Common pre-storage practices used in stormwater harvesting and use systems
Link to this table
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Grassed Swales | A swale is a wide, shallow, vegetated depression in the ground designed to channel drainage of water. Grassed swales can reduce the velocity of flowing stormwater which allows larger particle to drop out of suspension in the water column. Swales are considered permanent primary treatment practices. Information on design, construction, maintenance, and performance assessment can be found here. |
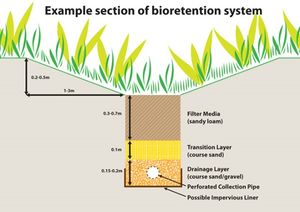
| BMPs with an underdrain | BMPs having an underdrain are designed to filter water prior to being discharged to the underdrain. These BMPs include bioretention, permeable pavement, sand filters, and tree trenches/boxes. Most of the water entering these BMPs is passed to the underdrain. In a harvest and use system, water passing through the underdrain must be discharged back to the harvest and use system. As water passes through the filter media, particulates are trapped and nutrients are removed via plant uptake. Note that media mixes with high organic matter may contribute nutrients and impart a dark color to the discharge water. Information on design, construction, maintenance, and performance assessment can be found in the appropriate section of this manual. |
| Manufactured screens and filters | Filtration practices make use of porous media, mesh, or screens to trap pollutant as water flows through the filter. Filtration practices utilize sand filters or bio-filters, and include a number of proprietary devices. These devices are typically classified as pretreatment screen practices. Information on design, construction, maintenance, and performance assessment can be found here. |
| Debris Screens | Screens prevent large debris (gross solids) and animals from entering the collection system and contaminating harvested water. These devices are typically classified as pretreatment screen practices. They have limited utility in removing suspended solids and associated pollutants and additional treatment is needed prior to discharge to the storage unit. These devices may be prone to freezing over with ice in the winter. |
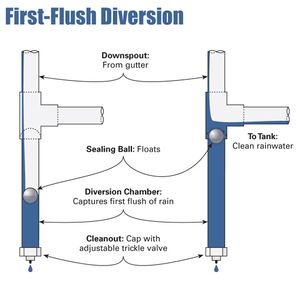
| First Flush Device | First flush devices reduce pollutant loads to the storage unit by diverting initial stormwater flows to other drainage networks. A majority of pollutants in urban runoff are carried in the initial runoff from a site (MPCA Stormwater Manual). Since these devices do not treat stormwater but instead divert untreated water away from the harvest and use system, they are technically not treatment practices. Special care must be taken to avoid problems with freezing, such as diverting water below the frost line and ensuring the system is drained and shut down in the winter. |
| Gutter Guards/Leaf Screens | Gutter guards and leaf screens prevent organic and other large debris (gross solids) or animals from entering roof gutters. This both prevents clogging of gutter and minimizes stormwater contact with potential sources of pollution. These devices are typically classified as pretreatment screen practices. They have limited utility in removing suspended solids and associated pollutants and additional treatment is needed prior to discharge to the storage unit. |
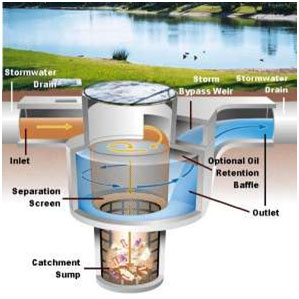
| Separators | Separators are flow-through structures with settling chamber or sediment traps that remove particulates and gross solids from stormwater. Some devices also remove floatable or include grease traps. These devices are typically classified as pretreatment settling practices. Information on design, construction, maintenance, and performance assessment can be found here. |
| X | X |
| X | X |
| X | X |
| X | X |
| X | X |
| X | X |