</sub>): This is the surface area at the bottom of the engineered media in a BMP. It represents the area where the engineered media changes to native soils. Units are typically in square feet. | + | *Bottom surface area (A<sub>B</sub>): This is the surface area at the bottom of the engineered media in a BMP. It represents the area where the engineered media changes to native soils. Units are typically in square feet. Engineered media is used in nearly all structural BMPs and includes media designed for vegetation (e.g. [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Materials_specifications_-_filter_media bioretention, [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Design_guidelines_for_soil_characteristics_-_tree_trenches_and_tree_boxes#Soil_quality_guidelines tree trenches/tree boxes], [green roofs]) |
*Canopy projection (CP): The tree canopy diameter at maturity. CP varies with species. | *Canopy projection (CP): The tree canopy diameter at maturity. CP varies with species. | ||
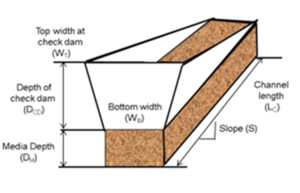
*Channel length (L<sub>C</sub>): This is the length of the swale channel from the furthest upstream point to the furthest downstream point. Units are typically in feet. | *Channel length (L<sub>C</sub>): This is the length of the swale channel from the furthest upstream point to the furthest downstream point. Units are typically in feet. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
*Total media depth (D<sub>M</sub>): This is the depth of the engineered media between the media surface and the native soils. Units are typically in feet. | *Total media depth (D<sub>M</sub>): This is the depth of the engineered media between the media surface and the native soils. Units are typically in feet. | ||
*Volume reduction below underdrain (V<sub>U</sub>): The volume of water that can be instantaneously stored in the media beneath an underdrain and above the native soil and that will infiltrate into the underlying soil. This volume is equal to the volume of the media below the underdrain and above the native soil times the difference between porosity and field capacity. | *Volume reduction below underdrain (V<sub>U</sub>): The volume of water that can be instantaneously stored in the media beneath an underdrain and above the native soil and that will infiltrate into the underlying soil. This volume is equal to the volume of the media below the underdrain and above the native soil times the difference between porosity and field capacity. | ||
| − | *Volume reduction from ET (V<sub>ET</sub>): Evapotranspiration (ET) of the portion of the water stored in the media between field capacity and wilting point. The volume of water lost through evapotranspiration ( | + | *Volume reduction from ET (V<sub>ET</sub>): Evapotranspiration (ET) of the portion of the water stored in the media between field capacity and wilting point. The volume of water lost through evapotranspiration (V<sub>ET</sub>) is assumed to be the smaller of two calculated values, potential ET and measured ET. Units are typically in cubic feet. |
*Volume reduction from basin bottom (V<sub>inf<sub>b</sub></sub>): Water that infiltrates through the bottom soils rather than pass through the underdrain. Units are typically in cubic feet. | *Volume reduction from basin bottom (V<sub>inf<sub>b</sub></sub>): Water that infiltrates through the bottom soils rather than pass through the underdrain. Units are typically in cubic feet. | ||
| − | *Volume reduction from basin sides (V<sub>inf<sub>s</sub></sub>): Under saturated conditions within the filter media, water that infiltrates through any existing sloped sidewalls of the basin as the stormwater draws down through the underdrain. Stormwater lost from a sloped sidewall (Vinfs) is considered to infiltrate vertically into the surrounding soil. Units are typically in | + | *Volume reduction from basin sides (V<sub>inf<sub>s</sub></sub>): Under saturated conditions within the filter media, water that infiltrates through any existing sloped sidewalls of the basin as the stormwater draws down through the underdrain. Stormwater lost from a sloped sidewall (Vinfs) is considered to infiltrate vertically into the surrounding soil. Units are typically in cubic feet. |
*Volume capacity of a bioretention base (V<sub>BB</sub>): a layer of engineered soils above the native soils in a swale, capable of storing water and allowing it to infiltrate into the underlying native soils | *Volume capacity of a bioretention base (V<sub>BB</sub>): a layer of engineered soils above the native soils in a swale, capable of storing water and allowing it to infiltrate into the underlying native soils | ||
| − | *Volume reduction capacity achieved through infiltration along the swale main channel ( | + | *Volume reduction capacity achieved through infiltration along the swale main channel (V<sub>MC</sub>): |
*Volume reduction capacity of a BMP (V): The total volume reduced by a BMP. Encompasses infiltration, ET, and interception, depending on the BMP. Units are typically in cubic feet. | *Volume reduction capacity of a BMP (V): The total volume reduced by a BMP. Encompasses infiltration, ET, and interception, depending on the BMP. Units are typically in cubic feet. | ||
*Volume reduction from interception (V<sub>I</sub>): The volume of water intercepted by a tree canopy. Intercepted water may evaporate or be slowly released such that it does not contribute to stormwater runoff. Units are typically in cubic feet. | *Volume reduction from interception (V<sub>I</sub>): The volume of water intercepted by a tree canopy. Intercepted water may evaporate or be slowly released such that it does not contribute to stormwater runoff. Units are typically in cubic feet. | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 22 January 2015
- Bottom surface area (AB): This is the surface area at the bottom of the engineered media in a BMP. It represents the area where the engineered media changes to native soils. Units are typically in square feet. Engineered media is used in nearly all structural BMPs and includes media designed for vegetation (e.g. bioretention, [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Design_guidelines_for_soil_characteristics_-_tree_trenches_and_tree_boxes#Soil_quality_guidelines tree trenches/tree boxes, [green roofs])
- Canopy projection (CP): The tree canopy diameter at maturity. CP varies with species.
