Difference between revisions of "Guidance and recommendations for conducting a higher level of engineering review for stormwater infiltration in DWSMAs and Wellhead Protection Areas"
m (→Example 1) |
m |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:Technical information page image.png|right|100px|alt=image]] | ||
| + | |||
The Construction Stormwater Permit requires a higher level of engineering review for proposed infiltration projects in areas overlying an Emergency Response Area (ERA) where the vulnerability of the DWSMA (Drinking Water Supply Management Area) is classified as moderate, or in areas outside the ERA where the vulnerability of the DWSMA (Drinking Water Supply Management Area) is classified as high or very high. This page provide guidance and recommendations for conducting a higher level of engineering review. | The Construction Stormwater Permit requires a higher level of engineering review for proposed infiltration projects in areas overlying an Emergency Response Area (ERA) where the vulnerability of the DWSMA (Drinking Water Supply Management Area) is classified as moderate, or in areas outside the ERA where the vulnerability of the DWSMA (Drinking Water Supply Management Area) is classified as high or very high. This page provide guidance and recommendations for conducting a higher level of engineering review. | ||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
The types of detailed geological investigations suggested under Condition 1 above could be very beneficial to public water suppliers and the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) when it comes time to re-assess the vulnerability of the ERA and DWSMA during wellhead protection plan amendment, which occurs every 10-years. If you conduct a higher engineering review, please consider submitting the data and/or reports associated with such investigations to MDH or MPCA. Similarly, if you complete a well-receptor survey under Condition 2 above, please consider providing this information to MDH or MPCA. All wellhead protection plans include an assessment of wells within the DWSMA, and any receptor survey results could be beneficial towards those efforts. | The types of detailed geological investigations suggested under Condition 1 above could be very beneficial to public water suppliers and the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) when it comes time to re-assess the vulnerability of the ERA and DWSMA during wellhead protection plan amendment, which occurs every 10-years. If you conduct a higher engineering review, please consider submitting the data and/or reports associated with such investigations to MDH or MPCA. Similarly, if you complete a well-receptor survey under Condition 2 above, please consider providing this information to MDH or MPCA. All wellhead protection plans include an assessment of wells within the DWSMA, and any receptor survey results could be beneficial towards those efforts. | ||
| − | + | ==Examples== | |
| + | {{alert|The following examples were developed by MPCA as guides for conducting a higher level of engineering review. In developing these examples, we did not conduct a thorough search of material that would assist in the review. There may therefore be additional materials available, such as specific wellhead protection plans or other maps and reports, that were not utilized in these examples but should be utilized in a more rigorous analysis.|alert-warning}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following examples represent hypothetical situations. The analysis and recommendations are based on professional judgement by MPCA staff. It is highly recommended that licensed geologists or engineers perform these analyses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In general, a higher level of engineering review should include the following: | ||
| + | *identifying the aquifer(s) of concern; | ||
| + | *determining direction of flow in the aquifer(s) of concern; | ||
| + | *determining wells down-gradient of the proposed infiltration practice(s); | ||
| + | *determining the likelihood that contaminants will move vertically through the unsaturated zone and into the aquifer(s) of concern; and | ||
| + | *determining time of travel for water within the aquifer(s) of concern. | ||
| − | + | Depending on site conditions, additional considerations include the following: | |
| − | + | *land use in the vicinity of the proposed infiltration practice; | |
| + | *the type of practice proposed; and | ||
| + | *existing response plans (e.g. spill response plans) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Typical sources of information include the following. | ||
| + | *Soil, geologic, and hydrogeologic information (e.g. boring logs, groundwater flow maps, aquifer and bedrock maps, aquifer sensitivity maps) | ||
| + | *Aerial photos, used to determine land use | ||
| + | *Well information, including well logs and locations | ||
| + | *Wellhead protection plans and maps | ||
===Example 1=== | ===Example 1=== | ||
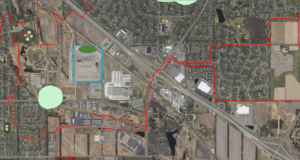
[[file:Wellhead example 1 site location.png|300px|thumb|alt=wellhead site schematic|<font size=3>Site proposed for infiltration shown in blue rectangle. The green polygon is an Emergency Response area.</font size>]] | [[file:Wellhead example 1 site location.png|300px|thumb|alt=wellhead site schematic|<font size=3>Site proposed for infiltration shown in blue rectangle. The green polygon is an Emergency Response area.</font size>]] | ||
| − | An infiltration basin is proposed for a site undergoing redevelopment. The site, located in Cottage Grove, Minnesota, is approximately 55 acres in size and consists of 100 percent impermeable surfaces. The entire site is within a [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection Drinking Water | + | An |
| + | <span title="Infiltration basins, infiltration trenches, dry wells, and underground infiltration systems capture and temporarily store stormwater before allowing it to infiltrate into the soil. As the stormwater penetrates the underlying soil, chemical, biological and physical processes remove pollutants and delay peak stormwater flows."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Infiltration '''infiltration basin''']</span> | ||
| + | is proposed for a site undergoing redevelopment. The site, located in Cottage Grove, Minnesota, is approximately 55 acres in size and consists of 100 percent impermeable surfaces. The entire site is within a | ||
| + | <span title="the surface and subsurface area surrounding a public water supply well, including the wellhead protection area, that must be managed by the entity identified in a wellhead protection plan. This area is delineated using identifiable landmarks that reflect the scientifically calculated wellhead protection area boundaries as closely as possible."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection '''Drinking Water Source Management Area (DWSMA),''']</span> | ||
| + | outside of an | ||
| + | <span title="The part of the wellhead protection area that is defined by a one-year time of travel within the aquifer that is used by the public water supply well (Minnesota Rules, part 4720.5250, subpart 3). It is used to set priorities for managing potential contamination sources within the DWSMA. This area is particularly relevant for assessing impacts from potential sources of pathogen contamination because this time of travel is believed to closely correspond with the survival period of many pathogens."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection '''Emergency Response Area.''']</span> | ||
| + | and within an area of the DWSMA classified as having high vulnerability. The redevelopment project requires a [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=2018_Minnesota_Construction_Stormwater_Permit Construction Stormwater Permit]. Infiltration at the site requires a higher level of engineering review to comply with the permit. | ||
The engineering review consists of the following steps. | The engineering review consists of the following steps. | ||
| − | 1. Identify the aquifer of concern: To make this determination, we used the [https://mnwellindex.web.health.state.mn.us/ County Well Index] to identify wells and well logs from nearby wells, the [https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/178852 2016 Washington County Geologic Atlas] (Part A, Plate 2, Bedrock geology), and the [https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/58492 1990 Washington County Geologic Atlas] (Plate 5, Hydrogeology). A water table aquifer is not utilized for drinking water supply, likely because the aquifer is thin or discontinuous and, where present, highly vulnerable to contamination. The uppermost bedrock unit is the Prairie du Chien formation, which is used for drinking water supply. | + | 1. Identify the aquifer(s) of concern: To make this determination, we used the [https://mnwellindex.web.health.state.mn.us/ County Well Index] to identify wells and |
| + | <span title="A well log is a record of the measurements of the geologic material (e.g. soil, rocks) penetrated in drilling a well"> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Understanding_and_interpreting_soils_and_soil_boring_reports_for_infiltration_BMPs '''well logs''']</span> | ||
| + | from nearby wells, | ||
| + | the [https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/178852 2016 Washington County Geologic Atlas] (Part A, Plate 2, Bedrock geology), and the [https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/58492 1990 Washington County Geologic Atlas] (Plate 5, Hydrogeology). | ||
| + | <span title="The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. ... Below the water table, in the phreatic zone (zone of saturation), layers of permeable rock that yield groundwater are called aquifers."> '''A water table aquifer'''</span> | ||
