Difference between revisions of "Design criteria for dry swale (grass swale)"
m |
m (→Related pages) |
||
| (63 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[File:Technical information page image.png|100px|left|alt=image]] | |
| + | [[File:Dry swale.jpg|300 px|thumb|alt=photo of a dry swale|<font size=3>Photo of a dry swale. Courtesy of Limnotech.</font size>]] | ||
| + | [[File:Dry swale with underdrain.jpg|300px|thumb|alt=photo dry swale with underdrain|<font size=3>Photo of a dry swale with an underdrain. Courtesy H.R. Green</font size>]] | ||
| − | This page provides a discussion of design elements and design steps for dry swales, which are often called grass swales. The following discussion includes dry swales used as filtration or infiltration practices, with the distinction being the presence of an underdrain for filtration practices. | + | This page provides a discussion of design elements and design steps for dry swales, which are often called grass swales. The following discussion includes dry swales used as [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Glossary#F filtration] or [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Glossary#I infiltration] practices, with the distinction being the presence of an [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Glossary#U underdrain] for filtration practices. |
| − | {{alert| | + | {{alert|Swales can be an important tool for retention and detention of stormwater runoff. Depending on design and construction, swales may provide additional benefits, including cleaner air, carbon sequestration, improved biological habitat, and aesthetic value. See the section [[Green Stormwater Infrastructure (GSI) and sustainable stormwater management]].|alert-success}} |
==Terminology== | ==Terminology== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 16: | ||
==Details and CADD images== | ==Details and CADD images== | ||
| + | {{alert|To obtain appropriate resolution on details, you must open the .pdf links below and increase the size as necessary to obtain the desired resolution|alert-info}} | ||
| + | |||
Use [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=CADD_images_for_individual_best_management_practices this link] to access .pdf diagrams of CADD drawings. To see all filtration CADD images in a combined pdf, [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=File:All_pdfs_CADD_images_combined.pdf click here]. | Use [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=CADD_images_for_individual_best_management_practices this link] to access .pdf diagrams of CADD drawings. To see all filtration CADD images in a combined pdf, [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=File:All_pdfs_CADD_images_combined.pdf click here]. | ||
*[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Links_to_.dwg_files_for_swales Links to .dwg files for swales] | *[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Links_to_.dwg_files_for_swales Links to .dwg files for swales] | ||
| − | * | + | *Swale layout: [[File:Swale Layout2 (1).pdf]] |
| − | *Typical dry swale profile section with check dams and draintile: [[File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET | + | *Typical dry swale profile section with check dams and draintile: [[File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 2.pdf]] |
| − | *Typical grass channel cross-section without soil amendment: [[File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 2.pdf]] | + | *[[File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 2 (2).pdf]] |
| + | *Typical grass channel cross-section without soil amendment: [[File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 1.pdf]] | ||
| + | *Typical wet swale check dam cross section, profile section with check dams, and profile section: [[File:MIDS WET Swale Sections SHEET 2 (1).pdf]] | ||
| + | *Cascade profile, riffle pool sequence profile, riffle weir cross-section: [[File:Stormwater-Step-Pool.pdf]] | ||
| + | *typical earthen, rock, structural check dams; profile and cross-section: [[File:VARIOUS CHECK DAMS Layout1 (1).pdf]] | ||
| + | *Typical wet and dry swale cross-sections: [[File:Wet and dry swales Layout2 (1).pdf]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Design phase maintenance considerations== | ||
| + | {{alert|Maintenance considerations are an important component of design|alert-warning}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Implicit in the design guidance is the fact that many design elements of infiltration and filtration systems can minimize the maintenance burden and maintain pollutant removal efficiency. Key examples include | ||
| + | *limiting drainage area; | ||
| + | *providing easy site access (''REQUIRED''); | ||
| + | *providing [[Glossary#P|pretreatment]] (''REQUIRED''); and | ||
| + | *utilizing native plantings (see [http://www.pca.state.mn.us/publications/manuals/stormwaterplants.html Plants for Stormwater Design]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information on design information for individual infiltration and filtration practices, [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Category:Design_criteria link here]. | ||
