
Difference between revisions of "Green Stormwater Infrastructure (GSI) and sustainable stormwater management"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*[[Planning green stormwater infrastructure projects and practices]] - <span title="This page provides information on green stormwater infrastructure planning, cost, ordinances, and financing.> '''Comment'''</span> | *[[Planning green stormwater infrastructure projects and practices]] - <span title="This page provides information on green stormwater infrastructure planning, cost, ordinances, and financing.> '''Comment'''</span> | ||
*[[Green stormwater infrastructure - planning case studies]] | *[[Green stormwater infrastructure - planning case studies]] | ||
| + | *[[Example]] | ||
==Green stormwater infrastructure best management practices== | ==Green stormwater infrastructure best management practices== | ||
Revision as of 18:38, 10 April 2023

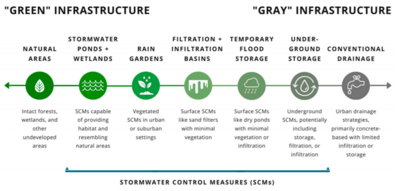
Green infrastructure encompasses a wide array of practices, including stormwater management. Green stormwater infrastructure (GSI) encompasses a variety of practices primarily designed for managing stormwater runoff but that provide additional benefits such as habitat or aesthetic value.
Water management using green infrastructure practices mimics the natural water cycle. Examples of green infrastructure practices include planting trees, restoring wetlands, enhancing biodiversity, and restoring floodplains. Green infrastructure incorporates both the natural environment and engineered systems to provide clean water, conserve ecosystem values and functions, and provide a wide array of benefits to people and wildlife. Green infrastructure can be applied on different scales, from the house or building level, to the broader landscape level. On the local level, green infrastructure practices include rain gardens, permeable pavements, green roofs, infiltration planters, trees and tree boxes, and rainwater harvesting systems. At the largest scale, the preservation and restoration of natural landscapes (such as forests, floodplains and wetlands) are critical components of green infrastructure.
Stormwater management using green infrastructure practices involves keeping and using water close to its point of origin (i.e. keeping the raindrop where it falls). Practices include those local practices mentioned above - rain gardens, permeable pavements, green roofs, infiltration planters, trees and tree boxes, and rainwater harvesting systems. Because there multiple benefits of these practices, in addition to stormwater management, the manual includes a variety of topics related to green infrastructure as illustrated below.
Acknowledgements for Green Stormwater Infrastructure (GSI) and sustainable stormwater management
This page provides links to information on green stormwater infrastructure, green infrastructure, and sustainable stormwater management.
Contents
Green stormwater infrastructure and sustainable stormwater management concepts and overview
- Overview of green stormwater infrastructure (GSI) and sustainable stormwater management
- Multiple benefits of green infrastructure and role of green infrastructure in sustainability and ecosystem services
- Multiple benefits of green stormwater infrastructure
- Green infrastructure and green stormwater infrastructure terminology
- Training and certification for green stormwater infrastructure
- Green Stormwater Infrastructure design strategies and practices for climate resilience
Green infrastructure planning
- Planning green stormwater infrastructure projects and practices - Comment
- Green stormwater infrastructure - planning case studies
- Example
Green stormwater infrastructure best management practices
- Design considerations for green stormwater infrastructure best management practices
- Operation and maintenance of green stormwater infrastructure best management practices
- Assessing the performance of green stormwater infrastructure best management practices
Additional information on green stormwater infrastructure
- Green stormwater infrastructure case studies
- Links for green stormwater infrastructure
- Stormwater runoff performance of natural and undeveloped systems
- Checklists, inspection sheets, maintenance agreements, and model ordinances for green stormwater infrastructure
- File:The role of green stormwater infrastructure in climate 3.pptx - PowerPoint file for a presentation delivered to the University of Minnesota in October, 2022.
Support documents
These are documents received as part of MPCA work orders. Most of this material is incorporated into the pages on this topic, with minor edits.
