Difference between revisions of "Fact sheet for filtration"
m |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[file:Swale city of Woodbury.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Photo of a Swale city of Woodbury MN|Photo of a Swale city of Woodbury MN]] | [[file:Swale city of Woodbury.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Photo of a Swale city of Woodbury MN|Photo of a Swale city of Woodbury MN]] | ||
| − | ==Design | + | ==Design criteria== |
*Ensure adequate space for [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] system | *Ensure adequate space for [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] system | ||
| − | *Some installations require 2 | + | *Some installations require 2 to 6 feet of head |
*Removal potential of the key pollutant | *Removal potential of the key pollutant | ||
*Parent material and potential for [[Glossary#G|ground water]] contamination | *Parent material and potential for [[Glossary#G|ground water]] contamination | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
*High pollutant removal rates | *High pollutant removal rates | ||
*May be used in a variety of soil types | *May be used in a variety of soil types | ||
| − | *Good for the treatment of [[Glossary#H|hotspots]] because it can be isolated from [[Glossary#G|groundwater]] if contamination concerns exist Limitations: | + | *Good for the treatment of [[Glossary#H|hotspots]] because it can be isolated from [[Glossary#G|groundwater]] by using a liner if contamination concerns exist |
| + | |||
| + | ==Limitations:== | ||
*Higher maintenance requirements | *Higher maintenance requirements | ||
*Some installations ([[Glossary#M|media filters]]) have higher construction costs | *Some installations ([[Glossary#M|media filters]]) have higher construction costs | ||
| − | |||
*Minimal treatment of soluble nutrients | *Minimal treatment of soluble nutrients | ||
*Potential for nitrification in [[Glossary#M|media filters]] where [[Glossary#A|anaerobic]] conditions exist | *Potential for nitrification in [[Glossary#M|media filters]] where [[Glossary#A|anaerobic]] conditions exist | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | + | [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] systems vary in their operation and applicability, but all can be described as structural BMPs that function mainly to enhance water quality by passing stormwater through a media. The media can be made of sand, peat, soil, or compost and should be assigned on a case-by-case basis. Filters can be off-line systems or designed as [[Glossary#P|pre-treatment]] before discharging to other stormwater features. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Glossary#M|Media filters]] can be located on the surface, underground, along the perimeter or an area, or in what is called a pocket design. | ||
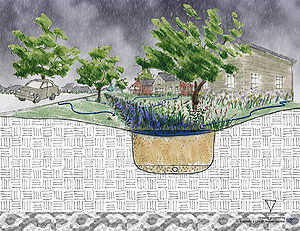
[[file:Filtration-stormevent.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage|Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage]] | [[file:Filtration-stormevent.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage|Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage]] | ||
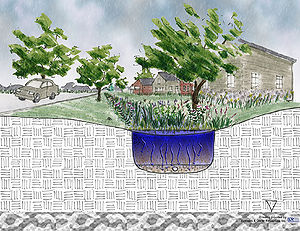
[[file:Filtration-storage.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration|Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration]] | [[file:Filtration-storage.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration|Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration]] | ||
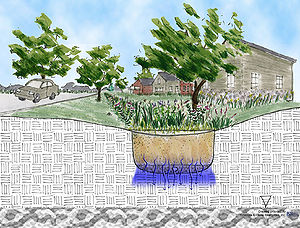
[[file:Infiltration.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown|Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown]] | [[file:Infiltration.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown|Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Mechanisms== | ==Mechanisms== | ||
| − | *[[Glossary#I|Infiltration]] with | + | *[[Glossary#I|Infiltration]] with raised underdrain |
*Screening/ [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] | *Screening/ [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] | ||
*[[Glossary#E|Evaporation]] | *[[Glossary#E|Evaporation]] | ||
| Line 45: | Line 40: | ||
==Pollutant removal== | ==Pollutant removal== | ||
| − | * | + | Pollutant removal varies with the design, construction and maintenance of the BMP. Values below are approximately mid-range removals for a standard designed BMP that is properly constructed and maintained. |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | Media filter |
| − | *35 percent | + | *85 percent [[Glossary#T|Total Suspended Solids (TSS)]] |
| − | *80 percent | + | *50 percent/35 percent Nutrients - [[Glossary#T|Total Phosphorus]] /Total Nitrogen |
| + | *40 to 80 percent Metals - Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc (will vary with metal) | ||
| + | *35 percent Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli | ||
| + | *80 percent Hydrocarbon | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vegetative filter | ||