| + | is not utilized for drinking water supply, likely because the aquifer is thin or discontinuous and, where present, highly vulnerable to contamination. The uppermost bedrock unit is the | ||
| + | <span title="The Prairie du Chien aquifer is the principle aquifer used for drinking water supply in southeast Minnesota. It consists primarily of dolomite. In most areas it is overlain by the St. Peter sandstone, which often acts as a confining bedrock unit. The Jordan sandstone underlies the Prairie du Chien and comprises an important aquifer. The Prairie du Chien and Jordan aquifers are often treated as a single aquifer."> '''Prairie du Chien formation''',</span> | ||
| + | which is used for drinking water supply. | ||
2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: We used the 2016 Washington County Geologic Atlas (Part A, Plate 2, Bedrock geology). Groundwater flow in the Prairie du Chien aquifer is to the southwest. | 2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: We used the 2016 Washington County Geologic Atlas (Part A, Plate 2, Bedrock geology). Groundwater flow in the Prairie du Chien aquifer is to the southwest. | ||
| Line 116: | Line 149: | ||
[[File:Wellhead example 1 well log.png|600px|thumb|alt=well log image|<font size=3>Stratigraphic log for well 826033, illustrating the material overlying the Prairie du Chien consists of sand and gravel. Click on image to enlarge</font size>]] | [[File:Wellhead example 1 well log.png|600px|thumb|alt=well log image|<font size=3>Stratigraphic log for well 826033, illustrating the material overlying the Prairie du Chien consists of sand and gravel. Click on image to enlarge</font size>]] | ||
| − | 4. Estimate travel time to the nearest receptor. The public supply well associated with the ERA is the nearest receptor. The travel time can be calculated using literature values, through modeling, or by using Darcy’s equation. The travel time is the distance to the nearest receptor divided by the average linear velocity in the horizontal direction. The average linear velocity is the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer material (k), times the hydraulic gradient (i), divided by the effective porosity (f) of the aquifer material (ki/f). | + | 4. Estimate |
| + | <span title="Groundwater travel time is the time it takes for water to move horizontally from one location to another. Travel times are typically calculated using Darcy's equation."> '''travel time'''</span> | ||
| + | to the nearest receptor. The public supply well associated with the ERA is the nearest receptor. The travel time can be calculated using literature values, through modeling, or by using Darcy’s equation. The travel time is the distance to the nearest receptor divided by the average linear velocity in the horizontal direction. The average linear velocity is the | ||
| + | <span title="Hydraulic conductivity is a property of soils and rocks that describes the ease with which a fluid (usually water) can move through pore spaces or fractures."> '''hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer material (k),'''</span> | ||
| + | times the | ||
| + | <span title="The hydraulic gradient is the change in total head divided the distance over which the change occurs."> '''hydraulic gradient (i),'''</span> | ||
| + | divided by the effective | ||
| + | <span title="Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. empty) spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%."> '''porosity (f)'''</span> | ||
| + | of the aquifer material (ki/f). | ||
:a. Hydraulic conductivity (k) for the Prairie du Chien Aquifer was calculated using values reported in the literature (Lindgren, 1997; Ruhl, 1999; Seaberg, 2000; Stark and Hult, 1985). The median value from the literature is 0.00046 feet/second. | :a. Hydraulic conductivity (k) for the Prairie du Chien Aquifer was calculated using values reported in the literature (Lindgren, 1997; Ruhl, 1999; Seaberg, 2000; Stark and Hult, 1985). The median value from the literature is 0.00046 feet/second. | ||
| − | :b. Hydraulic gradients (i) were calculated using information provided by Minnesota Department of Natural Resources County Atlas program staff and are summarized below | + | :b. Hydraulic gradients (i) were calculated using information provided by Minnesota Department of Natural Resources County Atlas program staff and are summarized below. |
::i. Surficial SE aquifer gradient = 20 feet/6800 feet = 0.003 ft/ft | ::i. Surficial SE aquifer gradient = 20 feet/6800 feet = 0.003 ft/ft | ||
::ii. Surficial S1 aquifer gradient = 40 feet/15800 feet = 0.0025 ft/ft | ::ii. Surficial S1 aquifer gradient = 40 feet/15800 feet = 0.0025 ft/ft | ||
| Line 129: | Line 170: | ||
[[File:Wellhead example 1 recommended infiltration location.png|300px|thumb|alt=image|<font size=3>Recommended infiltration area shown in dark green oval. This area is furthest up-gradient of the ERA and provides some separation from adjacent transportation areas.</font size>]] | [[File:Wellhead example 1 recommended infiltration location.png|300px|thumb|alt=image|<font size=3>Recommended infiltration area shown in dark green oval. This area is furthest up-gradient of the ERA and provides some separation from adjacent transportation areas.</font size>]] | ||
| − | 5. | + | 5. The |
| − | :a. Is a spill response plan appropriate? | + | <span title="the branch of geology concerned with water occurring underground or on the surface of the earth"> '''hydrogeology'''</span> |
| + | and land use at the site warrant further investigation. Well logs indicate the surficial material consists of coarse sand and gravel, ranging in thickness from 35 to 85 feet. Both the surficial and Prairie du Chien aquifers are highly vulnerable to groundwater contamination and the Prairie du Chien likely has | ||
| + | <span title="A geologic formation that contains sufficient fissures, fractures, cracks, joints and faults that yields economic quantities of water to boreholes and springs."> '''fractured flow'''.</span> | ||
| + | Land use at the site consists of industry and transportation, with major highways and railways near the site. These warrant a [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Screening_assessment_for_contamination_at_potential_stormwater_infiltration_sites site screening assessment]. If the screening assessment indicates no concerns with contamination, infiltration is appropriate with the following considerations. | ||
| + | :a. Is a <span title="An Emergency Response Plan defines the actions taken in the initial minutes of an emergency, such as a spill of hazardous material (e.g. gasoline)."> '''spill response plan'''</span> appropriate? | ||
:b. Is emergency diversion of runoff from the infiltration practice an appropriate design consideration? | :b. Is emergency diversion of runoff from the infiltration practice an appropriate design consideration? | ||
:c. Is the site contoured to minimize potential run-on from adjacent transportation areas? | :c. Is the site contoured to minimize potential run-on from adjacent transportation areas? | ||
| − | :d. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes engineered media with moderate to high concentration of organic matter be utilized? | + | :d. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Comparison_of_pros_and_cons_of_bioretention_soil_mixes engineered media] with moderate to high concentration of organic matter be utilized? |
| − | Considering this analysis and answers to the above questions, the figure to the right illustrates | + | '''Conclusion''': Considering this analysis and answers to the above questions, the figure to the right illustrates acceptable infiltration areas. This area is approximately 4 to 5 years travel time from the ERA and provides some buffering from adjacent transportation areas. |
| − | ''' | + | ===Example 2=== |
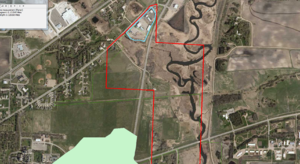
| + | [[File:Wellhead example 2 site location.png|300px|thumb|alt=image for example 2|<font size=3>Location for example 2. The proposed infiltration basins are shown as red squares. The boundaries of the Emergency Response Areas for two Edina municipal wells are shown in blue. The city wells are shown as yellow squares, with well 4 directly east of the proposed basins. </font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | An | ||
| + | <span title="Infiltration basins, infiltration trenches, dry wells, and underground infiltration systems capture and temporarily store stormwater before allowing it to infiltrate into the soil. As the stormwater penetrates the underlying soil, chemical, biological and physical processes remove pollutants and delay peak stormwater flows."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Infiltration '''infiltration basin''']</span> | ||
| + | is proposed for a highway reconstruction project in Edina, Minnesota. The infiltration basin must be built within highway right-of-way and is thus constrained to four potential locations within a highway interchange. All four locations are within an | ||
| + | <span title="The part of the wellhead protection area that is defined by a one-year time of travel within the aquifer that is used by the public water supply well (Minnesota Rules, part 4720.5250, subpart 3). It is used to set priorities for managing potential contamination sources within the DWSMA. This area is particularly relevant for assessing impacts from potential sources of pathogen contamination because this time of travel is believed to closely correspond with the survival period of many pathogens."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection '''Emergency Response Area,''']</span> | ||
| + | and within an area of the | ||
| + | <span title="the surface and subsurface area surrounding a public water supply well, including the wellhead protection area, that must be managed by the entity identified in a wellhead protection plan. This area is delineated using identifiable landmarks that reflect the scientifically calculated wellhead protection area boundaries as closely as possible."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection '''Drinking Water Source Management Area (DWSMA),''']</span> | ||
