Difference between revisions of "Fact sheet for filtration"
(Created page with "Filtration practices are structural stormwater controls that capture, temporarily store, and route stormwater runoff through a filter bed to improve water quali...") |
m |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<p>[[Glossary#F|Filtration]] systems vary in their operation and applicability, but all can be described as structural BMPs that function mainly to enhance water quality by passing stormwater through a media. The media can be made of sand, peat, grass, soil, compost or vegetation and should be assigned on a case-by-case basis. Filters can be off-line systems or designed as [[Glossary#P|pre-treatment]] before discharging to other stormwater features.</p> | <p>[[Glossary#F|Filtration]] systems vary in their operation and applicability, but all can be described as structural BMPs that function mainly to enhance water quality by passing stormwater through a media. The media can be made of sand, peat, grass, soil, compost or vegetation and should be assigned on a case-by-case basis. Filters can be off-line systems or designed as [[Glossary#P|pre-treatment]] before discharging to other stormwater features.</p> | ||
<p>The two main categories of filtration systems include: media filters, and vegetated filters. [[Glossary#M|media filters]] can be located on the surface, underground, along the perimeter or an area, or in what is called a pocket design. Vegetated channels may be grass channels, dry or wet [[Glossary#S|swales]], submerged gravel wetlands, or filter strips.</p> | <p>The two main categories of filtration systems include: media filters, and vegetated filters. [[Glossary#M|media filters]] can be located on the surface, underground, along the perimeter or an area, or in what is called a pocket design. Vegetated channels may be grass channels, dry or wet [[Glossary#S|swales]], submerged gravel wetlands, or filter strips.</p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
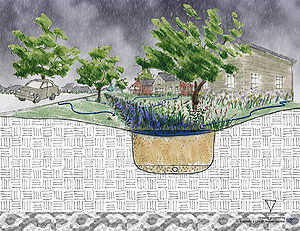
[[file:Filtration-stormevent.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage|Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage]] | [[file:Filtration-stormevent.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage|Drawing of the start of Storm Event - Initial runoff & storage]] | ||
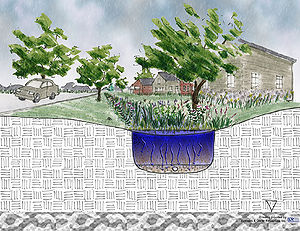
[[file:Filtration-storage.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration|Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration]] | [[file:Filtration-storage.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration|Drawing of the Duration of Storm Event - Storage & filtration/infiltration]] | ||
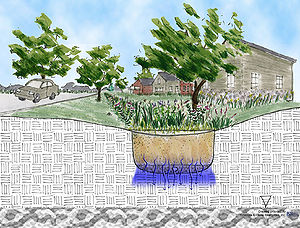
[[file:Infiltration.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown|Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown]] | [[file:Infiltration.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown|Drawing of the Following Storm Event - Remaining storage drawdown]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Management suitability== |
*Water Quality (V<sub>wq</sub>) = High | *Water Quality (V<sub>wq</sub>) = High | ||
*Channel Protection (V<sub>cp</sub>) = Med. | *Channel Protection (V<sub>cp</sub>) = Med. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 35: | ||
*Extreme Flood Protection (Vp<sub>100</sub>) = Low | *Extreme Flood Protection (Vp<sub>100</sub>) = Low | ||
*Recharge Volume (V<sub>re</sub>) = Med./ Low | *Recharge Volume (V<sub>re</sub>) = Med./ Low | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Mechanisms== | ||
*[[Glossary#I|Infiltration]] with appropriate soil & site conditions = | *[[Glossary#I|Infiltration]] with appropriate soil & site conditions = | ||
*Screening/ [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] | *Screening/ [[Glossary#F|Filtration]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 43: | ||
*Soil Adsorption | *Soil Adsorption | ||
*Biological/ Micro. Uptake | *Biological/ Micro. Uptake | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Pollutant removal== | ||
70 to 85 percent [[Glossary#T|Total Suspended Solids (TSS)]] | 70 to 85 percent [[Glossary#T|Total Suspended Solids (TSS)]] | ||
*0 to 50 percent/35 percent Nutrients - [[Glossary#T|Total Phosphorus]] /Total Nitrogen | *0 to 50 percent/35 percent Nutrients - [[Glossary#T|Total Phosphorus]] /Total Nitrogen | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
*35 percent Pathogens - Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli | *35 percent Pathogens - Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli | ||
*80 percent Toxins - Hydrocarbon | *80 percent Toxins - Hydrocarbon | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Site factors== | ||
*5 - AC Max Drainage Area | *5 - AC Max Drainage Area | ||
*20 percent - Max. Site Slope | *20 percent - Max. Site Slope | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 18 March 2013
Filtration practices are structural stormwater controls that capture, temporarily store, and route stormwater runoff through a filter bed to improve water quality.
Contents
Design Criteria
- Ensure adequate space for Filtration system
- Some installations require 2-6 feet of head
- Removal potential of the key pollutant
- Parent material and potential for ground water contamination
Benefits
- Good for highly impervious areas with low sediment/high pollutant load (e.g. urban land use and retrofit scenarios)
- High pollutant removal rates
- May be used in a variety of soil types
- Good for the treatment of hotspots because it can be isolated from groundwater if contamination concerns exist Limitations:
- Higher maintenance requirements
- Some installations (media filters) have higher construction costs
- Potential to cause odor problems
- Minimal treatment of soluble nutrients
- Potential for nitrification in media filters where anaerobic conditions exist
Description
Filtration systems vary in their operation and applicability, but all can be described as structural BMPs that function mainly to enhance water quality by passing stormwater through a media. The media can be made of sand, peat, grass, soil, compost or vegetation and should be assigned on a case-by-case basis. Filters can be off-line systems or designed as pre-treatment before discharging to other stormwater features.
The two main categories of filtration systems include: media filters, and vegetated filters. media filters can be located on the surface, underground, along the perimeter or an area, or in what is called a pocket design. Vegetated channels may be grass channels, dry or wet swales, submerged gravel wetlands, or filter strips.
Management suitability
- Water Quality (Vwq) = High
- Channel Protection (Vcp) = Med.
- Overbank Flood Protection (Vp10) = Low
- Extreme Flood Protection (Vp100) = Low
- Recharge Volume (Vre) = Med./ Low
Mechanisms
- Infiltration with appropriate soil & site conditions =
- Screening/ Filtration
- Evaporation
- Transpiration if vegetated
- Soil Adsorption
- Biological/ Micro. Uptake
Pollutant removal
70 to 85 percent Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
- 0 to 50 percent/35 percent Nutrients - Total Phosphorus /Total Nitrogen
- 45 to 85 percent Metals - Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc
- 35 percent Pathogens - Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli
- 80 percent Toxins - Hydrocarbon
Site factors
- 5 - AC Max Drainage Area
- 20 percent - Max. Site Slope
- 3 feet - Min. Depth to Bedrock
- 3 feet- Min. Depth to Seasonally high Water Table
- A,B,C,D -NRCS Soil Type
- Poor - Good Freeze/ Thaw Suitability
- Suitable - Potential Hotspot Runoff requires impermeable liner