==Major design elements - Physical feasibility initial check== | ==Major design elements - Physical feasibility initial check== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 55: | ||
*[http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Procedures_for_investigating_sites_with_potential_constraints_on_stormwater_infiltration Procedures for investigating sites with potential constraints] | *[http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Procedures_for_investigating_sites_with_potential_constraints_on_stormwater_infiltration Procedures for investigating sites with potential constraints] | ||
| − | ===Contributing drainage area=== | + | ===[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Contributing_drainage_area_to_stormwater_BMPs Contributing drainage area]=== |
The RECOMMENDED maximum drainage area is typically 5 acres. Dry swales can be designed to convey runoff from larger drainage areas. However, volume reduction, water quality function, and ability to meet the MPCA CGP requirements is diminished. | The RECOMMENDED maximum drainage area is typically 5 acres. Dry swales can be designed to convey runoff from larger drainage areas. However, volume reduction, water quality function, and ability to meet the MPCA CGP requirements is diminished. | ||
===Site topography and slopes=== | ===Site topography and slopes=== | ||
| − | Unless slope stability calculations demonstrate otherwise (for guidance on calculating slope stability, see [http://people.eng.unimelb.edu.au/stsy/geomechanics_text/Ch11_Slope.pdf], [http://www.gf.uns.ac.rs/~zbornik/doc/ZR25.51 | + | Unless slope stability calculations demonstrate otherwise (for guidance on calculating slope stability, see [http://people.eng.unimelb.edu.au/stsy/geomechanics_text/Ch11_Slope.pdf], [http://www.gf.uns.ac.rs/~zbornik/doc/ZR25.51.pdf]) it is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that swales be located a minimum horizontal distance of 200 feet from down-gradient slopes greater than 20 percent, and that slopes in contributing drainage areas be limited to 15 percent. |
===Site location/minimum setback=== | ===Site location/minimum setback=== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 66: | ||
If the swale is constructed as an infiltration practice, the following table summarizes required and recommended minimum horizontal and vertical setback distances from an infiltration practice to an above-ground or underground structure. It will be necessary to consult local ordinances for further guidance on siting infiltration practices. | If the swale is constructed as an infiltration practice, the following table summarizes required and recommended minimum horizontal and vertical setback distances from an infiltration practice to an above-ground or underground structure. It will be necessary to consult local ordinances for further guidance on siting infiltration practices. | ||
| − | {{alert|A minimum setback of 50 feet between a dry swale without an underdrain (infiltration practice) and a water supply well is REQUIRED by the Minnesota Department of Health Rule 4725.4350|alert-danger}} | + | {{alert|A minimum setback of 50 feet between a dry swale without an underdrain (infiltration practice) and a water supply well is REQUIRED by the Minnesota Department of Health Rule 4725.4350|alert-danger}} |
{{:Summary of horizontal and vertical setback distances}} | {{:Summary of horizontal and vertical setback distances}} | ||
===Depth to groundwater and bedrock=== | ===Depth to groundwater and bedrock=== | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:3 foot separation b.png|300px|thumb|alt=schematic illustrating separation distance from bottom of infiltration BMP to water table or top of bedrock|<font size=3>Schematic illustrating separation distance from bottom of infiltration BMP to water table or top of bedrock. This diagram includes a modified subsoil zone in which the subsoil has been ripped to alleviate compaction.</font size>]] |
A separation distance of at least 3 feet is REQUIRED under the MPCA CGP between the bottom elevation of infiltration swales and the elevation of the seasonally high water table. | A separation distance of at least 3 feet is REQUIRED under the MPCA CGP between the bottom elevation of infiltration swales and the elevation of the seasonally high water table. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 77: | ||
A [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Shallow_soils_and_shallow_depth_to_bedrock field soil properties investigation] is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED. | A [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Shallow_soils_and_shallow_depth_to_bedrock field soil properties investigation] is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{alert|Infiltration is prohibited when the infiltration system will be constructed in areas with less than three (3) feet of separation distance from the bottom of the infiltration system to the elevation of the seasonally saturated soils or the top of bedrock|alert-danger}} | ||
===Karst topography=== | ===Karst topography=== | ||
