Difference between revisions of "Green roofs"
m (→Description) |
m (→Green Roofs) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Several [[Fact sheets for green roofs|fact sheets]] for green roofs provide overview information and information on design, construction and maintenance, and volume and pollutant removal.--> | Several [[Fact sheets for green roofs|fact sheets]] for green roofs provide overview information and information on design, construction and maintenance, and volume and pollutant removal.--> | ||
| − | + | Green roofs consist of a series of layers that create an environment suitable for plant growth without damaging the underlying roof system. Green roofs create green space for public benefit, energy efficiency, and stormwater retention/ detention. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Design criteria== | |
[[file:Green roofs 2.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Photo of Green roof|Photo of Green roof]] | [[file:Green roofs 2.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=Photo of Green roof|Photo of Green roof]] | ||
| − | + | Structural load capacity, how much weight the roof can hold, is a major factor in determining whether the green roof is “extensive” or “intensive”. Vegetation selection is based on numerous factors including, growth medium depth, microclimate, irrigation availability and maintenance. | |
<p>A leak detection system is recommended to quickly detect and locate leaks. Modular products can increase installation and repair efficiency.</p> | <p>A leak detection system is recommended to quickly detect and locate leaks. Modular products can increase installation and repair efficiency.</p> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Benefits== | ||
*Reduce, delay, and cool stormwater runoff. | *Reduce, delay, and cool stormwater runoff. | ||
*Insulate buildings and lower energy consumption and costs. | *Insulate buildings and lower energy consumption and costs. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
*Increase longevity of traditional roofing systems by protecting from ultraviolet rays. | *Increase longevity of traditional roofing systems by protecting from ultraviolet rays. | ||
*Reduce carbon dioxide levels and heat island effect. | *Reduce carbon dioxide levels and heat island effect. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Limitations== | ||
*Cost is higher than traditional roofing systems – can be significant for retrofits. | *Cost is higher than traditional roofing systems – can be significant for retrofits. | ||
*Leaks can cause significant damage and can be hard to locate and repair without an electronic leak detection system. | *Leaks can cause significant damage and can be hard to locate and repair without an electronic leak detection system. | ||
*Conditions can be harsh for vegetation establishment. | *Conditions can be harsh for vegetation establishment. | ||
*Maintenance needs can be higher than traditional roofing system. | *Maintenance needs can be higher than traditional roofing system. | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Management suitability== | ||
*Water Quality (V<sub>wq</sub>) - High | *Water Quality (V<sub>wq</sub>) - High | ||
*Channel Protection (V<sub>cp</sub>) - Med. | *Channel Protection (V<sub>cp</sub>) - Med. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 43: | ||
*Extreme Flood Protection (Vp<sub>100</sub>) - Low | *Extreme Flood Protection (Vp<sub>100</sub>) - Low | ||
*Recharge Volume (V<sub>re</sub>) - Low | *Recharge Volume (V<sub>re</sub>) - Low | ||
| − | === | + | |
| + | ===Mechanisms=== | ||
*Screening/ Filtration | *Screening/ Filtration | ||
*Temperature Control | *Temperature Control | ||
| Line 48: | Line 52: | ||
*Biological/ Micro. Uptake | *Biological/ Micro. Uptake | ||
| − | == | + | ==Pollution removal=== |
*Total Suspended Solids - 90% | *Total Suspended Solids - 90% | ||
*Nutrients - Total Phosphorus/Total Nitrogen - 100%/ 20% | *Nutrients - Total Phosphorus/Total Nitrogen - 100%/ 20% | ||
| Line 54: | Line 58: | ||
*Pathogens - Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli - 65% | *Pathogens - Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli - 65% | ||
NA Toxins - Hydrocarbons, Pesticides | NA Toxins - Hydrocarbons, Pesticides | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Site factors== | ||
*Drainage Area - Rooftop | *Drainage Area - Rooftop | ||
*Max. Slope - NA. | *Max. Slope - NA. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 68: | ||
*Potential Hotspot Runoff (requires impermeable liner) - Suitable | *Potential Hotspot Runoff (requires impermeable liner) - Suitable | ||
| − | + | Note: Pollution removal percentages apply to volume of runoff treated, and not to volume by-passed | |