| + | *68 percent [[Glossary#T|Total Suspended Solids (TSS)]] | ||
| + | *40 percent/35 percent Nutrients - [[Glossary#T|Total Phosphorus]] /Total Nitrogen | ||
| + | *40 to 80 percent Metals - Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc (will vary with metal) | ||
| + | *0 percent Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli | ||
| + | *80 percent Hydrocarbon | ||
==Site factors== | ==Site factors== | ||
| − | *5 | + | *The RECOMMENDED maximum drainage area is typically 5 acres, but can be greater if the discharge to the basin has received adequate pretreatment and the basin is properly designed, constructed, and maintained. |
| − | *20 percent | + | *20 percent maximum Site Slope |
| − | *3 feet | + | *3 feet minimum Depth to Bedrock unless lined |
| − | *3 feet | + | *3 feet minimum Depth to Seasonally High Water Table unless lined |
| − | *A,B,C,D -NRCS Soil Type | + | *A,B,C,D - NRCS Soil Type |
| − | *Poor | + | *Poor to Good Freeze/ Thaw Suitability |
| − | *Suitable - | + | *Suitable with impermeable liner - [[Glossary#H|Hotspot]] Runoff |
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Dry swale]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Green roof]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Sand filter, iron enhanced sand filter, media filter]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Step pool]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Wet swale]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:39, 3 December 2022
Filtration practices are structural stormwater controls that capture, temporarily store, and route stormwater runoff through a filter bed to improve water quality.
Contents
Design criteria
- Ensure adequate space for Filtration system
- Some installations require 2 to 6 feet of head
- Removal potential of the key pollutant
- Parent material and potential for ground water contamination
Benefits
- Good for highly impervious areas with low sediment/high pollutant load (e.g. urban land use and retrofit scenarios)
- High pollutant removal rates
- May be used in a variety of soil types
- Good for the treatment of hotspots because it can be isolated from groundwater by using a liner if contamination concerns exist
Limitations:
- Higher maintenance requirements
- Some installations (media filters) have higher construction costs
- Minimal treatment of soluble nutrients
- Potential for nitrification in media filters where anaerobic conditions exist
Description
Filtration systems vary in their operation and applicability, but all can be described as structural BMPs that function mainly to enhance water quality by passing stormwater through a media. The media can be made of sand, peat, soil, or compost and should be assigned on a case-by-case basis. Filters can be off-line systems or designed as pre-treatment before discharging to other stormwater features.
Media filters can be located on the surface, underground, along the perimeter or an area, or in what is called a pocket design.
Mechanisms
- Infiltration with raised underdrain
- Screening/ Filtration
- Evaporation
- Transpiration if vegetated
- Soil Adsorption
- Biological/ Micro. Uptake
Pollutant removal
Pollutant removal varies with the design, construction and maintenance of the BMP. Values below are approximately mid-range removals for a standard designed BMP that is properly constructed and maintained.
Media filter
- 85 percent Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
- 50 percent/35 percent Nutrients - Total Phosphorus /Total Nitrogen
- 40 to 80 percent Metals - Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc (will vary with metal)
- 35 percent Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli
- 80 percent Hydrocarbon
Vegetative filter
- 68 percent Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
- 40 percent/35 percent Nutrients - Total Phosphorus /Total Nitrogen
- 40 to 80 percent Metals - Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc (will vary with metal)
- 0 percent Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli
- 80 percent Hydrocarbon
Site factors
- The RECOMMENDED maximum drainage area is typically 5 acres, but can be greater if the discharge to the basin has received adequate pretreatment and the basin is properly designed, constructed, and maintained.
- 20 percent maximum Site Slope
- 3 feet minimum Depth to Bedrock unless lined
- 3 feet minimum Depth to Seasonally High Water Table unless lined
- A,B,C,D - NRCS Soil Type
- Poor to Good Freeze/ Thaw Suitability
- Suitable with impermeable liner - Hotspot Runoff
- Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Dry swale
- Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Green roof
- Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Iron enhanced sand filter
- Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Sand filter, iron enhanced sand filter, media filter
- Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Step pool
- Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Wet swale
This page was last edited on 3 December 2022, at 22:39.