| + | classified as having <span title="Vulnerable public supply well – a public water supply well is vulnerable if the well water contains ten (10) milligrams per liter or more nitrate plus nitrite nitrogen; the well water contains quantifiable levels of pathogens as defined in part 7040.0100, subpart 26, or chemical compounds that indicate groundwater degradation as defined in Minnesota Statutes, section 103H.005, subdivision 6; the well water contains one tritium unit or more when measured with an enriched tritium detection method; or an enriched tritium analysis of the well water has not been performed within the past ten years; and information on the well construction is not available; or the geological material from the land surface to where the groundwater enters the public water supply well is fractured bedrock; solution weathered bedrock; sandstone bedrock; unconsolidated material 0.062 millimeters (fine sand) or larger; or a combination of these units."> | ||
| + | '''moderate vulnerability'''</span>. The project requires a [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=2018_Minnesota_Construction_Stormwater_Permit Construction Stormwater Permit]. Infiltration at the site requires a higher level of engineering review to comply with the permit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The engineering review consists of the following steps. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Identify the aquifer(s) of concern: To make this determination, we used the [https://mnwellindex.web.health.state.mn.us/ County Well Index] to identify wells and <span title="A well log is a record of the measurements of the geologic material (e.g. soil, rocks) penetrated in drilling a well"> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Understanding_and_interpreting_soils_and_soil_boring_reports_for_infiltration_BMPs '''well logs''']</span> from nearby wells, the [https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/58491 Hennepin County Geologic Atlas] (Plates 2 through 7), and the [http://edinadocs.edinamn.gov/WebLink/0/doc/236945/Page1.aspx City of Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan] (Part 1). Several wells from the County Well Index are completed in the <span title="Surficial aquifer is considered to be the uppermost aquifer. Generally it consists of sand or garvels aquifers, but can also be a bedrock aquifer if the bedrock aquifer is the aquifer closest to the land surface."> '''surficial aquifer.'''</span> Two Edina municipal wells and some private wells are completed in the <span title="The Prairie du Chien aquifer is the principle aquifer used for drinking water supply in southeast Minnesota. It consists primarily of dolomite. In most areas it is overlain by the St. Peter sandstone, which often acts as a confining bedrock unit. The Jordan sandstone underlies the Prairie du Chien and comprises an important aquifer. The Prairie du Chien and Jordan aquifers are often treated as a single aquifer."> '''Prairie du Chien-Jordan aquifer.'''</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: We used the 1989 Hennepin County Geologic Atlas (Plates 5 and 6) and the [http://edinadocs.edinamn.gov/WebLink/0/doc/236945/Page1.aspx City of Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan] (Part 1). Groundwater flow in the surficial and bedrock aquifers is to the southeast. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Identify wells down-gradient and side-gradient of the site and determine the distance to each well. There are relatively few wells used in the determination of groundwater flow within the aquifer. We therefore expanded the well search to include side-gradient wells. This encompasses City Well 4, which is directly east of the proposed infiltration area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! City Well !! Aquifer !! Casing/well depth (ft) !! Static water level (ft below ground surface) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4 || Prairie du Chien-Jordan || 266/500 || 80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 6 || Jordan || 316/503 || 90 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Well ID !! Depth (feet) !! Aquifer !! Direction from infiltration basin !! Distance from infiltration basin (feet) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 200563 || 88 || Quaternary (surficial) || East || 2040 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 200562 || 98 || St. Peter || East || 1400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 224343 || 410 || Prairie du Chien || East || 630 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 200565 || 115 || Quaternary (surficial) || South-southeast || 1580 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 200566 || 308 || Prairie du Chien || South-southeast || 1730 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 200567 || 95 || Quaternary (surficial) || South-southeast || 1740 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | City Well 4 || 503 || Prairie du Chien - Jordan || East || 1150 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Determine the likelihood contaminants will reach the surficial or bedrock aquifers. Using the <span title="Sensitivity maps, also called vulnerability maps, reflect the likelihood that water and pollutants will reach an aquifer"> '''sensitivity maps'''</span> from the 1989 Hennepin County Atlas, both the surficial (Quaternary) and Prairie du Chien aquifers have low vulnerability to contamination, although there are small areas of the Prairie du Chien mapped as moderate near the proposed infiltration basin(s). The low vulnerability is attributed to overlying glacial deposits, which are described as loamy till, and for the Prairie du Chien, the presence of the St. Peter bedrock, which is considered a confining later. The City of Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan lists City Well 4 as vulnerable based on the presence of <span title="Nitrate is an electron acceptor utilized by bacteria during consumption of organic matter. Presence of nitrate indicates the presence of oxygen in groundwater and is considered to represent recent recharge water."> '''nitrates'''</span> in sampling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery caption="Site information for determining feasibility of infiltration. Click on an image for enlarged view." widths="140px"> | ||
| + | File:Wellhead example 2 well locations.png|alt=image showing well locations|Location of private wells in the vicinity of the proposed infiltration basin(s) | ||
| + | File:Wellhead example 2 aquifer sensitivity.png|alt=image of aquifer sensitivity|Sensitivity of the Prairie du Chien aquifer. Blue and green are low sensitivity and white is moderate. | ||
| + | File:Wellhead example 2 flow direction surficial.png|alt=image of flow in surficial aquifer|Groundwater flow direction in the surficial aquifer | ||
| + | File:Wellhead example 2 flow direction.png|alt=image of flow direction in OPDC aquifer|Flow direction in the Prairie du Chien aquifer | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Wellhead example 2 well log.png|300px|thumb|alt=image of well log|<font size=3>Stratigraphic log for well 200566, illustrating the material overlying the Prairie du Chien consists of till (mixture of sand, gravel, and clay) and the St. Peter sandstone. Click on image to enlarge</font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Determine aquifer time of travel to nearby wells. City Well 4 is within the ERA and therefore considered to be within a <span title="A one year time of travel is considered to represent the maximum survival time for pathogens in groundwater and is therefore used as an indicator of vulnerability of a well to contamination."> '''one-year time of travel.'''</span> Using information from Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan (hydraulic conductivity, hydraulic gradient, and porosity), times of travel for the city well fields in the Prairie du Chien aquifer range from 124 to 7050 feet per year. For the ERA encompassing City Well 4, the time of travel is estimated at 2650 feet per year. The proposed infiltration basin is approximately 1150 feet from City well 4. Data for the surficial aquifer are lacking and travel times must be estimated based on typical values for the geologic material comprising the aquifer. Assuming a coarse sand or gravelly sand aquifer, based on <span title=" the branch of geology concerned with the order and relative position of strata and their relationship to the geological time scale."> '''stratigraphic information'''</span> in well logs, the following table provides a range of travel time estimates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Scenario !! Conductivity (ft/year) !! Gradient (ft/ft) !! porosity !! Estimated travel time (ft/year) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Low conductivity || 3150 || 0.00217 || 0.3 || 23 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mid range conductivity || 31500 || 0.00217 || 0.3 || 230 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | High conductivity || 315000 || 0.00217 || 0.3 || 2275 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wells within the surficial aquifer are 1500 to 2000 feet from the proposed infiltration basin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Based on the information above, there are some potential concerns with infiltration at this site, including the following. | ||
| + | *The locations for the infiltration basin are within a one-year time of travel for City well 4 and potentially within the one-year time of travel for wells in the surficial aquifer. | ||
| + | *Geologic data for the unsaturated zone are based on stratigraphic records from driller logs rather than borings taken by professional geoscientists | ||