It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that underdrains and an impermeable liner be used for dry swales with filter media in active [[Karst|karst]] terrain because infiltration is typically not allowed in karst areas.. [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Karst#How_to_investigate_for_karst_on_a_site Geotechnical investigations] are HIGHLY RECOMMENDED in karst areas. | It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that underdrains and an impermeable liner be used for dry swales with filter media in active [[Karst|karst]] terrain because infiltration is typically not allowed in karst areas.. [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Karst#How_to_investigate_for_karst_on_a_site Geotechnical investigations] are HIGHLY RECOMMENDED in karst areas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{alert|The CSW permit prohibits infiltration when the infiltration system will be constructed in areas within 1,000 feet up‐gradient, or 100 feet down‐gradient of active karst features|alert-danger}} | ||
===Wellhead protection areas=== | ===Wellhead protection areas=== | ||
| − | See [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection stormwater and wellhead protection] for guidance and recommendations for determining the appropriateness of infiltrating stormwater in a Drinking Water Supply Management Area (DWSMA). For more information on source water protection see [ | + | See [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_and_wellhead_protection stormwater and wellhead protection] for guidance and recommendations for determining the appropriateness of infiltrating stormwater in a Drinking Water Supply Management Area (DWSMA). For more information on source water protection see [https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/water/swp/index.htm Minnesota Department of Health]. |
| − | {{alert|Infiltration is prohibited in areas within a Drinking Water Supply Management Area (DWSMA) as defined in Minn | + | {{alert|Infiltration is prohibited in areas within a Drinking Water Supply Management Area (DWSMA) as defined in Minn. R. 4720.5100, subp. 13., if the system will be located: |
| + | *in an Emergency Response Area (ERA) within a DWSMA classified as having high or very high vulnerability as defined by the Minnesota Department of Health; or | ||
| + | *in an ERA within a DWSMA classified as moderate vulnerability unless a regulated MS4 Permittee performed or approved a higher level of engineering review sufficient to provide a functioning treatment system and to prevent adverse impacts to groundwater; or | ||
| + | *outside of an ERA within a DWSMA classified as having high or very high vulnerability, unless a regulated MS4 Permittee performed or approved a higher level of engineering review sufficient to provide a functioning treatment system and to prevent adverse impacts to groundwater|alert-danger}} | ||
===Soils hydrologic soil group mapping (see [[Design infiltration rates]])=== | ===Soils hydrologic soil group mapping (see [[Design infiltration rates]])=== | ||
See [https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm NRCS Web Soil Survey] for hydrologic soil descriptions for the swale location. [[Design infiltration rates|A and B soils]] are potentially suitable for a dry swale without an underdrain (infiltration swale). C and D soils are potentially suitable for a dry swale with an underdrain (filtration practice). The maximum allowed field-measured infiltration rate shall not exceed 8.3 inches per hour for an infiltration swale. | See [https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm NRCS Web Soil Survey] for hydrologic soil descriptions for the swale location. [[Design infiltration rates|A and B soils]] are potentially suitable for a dry swale without an underdrain (infiltration swale). C and D soils are potentially suitable for a dry swale with an underdrain (filtration practice). The maximum allowed field-measured infiltration rate shall not exceed 8.3 inches per hour for an infiltration swale. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{alert|Infiltration is prohibited when the infiltration system will be constructed in areas of predominately Hydrologic Soil Group D (clay) soils, and in areas where soil infiltration rates are more than 8.3 inches per hour unless soils are amended to slow the infiltration rate below 8.3 inches per hour.|alert-danger}} | ||
==Major design elements - Practice and site considerations== | ==Major design elements - Practice and site considerations== | ||
| Line 116: | Line 145: | ||
===Filter media=== | ===Filter media=== | ||
| − | Swales designed for filtration (i.e. swales that have an underdrain) typically have engineered media. The media is comprised of a combination of sand and organic material on top of a pea gravel bed that encases a perforated drain pipe. The media assists in the removal of fine particulate and dissolved pollutants, improving on the overall performance of swale systems. See [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_dry_swale_(grass_swale)#Filter_media_2 design specifications for media]. If the filtered water is eventually discharged to a receiving water impaired for phosphorus, the practice should be [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Addressing_phosphorus_leaching_concerns_with_media_mixes designed to minimize phosphorus loss]. | + | Swales designed for filtration (i.e. swales that have an underdrain) typically have [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Materials_specifications_-_filter_media bioretention engineered media]. The media is comprised of a combination of sand and organic material on top of a pea gravel bed that encases a perforated drain pipe. The media assists in the removal of fine particulate and dissolved pollutants, improving on the overall performance of swale systems. See [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_dry_swale_(grass_swale)#Filter_media_2 design specifications for media]. If the filtered water is eventually discharged to a receiving water impaired for phosphorus, the practice should be [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Addressing_phosphorus_leaching_concerns_with_media_mixes designed to minimize phosphorus loss]. |
| − | Soils with high infiltration rates (A and B soils) typically do not utilize engineered media. Swales constructed on these soils are suitable for infiltration and underdrains are not needed. | + | Soils with [[Design infiltration rates|high infiltration rates]] (A and B soils) typically do not utilize engineered media. Swales constructed on these soils are suitable for infiltration and underdrains are not needed. |
===Underdrains=== | ===Underdrains=== | ||
| Line 128: | Line 157: | ||
For swales designed as filtration practices, pollutants are attenuated through settling of sediment and adsorption of pollutants. Engineered media, which typically has a relatively organic matter content, is effective in attenuating metals, most organics, and bacteria. Soluble pollutants, such as nitrate, dissolved phosphorus, and chloride, may be taken up by vegetation but will largely be captured by the underdrain and returned to the stormwater drainage system. Unless lined, some infiltration will occur below the underdrain in filtration systems. | For swales designed as filtration practices, pollutants are attenuated through settling of sediment and adsorption of pollutants. Engineered media, which typically has a relatively organic matter content, is effective in attenuating metals, most organics, and bacteria. Soluble pollutants, such as nitrate, dissolved phosphorus, and chloride, may be taken up by vegetation but will largely be captured by the underdrain and returned to the stormwater drainage system. Unless lined, some infiltration will occur below the underdrain in filtration systems. | ||
| − | The use of impermeable check dams or weirs can enhance treatment by increasing the volume of water retained and increasing the contact time between soil or media and runoff water. | + | The use of impermeable [[Check dams for stormwater swales|check dams]] or weirs can enhance treatment by increasing the volume of water retained and increasing the contact time between soil or media and runoff water. |
===Vegetation=== | ===Vegetation=== | ||
Vegetation plays a crucial role in dry swale treatment capacity, flow attenuation and stabilization of the swale itself (i.e., erosion control). It is HIGHLY RECEOMMENDED that preference is given to robust native, non-clump forming grasses as the predominant plant type within the swale flow area. Care must also be taken to consider species selection in light of sun exposure duration/timing as well as soil moisture, ponding depth and ponding duration. | Vegetation plays a crucial role in dry swale treatment capacity, flow attenuation and stabilization of the swale itself (i.e., erosion control). It is HIGHLY RECEOMMENDED that preference is given to robust native, non-clump forming grasses as the predominant plant type within the swale flow area. Care must also be taken to consider species selection in light of sun exposure duration/timing as well as soil moisture, ponding depth and ponding duration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information, see the section [[Plants for swales]]. | ||
===Landscaping=== | ===Landscaping=== | ||
| Line 141: | Line 172: | ||
*Plan for snow storage (both temporary during construction and permanent). Don’t plow into dry swales routinely. Dry swales should be a last resort for snow storage (i.e. only for very large snow events as “emergency overflow”. | *Plan for snow storage (both temporary during construction and permanent). Don’t plow into dry swales routinely. Dry swales should be a last resort for snow storage (i.e. only for very large snow events as “emergency overflow”. | ||
*Snow storage could be, for example, a designed pretreatment area. | *Snow storage could be, for example, a designed pretreatment area. | ||
| − | For more information and example photos, see the section on snow and ice management. | + | For more information and example photos, see the section on [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Cold_climate_impact_on_runoff_management#Snow_and_ice_management snow and ice management]. |
===Safety=== | ===Safety=== | ||
| Line 148: | Line 179: | ||
==Materials specification== | ==Materials specification== | ||
| − | ===Erosion control ([ | + | ===Erosion control ([https://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/ MNDOT Standard Specifications 2575, 3861-3898])=== |