| − | + | ==Description== | |
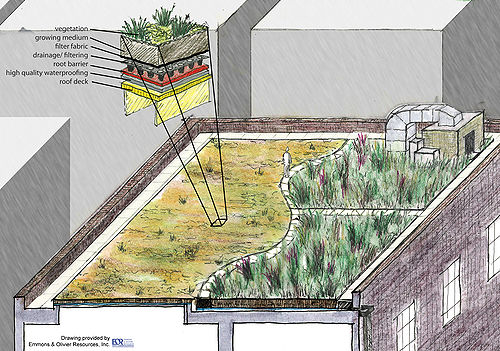
[[file:green roof schematic.jpg|thumb|500px|alt=Schematic of green roof|Schematic of green roof]] | [[file:green roof schematic.jpg|thumb|500px|alt=Schematic of green roof|Schematic of green roof]] | ||
| − | + | There are two systems of green roofs, extensive and intensive, composed of the same system of layers. Extensive systems are lighter, typically have 4 inches or less of growing medium, use drought tolerant vegetation, and can structurally support limited uses (such as maintenance personnel). Intensive systems are heavier, have a greater soil depth, can support a wider range of plants, and can support increased pedestrian traffic. | |
<p>Rainfall is initially intercepted by vegetation, held on foliage, or soaked up by plant roots. Any remaining runoff filters through the growing medium and is drained away from the roof’s surface by the drainage layer. Some drainage systems use small depressions to store excess water for uptake during drier conditions (RCWD 2005), while others provide an overflow for larger rainfall events.</p> | <p>Rainfall is initially intercepted by vegetation, held on foliage, or soaked up by plant roots. Any remaining runoff filters through the growing medium and is drained away from the roof’s surface by the drainage layer. Some drainage systems use small depressions to store excess water for uptake during drier conditions (RCWD 2005), while others provide an overflow for larger rainfall events.</p> | ||
Revision as of 19:44, 15 March 2013
Green roofs consist of a series of layers that create an environment suitable for plant growth without damaging the underlying roof system. Green roofs create green space for public benefit, energy efficiency, and stormwater retention/ detention.
Contents
Design criteria
Structural load capacity, how much weight the roof can hold, is a major factor in determining whether the green roof is “extensive” or “intensive”. Vegetation selection is based on numerous factors including, growth medium depth, microclimate, irrigation availability and maintenance.
A leak detection system is recommended to quickly detect and locate leaks. Modular products can increase installation and repair efficiency.
Benefits
- Reduce, delay, and cool stormwater runoff.
- Insulate buildings and lower energy consumption and costs.
- Provide habitat for birds and insects.
- Increase longevity of traditional roofing systems by protecting from ultraviolet rays.
- Reduce carbon dioxide levels and heat island effect.
Limitations
- Cost is higher than traditional roofing systems – can be significant for retrofits.
- Leaks can cause significant damage and can be hard to locate and repair without an electronic leak detection system.
- Conditions can be harsh for vegetation establishment.
- Maintenance needs can be higher than traditional roofing system.
Management suitability
- Water Quality (Vwq) - High
- Channel Protection (Vcp) - Med.
- Overbank Flood Protection (Vp10) - Low
- Extreme Flood Protection (Vp100) - Low
- Recharge Volume (Vre) - Low
Mechanisms
- Screening/ Filtration
- Temperature Control
- Evaporation
- Transpiration (if vegetated)
- Soil Adsorption
- Biological/ Micro. Uptake
Pollution removal=
- Total Suspended Solids - 90%
- Nutrients - Total Phosphorus/Total Nitrogen - 100%/ 20%
- Metals - Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc - 80%
- Pathogens - Coliform, Streptococci, E. Coli - 65%
NA Toxins - Hydrocarbons, Pesticides
Site factors
- Drainage Area - Rooftop
- Max. Slope - NA.
- Min. Depth to Bedrock - NA.
- Min. Depth to Water Table - NA.
SCS Soil Type (can be used in C&D soil types with modifications (e.g. underdrains)) - NA
- Freeze/ Thaw Suitability - Good
- Potential Hotspot Runoff (requires impermeable liner) - Suitable
Note: Pollution removal percentages apply to volume of runoff treated, and not to volume by-passed
Description
There are two systems of green roofs, extensive and intensive, composed of the same system of layers. Extensive systems are lighter, typically have 4 inches or less of growing medium, use drought tolerant vegetation, and can structurally support limited uses (such as maintenance personnel). Intensive systems are heavier, have a greater soil depth, can support a wider range of plants, and can support increased pedestrian traffic.
Rainfall is initially intercepted by vegetation, held on foliage, or soaked up by plant roots. Any remaining runoff filters through the growing medium and is drained away from the roof’s surface by the drainage layer. Some drainage systems use small depressions to store excess water for uptake during drier conditions (RCWD 2005), while others provide an overflow for larger rainfall events.