Difference between revisions of "Wildlife friendly erosion prevention and sediment control"
PKalinosky (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{alert|This fact sheet is still under construction and its contents may change or be inaccurate. |alert-under-construction}} | {{alert|This fact sheet is still under construction and its contents may change or be inaccurate. |alert-under-construction}} | ||
| + | [[File:Pdf image.png|100px|thumb|alt=pdf image|<font size=3>[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=File:Wq-strm2-73.pdf Download pdf]</font size>]] | ||
| + | [[File:General information page image.png|right|100px|alt=image]] | ||
Erosion control is important for protecting soil after disturbance and to minimize impacts to receiving waters from excessive sediment. Proper erosion control protects the environment by preventing topsoil movement and by helping vegetation establish itself. However, depending on the type of erosion control material used, it can also hurt wildlife and the environment. | Erosion control is important for protecting soil after disturbance and to minimize impacts to receiving waters from excessive sediment. Proper erosion control protects the environment by preventing topsoil movement and by helping vegetation establish itself. However, depending on the type of erosion control material used, it can also hurt wildlife and the environment. | ||
Revision as of 12:30, 24 January 2024
This fact sheet is still under construction and its contents may change or be inaccurate.
Erosion control is important for protecting soil after disturbance and to minimize impacts to receiving waters from excessive sediment. Proper erosion control protects the environment by preventing topsoil movement and by helping vegetation establish itself. However, depending on the type of erosion control material used, it can also hurt wildlife and the environment. Erosion control products (ECPs) come in many different forms. They can include mulch, silt fences, erosion control blankets (ECBs) and more. However, the type that presents the most danger to wildlife and the environment is mesh netting, commonly found in ECBs and as a component of silt fencing. Wildlife can become entangled in plastic or metal mesh and become injured or killed. Machinery can become entangled and damaged by plastic mesh. Plastic netting also pollutes the environment when it degrades, forming microplastics.
Contents
Safer products
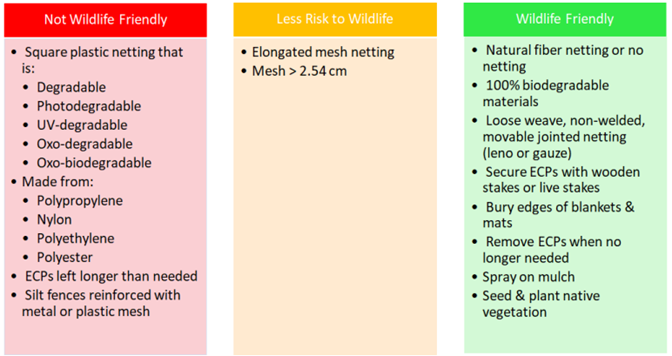
The shape and structure of erosion control netting has a large impact on its safety to wildlife. Elongated, rectangular openings are preferable over square shaped netting, as the elongated apertures allow wildlife to free themselves more easily and avoid injuries. Structurally speaking, moveable, woven joints, such as those found in leno or gauze netting are preferred over welded joints, since the added flexibility allows wildlife to stretch the netting while passing through. This reduces the odds of wildlife becoming entrapped in netting.
Netting material is another important factor for wildlife safety. Because it does not degrade the same way that organic material like mulch or straw does, intact plastic netting can be released into the environment and has even been found as a nest material for birds, causing young birds to be entangled or ingest plastic.
Plastic netting breaks down in the environment, releasing microplastics. Ingesting these microplastics can cause blockage or abrasion of the digestive tract, which can kill wildlife. In addition, other pollutants such as harmful chemicals or pathogens tend to collect on the surface of microplastics. These pollutants then accumulate in biomass and make their way up the food chain, where they can harm human and animal health. However, some of the language surrounding plastic products can be confusing.
Potentially misleading terms
These products are not wildlife friendly, but sound like they are. Many plastic products are labeled as being “degradable”, but only some are safe for the environment. All plastics degrade, breaking down into smaller parts over time. This is where many microplastics come from. Plastics labeled as just “degradable” fall into this category. Similarly misleading terms include:
- Photodegradable: in erosion control settings, vegetation will block the light and netting won’t degrade.
- UV-degradable: same issue as with photodegradable plastics. Additionally, even if the plastic does degrade, there is no guarantee the degraded plastic particles are safe for the environment.
- Oxo-degradable: refers to conventional plastic mixed with an additive to make it break down. This creates large quantities of microplastics, which don’t break down at the molecular level like biodegradable plastics do.
The only materials that are safe for the environment and for wildlife are 100% biodegradable products. The key difference is that biodegradable products, such as those made of natural fibers, are completely broken down by bacteria in the environment to form carbon dioxide, water, and biomass. Note that some biodegradable plastics are only industrially compostable and don’t biodegrade in the environment. This means they must be disposed of properly or risk becoming just as harmful to the environment as normal plastics. Natural fiber products are therefore the safest bet for avoiding environmental plastic contamination.
Implementing wildlife-friendly practices
The ability to use wildlife-friendly erosion control products will depend on site conditions including slope, water flow, soil conditions, and more. It is important to avoid using plastic mesh wherever possible. Safer products to implement include natural fiber mesh or hydraulically-applied erosion control products (“hydromulch,” or HECPs). It is still important to be aware of the contents of HECPs, as some contain environmentally harmful products such as synthetic (plastic) fibers and dyes that are toxic to wildlife, such as malachite green. MnDOT maintains a list for approved products that can be used on their projects at https://www.dot.state.mn.us/products/erosioncontrolandlandscaping/hydraulicerosioncontrol.html.
If plastic netting cannot be avoided, there are methods to minimize the damage done. These methods are also generally applicable best practices to protect wildlife:
- Don’t leave netting out for longer than necessary- remove once vegetation is established.
- Plan and stage projects to minimize bare soil and soil disturbance.
- In some cases, it can be possible to change the site slope to be suitable for wildlife-friendly products by using terracing.
- Inspect netting regularly and release trapped animals if any are present.
- Work with natural resource specialists such as the DNR or Fish and Wildlife to identify and protect ecologically sensitive areas and rare species.
- Bury the edges of erosion control blankets and secure them using wooden or live stakes. This reduces reptile entrapment.
Summary
- Erosion control products can trap and kill wildlife.
- To protect wildlife, use biodegradable mesh with rectangular openings and woven joints.
- Avoid plastic products, including those that call themselves “photo-“, “UV-“, or “oxo-degradable”, as these types of plastics do not break down adequately or safely in natural erosion control environments.
- Install netting with stakes and bury the edges, then remove them as soon as possible.
Further Reading
- Wildlife-friendly erosion control (2013). Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. http://files.dnr.state.mn.us/eco/nongame/wildlife-friendly-erosion-control.pdf
- Wildlife and environmentally friendly erosion control (accessed 2023). United States Fish and Wildlife Service. https://www.fws.gov/sites/default/files/documents/WLfriendlyErosionControl__final.pdf
- Erosion control and landscaping products (accessed 2023). Minnesota Department of Transportation. https://www.dot.state.mn.us/products/erosioncontrolandlandscaping/index.html
- Plastics (synthetic fibers) in Erosion Prevention & Sediment Control Practices (2019). Minnesota Department of Natural Resources and Minnesota Department of Transportation. https://www.house.mn.gov/comm/docs/de982bcd-7354-4e2d-a95c-3433c646095a.pdf