| − | The use of [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Construction_stormwater_program#Best_Management_Practices temporary erosion control materials] is REQUIRED in the design and construction of all swale types to allow for the establishment of firmly-rooted, dense vegetative cover. The dry swale bottom and side slopes up to the 10 year event should use robust erosion control matting that can resist the expected shear stresses associated with channelized flows. The matting should have a minimum life expectancy of three years. Upper banks of the swale slope should be protected by either similar matting or a straw/coconut blend erosion control blanket. See MNDOT specifications for guidance on selection of erosion control products. | + | The use of [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Construction_stormwater_program#Best_Management_Practices temporary erosion control materials] is REQUIRED in the design and construction of all swale types to allow for the establishment of firmly-rooted, dense vegetative cover. The dry swale bottom and side slopes up to the 10 year event should use robust [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Erosion_prevention_practices erosion control matting] that can resist the expected shear stresses associated with channelized flows. The matting should have a minimum life expectancy of three years. Upper banks of the swale slope should be protected by either similar matting or a straw/coconut blend erosion control blanket. See MNDOT specifications for guidance on selection of erosion control products. |
===Filter media=== | ===Filter media=== | ||
Filter media used in dry swale designs should follow guidance on material specifications within the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Materials_specifications_-_filter_media bioretention section of the MN Stormwater Manual]. | Filter media used in dry swale designs should follow guidance on material specifications within the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Materials_specifications_-_filter_media bioretention section of the MN Stormwater Manual]. | ||
| − | ===Underdrains ([ | + | ===Underdrains ([https://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/ MNDOT Specifications 3245, 3247, 3248, 3278])=== |
{{:Infiltration design guideline - underdrains}} | {{:Infiltration design guideline - underdrains}} | ||
===Rock=== | ===Rock=== | ||
| − | See [ | + | See [https://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/ MNDOT Standard Specification 3601]. |
===Weir=== | ===Weir=== | ||
| − | See MNDOT Standard Specifications [ | + | See MNDOT Standard Specifications [https://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/ 2461, 2573, 3137, 3301, 3491, 3601]. |
===Plants=== | ===Plants=== | ||
See MNDOT Standard Specifications [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A733%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C468%2C0%5D 2571], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A756%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C434%2C0%5D 2574], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A760%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C400%2C0%5D 2575], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A1129%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C676%2C0%5D 3861], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A1136%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C380%2C0%5D 3876], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A1144%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C420%2C0%5D 3878]. | See MNDOT Standard Specifications [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A733%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C468%2C0%5D 2571], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A756%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C434%2C0%5D 2574], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A760%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C400%2C0%5D 2575], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A1129%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C676%2C0%5D 3861], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A1136%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C380%2C0%5D 3876], [http://www.dot.state.mn.us/pre-letting/spec/2018/2018-spec-book-final.pdf#%5B%7B%22num%22%3A1144%2C%22gen%22%3A0%7D%2C%7B%22name%22%3A%22XYZ%22%7D%2C69%2C420%2C0%5D 3878]. | ||
| − | Refer to the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Plants_for_swales swales plant list section of the manual] for selection of Minnesota native plants to be used in swales. Care must be taken to specify plants for their position in the system (swale bottom, side slopes and buffer). For the bottom of the swale, preference should be given to robust non-clump forming grasses or sedges that can withstand flow forces as well as provide adequate filtration functions. It is also important to understand draw-down time not only within the channel itself, but in either in-situ soils or the filter media as plants have variable tolerance to the depth and duration of inundation as well as soil moisture period. Lastly, care should be taken to understand sun exposure and salt tolerance requirements of various plants to ensure a