| + | *There is a discrepancy in vulnerability assessment for City well 4. Since nitrates were detected in well 4, there is some indication that pollutants may readily travel through the unsaturated zone and into the underlying prairie du Chien aquifer | ||
| + | *Although the County Atlas shows the bedrock aquifer as having low vulnerability, there are areas mapped as medium vulnerability near the proposed infiltration basins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These concerns warrant further investigation, including the following. | ||
| + | *The Hennepin County atlas is undergoing revision. Additional analysis should occur using the updated information if it is available. | ||
| + | *The private wells identified above should be located and a determination made concerning their status (i.e. are they active or not) | ||
| + | *Additional <span title="Water chemistry sampling can be used to determine the likely age of water. Presence of oxygen and nitrate typically indicate relatively young water, while presence high concentrations of iron and other metals generally reflects older water."> '''water chemistry sampling'''</span> in City well 4 might provide better estimates of the age and vulnerability of the well to contamination | ||
| + | |||
| + | If further investigation indicates infiltration is appropriate, consider the following. | ||
| + | :a. The Wellhead Protection Plan will include a <span title="An Emergency Response Plan defines the actions taken in the initial minutes of an emergency, such as a spill of hazardous material (e.g. gasoline)."> '''spill response and emergency response plan.'''</span> These should be reviewed. Additional design concsiderations may be appropriate, such as <span title="Infiltration practices can be designed to divert runoff under certain conditions. Examples include preventing inflow of runoff into the practice or diverting captured water back into the stormwater drainage system."> emergency diversion from the infiltration practice.</span> | ||
| + | :b. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes <span title="that is designed to support plant growth but allow water to pass through quickly. This media consists mostly of sand but has organic matter (e.g. compost) and some clay. The sand allows water to pass through the media quickly, while the clay and organic matter hold enough water and nutrients to support plants. The organic matter and clay are also effective at adsorbing pollutants from the runoff water."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Comparison_of_pros_and_cons_of_bioretention_soil_mixes '''engineered media'''] with moderate to high concentration of <span title="Organic matter effectively retains most pollutants in stormwater runoff, including metals, bacteria, and organic compounds"> '''organic matter'''</span> be utilized? | ||
| + | :c. Should multiple independent infiltration practices be utilized? | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Conclusion''': Additional investigation, described above, is warranted for this site. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example 3=== | ||
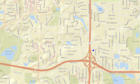
| + | [[File:Wellhead example 3 site location.png|300px|thumb|alt=image for example 3|<font size=3>Location for example 3. The proposed infiltration area is outlined in blue. The boundaries of the DWSMA area designated as having very high vulnerability is outlined in red. The upper portion of the Emergency Response Area is shown by the blue shaded polygon south of the proposed infiltration area. </font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | An | ||
| + | <span title="Infiltration basins, infiltration trenches, dry wells, and underground infiltration systems capture and temporarily store stormwater before allowing it to infiltrate into the soil. As the stormwater penetrates the underlying soil, chemical, biological and physical processes remove pollutants and delay peak stormwater flows."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Infiltration '''infiltration basin''']</span> | ||
| + | is proposed for a parking lot reconstruction project in Morris, Minnesota. The impervious area is approximately 5 acres. The site is within a | ||
| + | <span title="the surface and subsurface area surrounding a public water supply well, including the wellhead protection area, that must be managed by the entity identified in a wellhead protection plan. This area is delineated using identifiable landmarks that reflect the scientifically calculated wellhead protection area boundaries as closely as possible."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection '''Drinking Water Source Management Area (DWSMA)''']</span> | ||
| + | but outside the | ||
| + | <span title="The part of the wellhead protection area that is defined by a one-year time of travel within the aquifer that is used by the public water supply well (Minnesota Rules, part 4720.5250, subpart 3). It is used to set priorities for managing potential contamination sources within the DWSMA. This area is particularly relevant for assessing impacts from potential sources of pathogen contamination because this time of travel is believed to closely correspond with the survival period of many pathogens."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection '''Emergency Response Area.''']</span> | ||
| + | <span title="Aquifer vulnerability indicates the likelihood that physical and biochemical characteristics of the subsurface prevent or favor the transport of pollutants to aquifers and is often based on time of travel estimates from the land surface to an aquifer. It does not consider pollutant loading."> [https://www.dnr.state.mn.us/waters/groundwater_section/mapping/sensitivity.html '''Aquifer vulnerability''']</span> | ||
| + | is mapped as very high. The project requires a [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=2018_Minnesota_Construction_Stormwater_Permit Construction Stormwater Permit]. Infiltration at the site requires a higher level of engineering review to comply with the permit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The engineering review consists of the following steps. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Identify the aquifer(s) of concern: To make this determination, we used the [https://mnwellindex.web.health.state.mn.us/ County Well Index] (CWI) to identify wells and <span title="A well log is a record of the measurements of the geologic material (e.g. soil, rocks) penetrated in drilling a well"> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Understanding_and_interpreting_soils_and_soil_boring_reports_for_infiltration_BMPs '''well logs''']</span> from nearby wells, and the [https://swareport.web.health.state.mn.us/SWA_Factsheet.html?pwsid=1750005 Morris Source Water Assessment]. Five City wells are completed in <span title="unconsolidated geologic materials (sand, silt, clay) deposited as a result of glacial processes during the Quaternary period"> '''Quaternary deposits'''</span> and range in depth from 58 to 78 feet. Private wells in the vicinity are completed in the same geologic deposits and have similar depths. | ||
| + | |||
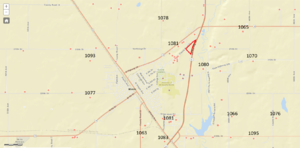
| + | 2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: Static water elevations from well logs in CWI, plotted in the image to the right, indicate no discernible pattern to groundwater flow. The elevation of the Pomme de Terre River, located just east of the proposed infiltration area, is approximately 1080 feet above sea level. There are several <span title="Irrigation and city wells are high withdrawal wells that can significantly lower the water elevation in an aquifer and thus affect local flow in the aquifer"> '''irrigation wells'''</span> in the area that may impact water elevations. City wells, located south of the proposed infiltration, may also influence flow. Finally, well logs indicate alternating layers of sand/gravel and clay/till, suggesting there may be multiple hydraulic units. Without more detailed analysis and more precise measurements of static water elevations, groundwater flow direction cannot be positively determined. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Wellhead example 3 flow direction.png|300px|thumb|alt=image with static water elevations|<font size=3>Static water elevations for wells in the vicinity of the proposed infiltration area. Elevations are from County Well Index.</font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Identify the distance from the infiltration area to nearby wells. Because flow direction is uncertain, we must consider all nearby wells. There are several wells near the proposed practice. Some of these are summarized in the table below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Well ID !! Depth (feet) !! Aquifer !! Direction from infiltration basin !! Distance from infiltration basin (closest and furthest, in feet) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 530879 || 78 || Quaternary (buried) || Southwest || 675 - 1625 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 117441 || 62 || Quaternary (buried) || West || 1000 - 1900 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 689691 || 80 || Quaternary (buried) || Northwest || 630 - 1000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 601722 || 65 || Quaternary (buried) || North || 315 - 1275 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 589046 || 110 || Quaternary (buried) || East || 2275 - 2900 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 464752 || 95 || Quaternary (buried) || Southeast || 2600 - 3500 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Wellhead example 3 well log.png|300px|thumb|alt=image of well logs|<font size=3>Well logs from two wells located south of the proposed infiltration. Both wells are in the area of the DWSMA classified as highly vulnerable.