This page is in development
Filter strips
City of Burnsville - vegetated filter strip pretreatment
- Location: Neighborhood surrounding Crystal Lake in Burnsville, Minnesota
- Owners: Homeowners
- Designer: Barr Engineering
- Contractor: Mike’s Lawn and Landscape
- Year of Completion: 2004
- Pretreatment Practice: Filtration and settling
- Practice Description: Vegetated filter strip
- Design Features: The vegetated filter strip design filters stormwater runoff which minimizes erosion risks and filters out sediment prior to entering the rain gardens.
- Downstream Best Management Practice (BMP) Benefitting from Pretreatment: Rain garden
- Total Drainage Area and Land Use: 5.3 acres (primarily residential)
- Construction Cost: $8.00 per square foot (rain garden)
- Pollutant Removal: Vegetated filter strips provide 90 percent stormwater runoff volume reductions
- Is the Site Publicly Accessible: No
- Contact: Barr Engineering (kleuthold@barr.com)
Design summary
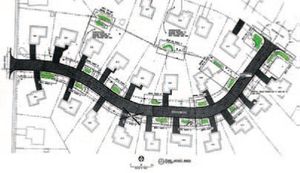
In 2002, the City of Burnsville worked with Barr Engineering to design rain gardens in a residential neighborhood surrounding Crystal Lake to reduce the pollutant runoff into the lake. Using city funding and a grant from the Metropolitan Council, 17 raingardens were installed along a street near Lake Crystal (Figure 1) as part of a stormwater retrofit study [Land and Water Magazine, 2004]. Vegetated filter strips provide stormwater pretreatment between the curb cutout and rain garden (Figure 2). The vegetated filter strip treats stormwater runoff that enters the raingarden by dissipating the flow to minimize erosion and remove sediment from the runoff via filtration and settling into the vegetation. This design reduces the total suspended solids (TSS) load to the rain garden and allows the rain garden to function as designed and minimize costly maintenance that results from sedimentation.
Maintenance
The homeowners are responsible for performing routine maintenance such as weeding, raking, and removal of accumulated sediment for the filter strips and rain gardens. The elevation of the filter strip increases over time because of solids settling into the vegetation, so the City of Burnsville has removed the vegetated filter strips, removed the sediment, and replaced the filter strips every five to seven years. Over the 15-year lifespan of the project, filter strips have been replaced twice by the city.
Lessons learned
- Incorporate “drop waterfalls” at curb cutout to slow the speed and reduce erosion potential of the runoff entering the vegetated filter strip.
- Vegetated filter strips have performed as designed and prolonged the lifespan and reduced maintenance of the rain gardens
References
- Barr Engineering Company. (2006). Rain Garden Project Summary. Retrieved February 5, 2019, from City of Burnsville
- Land and Water Magazine. (2004, September). Burnsville Rainwater Gardens. Land and Water Magazine, 48(5), p. 47. Retrieved February 5, 2019, from Land and Water Magazine
Project Name
Project Overview
Narrative description of pretreatment project
- Project Location:
- Year Constructed:
- Type of Pretreatment Practice: (e.g., forebay, proprietary settling device, etc.)
- Specific Practice: (e.g., rock inlet, name of proprietary device)
- Practice Owner:
- Practice Designer:
Design Considerations
- Design Cost:
- Design Year:
Narrative description of contributing drainage area, including description of land use
List of existing impairments and TMDLs that the BMP drains to
- Total Contributing Drainage Area (acres):
- Total Impervious Area (acres):
- Watershed Slope (%):
- Downstream Structural Best Management Practice:
- Design Pollutant Removal Performance:
Discussion of why that particular pretreatment system was chosen for that project location, specific rationale (e.g., site characteristics, ease of maintenance, etc.)
Description of sizing criteria used to design pretreatment practice
Construction Considerations
- Construction Cost:
- Construction Year:
Description of adverse site conditions/other construction challenges encountered during installation
Maintenance Considerations
List or description of types of maintenance practices used for the upkeep of the pretreatment system
- Maintenance Frequency:
- Maintenance Cost:
- Disposal Cost:
Description of maintenance challenges, discussion of ease of maintenance
Discussion of any additional maintenance considerations
Results
Discussion of how the performance was measured or estimated
- Measured or Estimated Pollutant Removal Performance:
For proprietary practices, did were the manufacturer claims met?
Discussion of lessons learned through the implementation of this pretreatment practice
Villa Park Stormwater Improvements - Preserver
Project Overview
Narrative description of pretreatment project
- Project Location: Roseville, MN
- Year Constructed:
- Type of Pretreatment Practice: Proprietary settling device
- Specific Practice: The Preserver
- Practice Owner:
- Practice Designer:
Design Considerations
- Design Cost:
- Design Year:
The total contributing drainage area to the Preserver was 242 acres, with 8 acres of direct drainage area. An estimated 30% of the direct drainage area to the Preserver was impervious (2.4 acres). The land use of the contributing drainage area was residential, with a mature tree canopy.
List of existing impairments and TMDLs that the BMP drains to
- Total Contributing Drainage Area (acres): 242
- Total Impervious Area (acres): ~30%
- Watershed Slope (%):
- Downstream Structural Best Management Practice: Irrigation cistern
- Design Pollutant Removal Performance:
Discussion of why that particular pretreatment system was chosen for that project location, specific rationale (e.g., site characteristics, ease of maintenance, etc.)
Description of sizing criteria used to design pretreatment practice
Construction Considerations
- Construction Cost:
- Construction Year:
Description of adverse site conditions/other construction challenges encountered during installation
Maintenance Considerations
List or description of types of maintenance practices used for the upkeep of the pretreatment system
- Maintenance Frequency:
- Maintenance Cost:
- Disposal Cost:
The mature tree canopy in the contributing drainage area contributed to heavy organic loads, including large debris. The total captured material would likely be greater with more frequent cleaning of the system - the sump was full approximately halfway through the monitoring period.
Discussion of any additional maintenance considerations
Results
Discussion of how the performance was measured or estimated
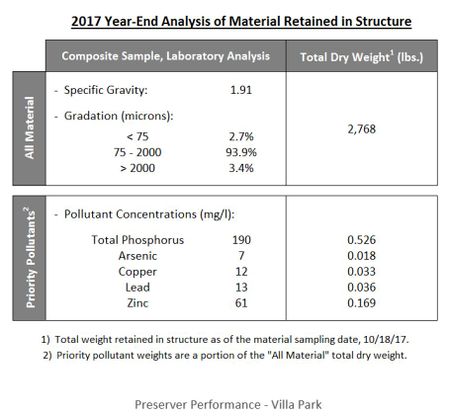
- Measured or Estimated Pollutant Removal Performance: 2,768 lbs of material captured by the pretreatment device, including:
- 0.526 lbs phosphorus
- Significant heavy metals
For proprietary practices, did were the manufacturer claims met?
Discussion of lessons learned through the implementation of this pretreatment practice