- Channel length (LC): This is the length of the swale channel from the furthest upstream point to the furthest downstream point. Units are typically in feet.
- Channel slope (S): This is the slope of the channel. Units are typically in percent. The slope is calculated by taking the difference between vertical elevations at the upstream and downstream points of the swale and dividing by the horizontal distance between the two locations. The slope therefore represents an average slope over the length of the swale.
- DDTcalc: The time from the high water level in a BMP to 1 to 2 inches above the bottom of the facility at the lowest part of the BMP. Units are typically in hours.
- Depth at check dam (DCD): The elevation change between the overflow point of the check dam (top of check dam) and the soil surface of the swale. Units are typically in feet.
- Depth below underdrain (DU): The depth of the media between the underdrain invert and the native soils. Units are typically in feet.
- Interception capacity (IC): Depth of water (precipitation) that is intercepted by a tree. Average values used in the MIDS calculator are 0.043 inches for deciduous trees and 0.087 inches for conifers. Units are typically in inches.
- Infiltration rate of native soils (IR): The rate at which water infiltrates into soils beneath a BMP. Usually assumed to be equal to the saturated hydraulic conductivity for a soil. Typically expressed in inches per hour.
- Leaf area index (LAI): a dimensionless quantity that characterizes plant canopies, defined as the one-sided green leaf area per unit ground surface area (LAI = leaf area / ground area, m2 / m2) in broadleaf canopies. Varies with tree type and tree size.
- Measured ET (ETmea): The amount of water lost to ET as measured using available data. Units are typically cubic feet.
- Media field capacity minus wilting point (FC-WP): This is the amount of water between field capacity and the permanent wilting point stored in the media above the underdrain. This is water often considered to be available for uptake by plants. If multiple types of media are used in the BMP, this value should be a weighted average of the soil water storage values of the media installed above the underdrain. Values for field capacity and wilting point based on soil type can be found here. Units are typically in cubic feet of water per cubic feet of media. The recommended range for this value is 0.05 to 0.17.
- Media porosity minus field capacity (n - FC): This is the amount of water between media porosity and field capacity stored in the media between the underdrain invert and the bottom of the media (top of native soil). If multiple types of media are used in the BMP, this value should be a weighted average of the soil water storage values of the media installed between the underdrain and the native soils. Values for porosity and field capacity based on soil type can be found here. Units are typically in cubic feet of pore space per cubic feet of media. The recommended range for this value is 0.15 to 0.35.
- Media surface area (AM): This is the surface area at the bottom of the ponded water within a BMP. This is therefore the area at the surface of the engineered media. Units are typically in square feet.
- Overflow depth (DO): This is the maximum depth of ponded water within a BMP (i.e., vertical distance from the overflow elevation to the top of the soil or media). Units are typically in feet.
- Potential ET (ETpot): The amount of water stored between field capacity and the wilting point in the media above the underdrain. This water is assumed to be taken up by plants and evapotranspired. Units are typically cubic feet.
- Side slope (H:V): The ratio between the horizontal (H) and vertical (V) components of a side slope (H:V).
- Soil volume per tree (SV): The soil volume available for each individual tree in a tree trench system. Units are typically cubic feet
- Storage volume behind a check dam (VCD): The volume of ponded water in a swale main channel stored behind a check dam that will infiltrate into the soils.
- Surface area at overflow (AO): This is the surface area of the BMP at the lowest outlet point of the surface overflow from the ponding area of the BMP. Units are typically in square feet.
- Surface area at underdrain (AU): This is the surface area of the BMP at the invert elevation of the underdrain. Units are in typically square feet.
- Swale bottom width (WB): This is the average bottom width of the swale main channel. Units are typically in feet.
- Top width at check dam (WT): This is the width of the check dam at the overflow elevation (top of check dam) and is used to calculate the storage volume behind the check dam. Units are typically in feet.
- Total media depth (DM): This is the depth of the engineered media between the media surface and the native soils. Units are typically in feet.
- Volume reduction below underdrain (VU): The volume of water that can be instantaneously stored in the media beneath an underdrain and above the native soil and that will infiltrate into the underlying soil. This volume is equal to the volume of the media below the underdrain and above the native soil times the difference between porosity and field capacity.
- Volume reduction from ET (VET): Evapotranspiration (ET) of the portion of the water stored in the media between field capacity and wilting point. The volume of water lost through evapotranspiration (VET) is assumed to be the smaller of two calculated values, potential ET and measured ET. Units are typically in cubic feet.
- Volume reduction from basin bottom (Vinfb): Water that infiltrates through the bottom soils rather than pass through the underdrain. Units are typically in cubic feet.
- Volume reduction from basin sides (Vinfs): Under saturated conditions within the filter media, water that infiltrates through any existing sloped sidewalls of the basin as the stormwater draws down through the underdrain. Stormwater lost from a sloped sidewall (Vinfs) is considered to infiltrate vertically into the surrounding soil. Units are typically in cubic feet.
- Volume capacity of a bioretention base (VBB): a layer of engineered soils above the native soils in a swale, capable of storing water and allowing it to infiltrate into the underlying native soils
- Volume reduction capacity achieved through infiltration along the swale main channel (VMC):
- Volume reduction capacity of a BMP (V): The total volume reduced by a BMP. Encompasses infiltration, ET, and interception, depending on the BMP. Units are typically in cubic feet.
- Volume reduction from interception (VI): The volume of water intercepted by a tree canopy. Intercepted water may evaporate or be slowly released such that it does not contribute to stormwater runoff. Units are typically in cubic feet.