</font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Determine the likelihood contaminants will reach the surficial or bedrock aquifers. Only two wells in CWI are within the area delineated as being highly vulnerable, and these wells are 3500 feet or more from the proposed infiltration practice. Both well logs show alternating layers of sand, gravel, and clay. <span title="Clay is considered a restrictive layer that impedes movement of water and pollutants through geologic media. While continuous, thick layers of clay are more effective at restricting water and chemical movement than multiple thin layers, the thickness of multiple layers can be added to give a cumulative thickness. Cumulative thickness of 10 feet or more are generally considered to be restrictive to water and chemical movement."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Understanding_and_interpreting_soils_and_soil_boring_reports_for_infiltration_BMPs#Restrictive_layers_in_soil_profiles '''Cumulative thickness of clay material''']</span> in both logs exceeds 25 feet. Clay color is noted as blue, indicating <span title="Bacteria in groundwater utilize organic matter as an energy source. To utilize organic matter as a food source bacteria require presence of an electron acceptor. Oxygen is the first electron acceptor utilized. once oxygen is consumed, nitrate is utilized, followed by manganese and iron. Reducing conditions represent conditions where oxygen and nitrate have been utilized and are considered representative of water that is older."> '''reducing conditions.'''</span> City wells have consistently tested negative for <span title="Nitrate is an electron acceptor utilized by bacteria during consumption of organic matter. Presence of nitrate indicates the presence of oxygen in groundwater and is considered to represent recent recharge water."> '''nitrate'''</span>, while several wells in the area have high concentrations of <span title="Arsenic is a naturally-ocurring chemical in groundwater but is only present under relatively reducing conditions. Presence of arsenic therefore reflects water that is older"> '''arsenic'''</span> [https://www.morrismn.info/water.htm][https://www.stevensswcd.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/StevensCLWP.pdf]. These results suggest water in sampled wells is likely not vulnerable to contamination. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Determine aquifer time of travel to nearby wells. Data for calculating travel time is lacking. In particular, the hydraulic gradient is difficult to determine based on data. If we assume a coarse sand or gravelly sand aquifer and utilize inputs from Example 2 above, the following table provides a range of travel time estimates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Scenario !! Conductivity (ft/year) !! Gradient (ft/ft) !! porosity !! Estimated travel time (ft/year) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Low conductivity || 3150 || 0.00217 || 0.3 || 23 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mid range conductivity || 31500 || 0.00217 || 0.3 || 230 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | High conductivity || 315000 || 0.00217 || 0.3 || 2275 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Several wells within the Quaternary aquifer are within 1000 feet of the proposed infiltration. An infiltration practice cannot be constructed to be more than 1000 feet from the nearest domestic well. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The primary concern at the site is the lack of <span title="the branch of geology concerned with water occurring underground or on the surface of the earth"> '''hydrogeologic'''</span> information. Available well logs suggest there are <span title="A confining layer is a geologic material that restricts or impedes movement of water and chemicals. Examples include clay and shale"> '''confining layers of clay.'''</span> However, the closest wells are likely within | ||
| + | <span title="A one year time of travel is considered to represent the maximum survival time for pathogens in groundwater and is therefore used as an indicator of vulnerability of a well to contamination."> '''one year travel time'''</span> | ||
| + | of any proposed infiltration practice. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Conclusion''': Additional investigation is recommended if infiltration is pursued at this site. Additional investigation includes the following options. | ||
| + | *Conduct appropriate soil borings to confirm the presence of adequate confining layers | ||
| + | *Sample nearby wells to determine age and sensitivity to pollution (<span title="Numerous methods exist for dating the age of groundwater, including tritium, isotopes of oxygen and hydrogen, chlorofluorocarbons, carbon-14, krypton-85, and chlorine-36."> [http://www.primarywaterinstitute.org/images/pdfs/Tritium_in_groundwater.pdf '''age dating''']</span> and/or sampling for nitrate and <span title="Presence of oxygen typically represents recent recharge water. Bacteria in groundwater utilize oxygen to convert organic material into energy. Thus, the presence of oxygen indicates relatively young water in which there has been insufficient time to consume the oxygen present in the aquifer."> '''presence of oxygen'''</span>) | ||
| + | |||
| + | If further investigation indicates infiltration is appropriate, consider the following. | ||
| + | :a. The Wellhead Protection Plan will include a <span title="An Emergency Response Plan defines the actions taken in the initial minutes of an emergency, such as a spill of hazardous material (e.g. gasoline)."> '''spill response and emergency response plan.'''</span> These should be reviewed. Additional design considerations may be appropriate, such as <span title="Infiltration practices can be designed to divert runoff under certain conditions. Examples include preventing inflow of runoff into the practice or diverting captured water back into the stormwater drainage system."> '''emergency diversion from the infiltration practice.'''</span> | ||
| + | :b. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes <span title="that is designed to support plant growth but allow water to pass through quickly. This media consists mostly of sand but has organic matter (e.g. compost) and some clay. The sand allows water to pass through the media quickly, while the clay and organic matter hold enough water and nutrients to support plants. The organic matter and clay are also effective at adsorbing pollutants from the runoff water."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Comparison_of_pros_and_cons_of_bioretention_soil_mixes '''engineered media'''] with moderate to high concentration of <span title="Organic matter effectively retains most pollutants in stormwater runoff, including metals, bacteria, and organic compounds"> '''organic matter'''</span> be utilized? | ||
| + | :c. Should multiple independent infiltration practices be utilized? | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====References for examples==== | ||
*Lindgren, Richard J. 1997. Hydraulic Properties and Ground-Water Flow in the St. Peter-Prairie du Chien-Jordan Aquifer, Rochester Area, Southeastern Minnesota. Water-Resources Investigations Report 97-4015. | *Lindgren, Richard J. 1997. Hydraulic Properties and Ground-Water Flow in the St. Peter-Prairie du Chien-Jordan Aquifer, Rochester Area, Southeastern Minnesota. Water-Resources Investigations Report 97-4015. | ||
*Ruhl, James F. 1999. Hydraulic properties of the Prairie du Chien-Jordan aquifer, Shakopee Mdewakanton Sioux Community, southeastern Minnesota, 1997. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4183. | *Ruhl, James F. 1999. Hydraulic properties of the Prairie du Chien-Jordan aquifer, Shakopee Mdewakanton Sioux Community, southeastern Minnesota, 1997. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4183. | ||
*Seaberg, John. 2000. Overview of the Twin Cities Metropolitan Groundwater Model. | *Seaberg, John. 2000. Overview of the Twin Cities Metropolitan Groundwater Model. | ||
*Stark, J.R., and M.F. Hult. 1985. Ground-water Flow in the Prairie du Chien-Jordan Aquifer Related to Contamination by Coal-Tar Derivatives, St. Louis Park, Minnesota. Water-Resources Investigations Report 85-4087. | *Stark, J.R., and M.F. Hult. 1985. Ground-water Flow in the Prairie du Chien-Jordan Aquifer Related to Contamination by Coal-Tar Derivatives, St. Louis Park, Minnesota. Water-Resources Investigations Report 85-4087. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Level 2 - Technical and specific topic information/infiltration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:39, 9 April 2023
The Construction Stormwater Permit requires a higher level of engineering review for proposed infiltration projects in areas overlying an Emergency Response Area (ERA) where the vulnerability of the DWSMA (Drinking Water Supply Management Area) is classified as moderate, or in areas outside the ERA where the vulnerability of the DWSMA (Drinking Water Supply Management Area) is classified as high or very high. This page provide guidance and recommendations for conducting a higher level of engineering review.
Contents
Description of Emergency Response Areas, DWSMAs, and vulnerability of DWSMAs
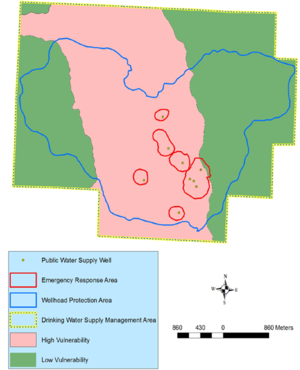
The figure at the right illustrates protection designations used to manage public water supply wells that have wellhead protection plans.
- Drinking Water Supply Management Area (DWSMA) - the surface and subsurface area surrounding a public water supply well, including the wellhead protection area, that must be managed by the entity identified in a wellhead protection plan. This area is delineated using identifiable landmarks that reflect the scientifically calculated wellhead protection area boundaries as closely as possible.
- Drinking Water Supply Management Area Vulnerability. An assessment of the likelihood that the aquifer within the DWSMA is subject to impact from overlying land and water uses. It is based upon criteria that are specified under Minnesota Rules, part 4720.5210, subpart 3.
