
Difference between revisions of "File:Minnesota surficial geology.jpg"
m |
m |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Except for the southeastern corner of the state, Minnesota's surficial geology is dominated by glaciation. Glacial lobes advanced from the northeast (Superior and Rainy lobes), north (Wadena Lobe) and northwest (Des Moines Lobe). These glaciers left outwash plains (coarse-textured deposits), till (unsorted material) in ground and end moraines, and lake plains (fine-textured sediments). More information can be found at the following: | |
| − | [[Category:Maps]] | + | *[http://www.dnr.state.mn.us/snas/naturalhistory.html Natural history - Minnesota's geology] |
| + | *[http://files.dnr.state.mn.us/lands_minerals/geologyhandbook.pdf Geology of Minnesota - a guide for teachers] | ||
| + | *[http://www.d.umn.edu/prc/fieldcamp/Forms/Mn_Quaternary.pdf Minnesota at a glance - Quaternary glacial geology] | ||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - General information, reference, tables, images, and archives/Images/Maps]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:58, 14 December 2022
Except for the southeastern corner of the state, Minnesota's surficial geology is dominated by glaciation. Glacial lobes advanced from the northeast (Superior and Rainy lobes), north (Wadena Lobe) and northwest (Des Moines Lobe). These glaciers left outwash plains (coarse-textured deposits), till (unsorted material) in ground and end moraines, and lake plains (fine-textured sediments). More information can be found at the following:
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:51, 18 December 2012 | 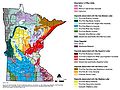 | 959 × 721 (89 KB) | Mtrojan (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file:
This page was last edited on 14 December 2022, at 01:58.