- Emergency Response Area (ERA). The part of the wellhead protection area that is defined by a one-year time of travel within the aquifer that is used by the public water supply well (Minnesota Rules, part 4720.5250, subpart 3). It is used to set priorities for managing potential contamination sources within the DWSMA. This area is particularly relevant for assessing impacts from potential sources of pathogen contamination because this time of travel is believed to closely correspond with the survival period of many pathogens.
- Wellhead Protection Area (WHPA) – the surface and subsurface area surrounding a well or well field that supplies a public water system, through which contaminants are likely to move toward and reach the well or well field (Minnesota Statutes, section 103I.005, subdivision 24).
A public water supply well is vulnerable if:
- the well water contains ten (10) milligrams per liter or more nitrate plus nitrite nitrogen;
- the well water contains quantifiable levels of pathogens as defined in part 7040.0100, subpart 26, or chemical compounds that indicate groundwater degradation as defined in Minnesota Statutes, section 103H.005, subdivision 6;
- the well water contains one tritium unit or more when measured with an enriched tritium detection method; or
- an enriched tritium analysis of the well water has not been performed within the past ten years; and
- information on the well construction is not available; or
- the geological material from the land surface to where the groundwater enters the public water supply well is:
- fractured bedrock;
- solution weathered bedrock;
- sandstone bedrock;
- unconsolidated material 0.062 millimeters (fine sand) or larger; or
- a combination of the materials specified in units (a) to (d).
Five classes of vulnerability exist: very low, low, moderate, high, and very high. Within high and very high vulnerability designations, contaminants at the land surface have the potential to move quickly to the underlying aquifer.
Rationale for requiring a higher level of engineering review
There are two conditions in which infiltration is prohibited under the Construction Stormwater General Permit unless a higher level of engineering review is conducted and demonstrates that a functioning treatment system will prevent adverse impacts to groundwater.
- An Emergency Response Area (ERA) within a DWSMA classified as moderate vulnerability
- Outside of an ERA within a DWSMA classified as having high or very high vulnerability
Vulnerability assessments for wellhead protection are based on data that was existing at the time of plan development, and are often reliant on stratigraphic information from construction logs for wells and borings constructed for purposes other than characterizing the nature and continuity of confining units. Therefore they should be viewed as a best estimate at the time of plan development, and subject to change during future plan amendments depending on the availability of newer or higher quality data.
In the first condition above, a contaminant will potentially be transported to an underlying aquifer within a moderate time frame (e.g. one year to a decade). The concern is that contaminants reaching an aquifer within the ERA can be transported to a public supply well within a short time (less than one year). It is therefore important to collect additional information about the geologic materials overlying the aquifer or ensure a minimal risk of contaminant exposure in these settings.

In the second condition above, outside of the ERA, the wells most likely to be impacted by infiltration practices are those also completed in the highly vulnerable aquifer and situated within one-year time of travel of the infiltration site. Determinations of ERA are based on sound geologic analysis and modeling, but other receptors beyond the public water supply well are not considered. Thus, private wells in these settings are at risk. Engineering review in this situation entails either conducting more detailed geologic analysis or modeling or conducting a well receptor survey.
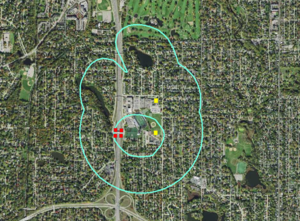
Note that aquifer vulnerability for a DWSMA considers only the aquifer in which public water supply wells are located. The vulnerability designation for private wells completed in other aquifers must be determined on a case by case basis. For example, in the schematic to the right, the public supply well is located in an aquifer designated as having low vulnerability. Private wells completed in the same aquifer as the public supply wells have the same aquifer vulnerability designation as the DWSMA for the public well. The private well completed in the shallow aquifer above the confining unit is likely to have very high vulnerability.
Since the CSW permit focuses only on DWSMAs and on the vulnerability designation for DWSMAs, many private wells located in aquifers other than the aquifer for the DWSMA, or private wells located outside of DWSMAs may be at risk from an infiltration practice. It is Highly recommended that receptor surveys be completed for any infiltration practice, including those outside a DWSMA and that engineering reviews be conducted when private wells are likely to be located within a year travel time of the infiltration practice. See the following section for guidance.
Guidance and recommendations for conducting a higher level of engineering review
The two conditions requiring higher levels of engineering review differ and therefore have different recommendations.
1. Condition 1: Moderate vulnerability overlying an ERA. Because there is a high degree of certainty regarding the boundaries of the ERA, the purpose of the engineering review in this case is to conduct a detailed geologic analysis or provide reasonable assurances that risk of contaminant exposure is limited.
- Detailed geologic analysis: The goal of this analysis is to determine the likelihood that contaminants will be attenuated or rapidly transported in the unsaturated (vadose) zone overlying the aquifer. Soil borings are highly recommended link here for guidance. There is no clear line defining when sufficient protective material exists in the unsaturated zone. Modifying Minnesota Department of Natural Resources guidance, we make the following recommendations.
- For non-carbonate aquifers, a minimum of 10 feet of low permeability units overlying the aquifer. The units may be aggregated (e.g. one 10-foot low permeability unit, two 5-foot low permeability units, etc.). Low permeability materials include Hydrologic Soil Group (HSG) D soils/material, clayey tills, lake clays, and shale.
- For non-carbonate aquifers, a minimum of 20 feet of moderate permeability units overlying the aquifer. The units may be aggregated (e.g. one 20-foot moderate permeability unit, two 10-foot moderate permeability units, etc.). Moderate permeability materials include HSG C soils/material.
- For carbonate aquifers, at least one continuous low permeability unit 10 feet or greater in thickness, or an aggregate of 20 feet of low permeability units.
If borings are not utilized, other sources of information may be used, but these should be used with caution. Examples include multiple well boring logs that show similar driller interpretation, or hydrogeologic assessments or studies conducted by professional organizations, such as the United States Geological Survey or Minnesota Pollution Control Agency.
An alternative approach to ensuring protection of a public water supply well is to ensure a minimum risk of contaminants exposure. This includes the following recommendations.
- Ensure there are no stormwater hotspots in the area contributing runoff to the infiltration practice.
- Ensure there are no existing contaminant sources within the area contributing to the infiltration practice. The Screening assessment for contamination at potential stormwater infiltration sites guidance may be used for this.
- Develop a spill response procedure for the area.
- Ensure there are land use controls in place to prevent introduction of contaminants sources into the future.
2. Condition 2: High and very high vulnerability outside an ERA. While a geologic assessment can be used in this situation, it is not necessary. If a geologic assessment is conducted, the goal would be to ensure there is sufficient protective material to retard contaminants before reaching the aquifer. The recommendations for conducting a geologic analysis described for condition 1 above can be used.
The primary concern for this condition, however, is to identify or protect other receptors, which typically will be private well owners. This can be achieved by limiting the risk of contaminant exposure, as described above for condition 1. A second option is to conduct a receptor survey. This is a two step process.
- Determine the one year travel time surrounding the infiltration practice. This can be estimated using simple calculators (example). For information on typical aquifer properties, link here. If the aquifer properties are unknown, assume a one mile radius around the infiltration practice.
- Determine if there are any active receptors utilizing the aquifer within the one year travel time area.
Note that these recommendations are relatively conservative and professional geoscientists or engineers may utilize other methods, including modeling.
Information gathered from engineering reviews
The types of detailed geological investigations suggested under Condition 1 above could be very beneficial to public water suppliers and the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) when it comes time to re-assess the vulnerability of the ERA and DWSMA during wellhead protection plan amendment, which occurs every 10-years. If you conduct a higher engineering review, please consider submitting the data and/or reports associated with such investigations to MDH or MPCA. Similarly, if you complete a well-receptor survey under Condition 2 above, please consider providing this information to MDH or MPCA. All wellhead protection plans include an assessment of wells within the DWSMA, and any receptor survey results could be beneficial towards those efforts.
Examples
The following examples represent hypothetical situations. The analysis and recommendations are based on professional judgement by MPCA staff. It is highly recommended that licensed geologists or engineers perform these analyses.
In general, a higher level of engineering review should include the following:
- identifying the aquifer(s) of concern;
- determining direction of flow in the aquifer(s) of concern;
- determining wells down-gradient of the proposed infiltration practice(s);
- determining the likelihood that contaminants will move vertically through the unsaturated zone and into the aquifer(s) of concern; and
- determining time of travel for water within the aquifer(s) of concern.
Depending on site conditions, additional considerations include the following:
- land use in the vicinity of the proposed infiltration practice;
- the type of practice proposed; and
- existing response plans (e.g. spill response plans)
Typical sources of information include the following.
- Soil, geologic, and hydrogeologic information (e.g. boring logs, groundwater flow maps, aquifer and bedrock maps, aquifer sensitivity maps)
- Aerial photos, used to determine land use
- Well information, including well logs and locations
- Wellhead protection plans and maps
Example 1
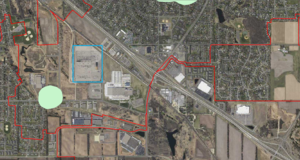
An infiltration basin is proposed for a site undergoing redevelopment. The site, located in Cottage Grove, Minnesota, is approximately 55 acres in size and consists of 100 percent impermeable surfaces. The entire site is within a Drinking Water Source Management Area (DWSMA), outside of an Emergency Response Area. and within an area of the DWSMA classified as having high vulnerability. The redevelopment project requires a Construction Stormwater Permit. Infiltration at the site requires a higher level of engineering review to comply with the permit.
The engineering review consists of the following steps.
1. Identify the aquifer(s) of concern: To make this determination, we used the County Well Index to identify wells and well logs from nearby wells, the 2016 Washington County Geologic Atlas (Part A, Plate 2, Bedrock geology), and the 1990 Washington County Geologic Atlas (Plate 5, Hydrogeology). A water table aquifer is not utilized for drinking water supply, likely because the aquifer is thin or discontinuous and, where present, highly vulnerable to contamination. The uppermost bedrock unit is the Prairie du Chien formation, which is used for drinking water supply.
2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: We used the 2016 Washington County Geologic Atlas (Part A, Plate 2, Bedrock geology). Groundwater flow in the Prairie du Chien aquifer is to the southwest.
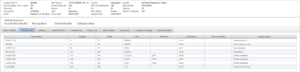
3. Identify wells down-gradient and side-gradient of the site and determine the distance to each well. There are relatively few wells used in the determination of groundwater flow within the aquifer. We therefore expanded the well search to include side-gradient wells. The following table summarizes distances to the closest wells. Note that a public supply well located in an ERA is the closest drinking water well. The SW corner of the site, which is closest to the ERA, is 0.13 miles from the ERA. The NE corner of the site is 0.50 miles from the ERA.
| Well | Closest distance (miles) | Furthest distance (miles) | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 826033 | 0.82 | 1.19 | Down-gradient |
| 131970 | 0.51 | 0.88 | Side-gradient W-NW |
| 257609 | 0.70 | 1.07 | Side-gradient S-SE |
| Emergency Response Area | 0.13 | 0.50 | Down-gradient |
- Site information for determining feasibility of infiltration. Click on an image for enlarged view.
4. Estimate travel time to the nearest receptor. The public supply well associated with the ERA is the nearest receptor. The travel time can be calculated using literature values, through modeling, or by using Darcy’s equation. The travel time is the distance to the nearest receptor divided by the average linear velocity in the horizontal direction. The average linear velocity is the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer material (k), times the hydraulic gradient (i), divided by the effective porosity (f) of the aquifer material (ki/f).
- a. Hydraulic conductivity (k) for the Prairie du Chien Aquifer was calculated using values reported in the literature (Lindgren, 1997; Ruhl, 1999; Seaberg, 2000; Stark and Hult, 1985). The median value from the literature is 0.00046 feet/second.
- b. Hydraulic gradients (i) were calculated using information provided by Minnesota Department of Natural Resources County Atlas program staff and are summarized below.
- i. Surficial SE aquifer gradient = 20 feet/6800 feet = 0.003 ft/ft
- ii. Surficial S1 aquifer gradient = 40 feet/15800 feet = 0.0025 ft/ft
- iii. St. Peter aquifer (OSTP) – gradient cannot be determined with data; aquifer discontinuous
- iv. Prairie du Chien aquifer (OPDC) = 20 feet/9700 feet = 0.002 ft/ft
- v. Median gradient = 0.0025 ft/ft
- c. Effective porosity (f) is estimated as 0.06 based on literature (Stark and Hult, 1985)
Utilizing these values, the estimated one-year travel time is 605 feet or 0.115 miles.
5. The hydrogeology and land use at the site warrant further investigation. Well logs indicate the surficial material consists of coarse sand and gravel, ranging in thickness from 35 to 85 feet. Both the surficial and Prairie du Chien aquifers are highly vulnerable to groundwater contamination and the Prairie du Chien likely has fractured flow. Land use at the site consists of industry and transportation, with major highways and railways near the site. These warrant a site screening assessment. If the screening assessment indicates no concerns with contamination, infiltration is appropriate with the following considerations.
- a. Is a spill response plan appropriate?
- b. Is emergency diversion of runoff from the infiltration practice an appropriate design consideration?
- c. Is the site contoured to minimize potential run-on from adjacent transportation areas?
- d. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes engineered media with moderate to high concentration of organic matter be utilized?
Conclusion: Considering this analysis and answers to the above questions, the figure to the right illustrates acceptable infiltration areas. This area is approximately 4 to 5 years travel time from the ERA and provides some buffering from adjacent transportation areas.
Example 2
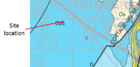
An infiltration basin is proposed for a highway reconstruction project in Edina, Minnesota. The infiltration basin must be built within highway right-of-way and is thus constrained to four potential locations within a highway interchange. All four locations are within an Emergency Response Area, and within an area of the Drinking Water Source Management Area (DWSMA), classified as having moderate vulnerability. The project requires a Construction Stormwater Permit. Infiltration at the site requires a higher level of engineering review to comply with the permit.
The engineering review consists of the following steps.
1. Identify the aquifer(s) of concern: To make this determination, we used the County Well Index to identify wells and well logs from nearby wells, the Hennepin County Geologic Atlas (Plates 2 through 7), and the City of Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan (Part 1). Several wells from the County Well Index are completed in the surficial aquifer. Two Edina municipal wells and some private wells are completed in the Prairie du Chien-Jordan aquifer.
2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: We used the 1989 Hennepin County Geologic Atlas (Plates 5 and 6) and the City of Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan (Part 1). Groundwater flow in the surficial and bedrock aquifers is to the southeast.
3. Identify wells down-gradient and side-gradient of the site and determine the distance to each well. There are relatively few wells used in the determination of groundwater flow within the aquifer. We therefore expanded the well search to include side-gradient wells. This encompasses City Well 4, which is directly east of the proposed infiltration area.
| City Well | Aquifer | Casing/well depth (ft) | Static water level (ft below ground surface) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Prairie du Chien-Jordan | 266/500 | 80 |
| 6 | Jordan | 316/503 | 90 |
| Well ID | Depth (feet) | Aquifer | Direction from infiltration basin | Distance from infiltration basin (feet) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200563 | 88 | Quaternary (surficial) | East | 2040 |
| 200562 | 98 | St. Peter | East | 1400 |
| 224343 | 410 | Prairie du Chien | East | 630 |
| 200565 | 115 | Quaternary (surficial) | South-southeast | 1580 |
| 200566 | 308 | Prairie du Chien | South-southeast | 1730 |
| 200567 | 95 | Quaternary (surficial) | South-southeast | 1740 |
| City Well 4 | 503 | Prairie du Chien - Jordan | East | 1150 |
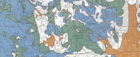
4. Determine the likelihood contaminants will reach the surficial or bedrock aquifers. Using the sensitivity maps from the 1989 Hennepin County Atlas, both the surficial (Quaternary) and Prairie du Chien aquifers have low vulnerability to contamination, although there are small areas of the Prairie du Chien mapped as moderate near the proposed infiltration basin(s). The low vulnerability is attributed to overlying glacial deposits, which are described as loamy till, and for the Prairie du Chien, the presence of the St. Peter bedrock, which is considered a confining later. The City of Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan lists City Well 4 as vulnerable based on the presence of nitrates in sampling.
- Site information for determining feasibility of infiltration. Click on an image for enlarged view.
5. Determine aquifer time of travel to nearby wells. City Well 4 is within the ERA and therefore considered to be within a one-year time of travel. Using information from Edina's Wellhead Protection Plan (hydraulic conductivity, hydraulic gradient, and porosity), times of travel for the city well fields in the Prairie du Chien aquifer range from 124 to 7050 feet per year. For the ERA encompassing City Well 4, the time of travel is estimated at 2650 feet per year. The proposed infiltration basin is approximately 1150 feet from City well 4. Data for the surficial aquifer are lacking and travel times must be estimated based on typical values for the geologic material comprising the aquifer. Assuming a coarse sand or gravelly sand aquifer, based on stratigraphic information in well logs, the following table provides a range of travel time estimates.
| Scenario | Conductivity (ft/year) | Gradient (ft/ft) | porosity | Estimated travel time (ft/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low conductivity | 3150 | 0.00217 | 0.3 | 23 |
| Mid range conductivity | 31500 | 0.00217 | 0.3 | 230 |
| High conductivity | 315000 | 0.00217 | 0.3 | 2275 |
Wells within the surficial aquifer are 1500 to 2000 feet from the proposed infiltration basin.
Based on the information above, there are some potential concerns with infiltration at this site, including the following.
- The locations for the infiltration basin are within a one-year time of travel for City well 4 and potentially within the one-year time of travel for wells in the surficial aquifer.
- Geologic data for the unsaturated zone are based on stratigraphic records from driller logs rather than borings taken by professional geoscientists
- There is a discrepancy in vulnerability assessment for City well 4. Since nitrates were detected in well 4, there is some indication that pollutants may readily travel through the unsaturated zone and into the underlying prairie du Chien aquifer
- Although the County Atlas shows the bedrock aquifer as having low vulnerability, there are areas mapped as medium vulnerability near the proposed infiltration basins.
These concerns warrant further investigation, including the following.
- The Hennepin County atlas is undergoing revision. Additional analysis should occur using the updated information if it is available.
- The private wells identified above should be located and a determination made concerning their status (i.e. are they active or not)
- Additional water chemistry sampling in City well 4 might provide better estimates of the age and vulnerability of the well to contamination
If further investigation indicates infiltration is appropriate, consider the following.
- a. The Wellhead Protection Plan will include a spill response and emergency response plan. These should be reviewed. Additional design concsiderations may be appropriate, such as emergency diversion from the infiltration practice.
- b. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes engineered media with moderate to high concentration of organic matter be utilized?
- c. Should multiple independent infiltration practices be utilized?
Conclusion: Additional investigation, described above, is warranted for this site.
Example 3
An infiltration basin is proposed for a parking lot reconstruction project in Morris, Minnesota. The impervious area is approximately 5 acres. The site is within a Drinking Water Source Management Area (DWSMA) but outside the Emergency Response Area. Aquifer vulnerability is mapped as very high. The project requires a Construction Stormwater Permit. Infiltration at the site requires a higher level of engineering review to comply with the permit.
The engineering review consists of the following steps.
1. Identify the aquifer(s) of concern: To make this determination, we used the County Well Index (CWI) to identify wells and well logs from nearby wells, and the Morris Source Water Assessment. Five City wells are completed in Quaternary deposits and range in depth from 58 to 78 feet. Private wells in the vicinity are completed in the same geologic deposits and have similar depths.
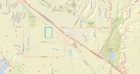
2. Determine the direction of groundwater flow in the aquifer of concern: Static water elevations from well logs in CWI, plotted in the image to the right, indicate no discernible pattern to groundwater flow. The elevation of the Pomme de Terre River, located just east of the proposed infiltration area, is approximately 1080 feet above sea level. There are several irrigation wells in the area that may impact water elevations. City wells, located south of the proposed infiltration, may also influence flow. Finally, well logs indicate alternating layers of sand/gravel and clay/till, suggesting there may be multiple hydraulic units. Without more detailed analysis and more precise measurements of static water elevations, groundwater flow direction cannot be positively determined.
3. Identify the distance from the infiltration area to nearby wells. Because flow direction is uncertain, we must consider all nearby wells. There are several wells near the proposed practice. Some of these are summarized in the table below.
| Well ID | Depth (feet) | Aquifer | Direction from infiltration basin | Distance from infiltration basin (closest and furthest, in feet) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 530879 | 78 | Quaternary (buried) | Southwest | 675 - 1625 |
| 117441 | 62 | Quaternary (buried) | West | 1000 - 1900 |
| 689691 | 80 | Quaternary (buried) | Northwest | 630 - 1000 |
| 601722 | 65 | Quaternary (buried) | North | 315 - 1275 |
| 589046 | 110 | Quaternary (buried) | East | 2275 - 2900 |
| 464752 | 95 | Quaternary (buried) | Southeast | 2600 - 3500 |
4. Determine the likelihood contaminants will reach the surficial or bedrock aquifers. Only two wells in CWI are within the area delineated as being highly vulnerable, and these wells are 3500 feet or more from the proposed infiltration practice. Both well logs show alternating layers of sand, gravel, and clay. Cumulative thickness of clay material in both logs exceeds 25 feet. Clay color is noted as blue, indicating reducing conditions. City wells have consistently tested negative for nitrate, while several wells in the area have high concentrations of arsenic [1][2]. These results suggest water in sampled wells is likely not vulnerable to contamination.
5. Determine aquifer time of travel to nearby wells. Data for calculating travel time is lacking. In particular, the hydraulic gradient is difficult to determine based on data. If we assume a coarse sand or gravelly sand aquifer and utilize inputs from Example 2 above, the following table provides a range of travel time estimates.
| Scenario | Conductivity (ft/year) | Gradient (ft/ft) | porosity | Estimated travel time (ft/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low conductivity | 3150 | 0.00217 | 0.3 | 23 |
| Mid range conductivity | 31500 | 0.00217 | 0.3 | 230 |
| High conductivity | 315000 | 0.00217 | 0.3 | 2275 |
Several wells within the Quaternary aquifer are within 1000 feet of the proposed infiltration. An infiltration practice cannot be constructed to be more than 1000 feet from the nearest domestic well.
The primary concern at the site is the lack of hydrogeologic information. Available well logs suggest there are confining layers of clay. However, the closest wells are likely within one year travel time of any proposed infiltration practice.
Conclusion: Additional investigation is recommended if infiltration is pursued at this site. Additional investigation includes the following options.
- Conduct appropriate soil borings to confirm the presence of adequate confining layers
- Sample nearby wells to determine age and sensitivity to pollution ( age dating and/or sampling for nitrate and presence of oxygen)
If further investigation indicates infiltration is appropriate, consider the following.
- a. The Wellhead Protection Plan will include a spill response and emergency response plan. These should be reviewed. Additional design considerations may be appropriate, such as emergency diversion from the infiltration practice.
- b. Should an infiltration practice that utilizes engineered media with moderate to high concentration of organic matter be utilized?
- c. Should multiple independent infiltration practices be utilized?
References for examples
- Lindgren, Richard J. 1997. Hydraulic Properties and Ground-Water Flow in the St. Peter-Prairie du Chien-Jordan Aquifer, Rochester Area, Southeastern Minnesota. Water-Resources Investigations Report 97-4015.
- Ruhl, James F. 1999. Hydraulic properties of the Prairie du Chien-Jordan aquifer, Shakopee Mdewakanton Sioux Community, southeastern Minnesota, 1997. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4183.
- Seaberg, John. 2000. Overview of the Twin Cities Metropolitan Groundwater Model.
- Stark, J.R., and M.F. Hult. 1985. Ground-water Flow in the Prairie du Chien-Jordan Aquifer Related to Contamination by Coal-Tar Derivatives, St. Louis Park, Minnesota. Water-Resources Investigations Report 85-4087.
This page was last edited on 9 April 2023, at 11:39.