robust, dense establishment of vegetative cover. | + | Refer to the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Plants_for_swales swales plant list section of the manual] for selection of Minnesota native plants to be used in swales. Care must be taken to specify plants for their position in the system (swale bottom, side slopes and buffer). For the bottom of the swale, preference should be given to robust non-clump forming grasses or sedges that can withstand flow forces as well as provide adequate filtration functions. It is also important to understand draw-down time not only within the channel itself, but in either in-situ soils or the filter media, as plants have variable tolerance to the depth and duration of inundation as well as soil moisture period. Lastly, care should be taken to understand sun exposure and [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Minnesota_plant_lists#Salt_tolerance salt tolerance] requirements of various plants to ensure a robust, dense establishment of vegetative cover. |
| − | {{: | + | {{:Dry swale materials specifications}} |
==Design procedure – design steps== | ==Design procedure – design steps== | ||
| Line 188: | Line 219: | ||
B. Determine how the swale will fit into the overall stormwater treatment system, including: | B. Determine how the swale will fit into the overall stormwater treatment system, including: | ||
*Decide whether the swale is the only BMP to be employed, or if are there other BMPs addressing some of the treatment requirements. | *Decide whether the swale is the only BMP to be employed, or if are there other BMPs addressing some of the treatment requirements. | ||
| − | *Decide where on the site the swale will most likely | + | *Decide where on the site the swale will most likely be located. |
===Step 2. Confirm design criteria and applicability=== | ===Step 2. Confirm design criteria and applicability=== | ||
| Line 196: | Line 227: | ||
===Step 3. Perform field verification of site suitability=== | ===Step 3. Perform field verification of site suitability=== | ||
| − | {{: | + | Consider the following when determining if a swale is suitable: |
| + | *The drainage area and area for swale | ||
| + | *The slope to get the drainage to the swale in addition to the swale slope to fully drain to a discharge point | ||
| + | *Any utility conflicts or roadway crossings that will need to be addressed in design | ||
| + | *MnDOT standards for roadway channel slopes and adequate depth for the 10-year drainage without overtopping the roadway | ||
| + | |||
| + | Consider the following when infiltration is desired in the swale design. | ||
| + | *[[Stormwater infiltration]]: This page contains links to several pages that address infiltration of stormwater runoff. | ||
| + | *[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_infiltration#Step_3._Perform_field_verification_of_site_suitability Confirm infiltration rate of in-situ soils] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{:Recommended number of soil boring, pits, and permeameter tests for bioretention design}} | ||
{{:Infiltration design guideline - perform groundwater mounding analysis}} | {{:Infiltration design guideline - perform groundwater mounding analysis}} | ||
| Line 205: | Line 246: | ||
===Step 5. Compute runoff control volumes and other key design parameters=== | ===Step 5. Compute runoff control volumes and other key design parameters=== | ||
| − | *Calculate the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Water Quality Volume] (V<sub>wq</sub>) | + | '''1. Calculate the following runoff control volumes.''' |
| − | If the swale is being designed to meet the requirements of the MPCA Permit, the REQUIRED treatment volume is the water quality volume of 1 inch of runoff from the new impervious surfaces created from the project. If part of the overall V<sub>wq</sub> is to be treated by other BMPs, subtract that portion from the V<sub>wq</sub> to determine the part of the V<sub>wq</sub> to be treated by the dry swale. | + | *Calculate the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Water Quality Volume] (V<sub>wq</sub>): If the swale is being designed to meet the requirements of the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Construction_stormwater_permit MPCA Construction Stormwater General Permit], the REQUIRED treatment volume is the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=III._STORMWATER_DISCHARGE_DESIGN_REQUIREMENTS#III.D._PERMANENT_STORMWATER_MANAGEMENT_SYSTEM water quality volume of 1 inch of runoff from the new impervious surfaces] created from the project. If part of the overall V<sub>wq</sub> is to be treated by other BMPs, subtract that portion from the V<sub>wq</sub> to determine the part of the V<sub>wq</sub> to be treated by the dry swale. |
| + | |||
| + | :V<sub>wq</sub> = 1 inch x Area<sub>impervious surface</sub> | ||
| + | |||
| + | To calculate the volume behind a check dam, see item 3 below. | ||
| + | |||
*Calculate [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Channel Protection Volume] (V<sub>cp</sub>) | *Calculate [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Channel Protection Volume] (V<sub>cp</sub>) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :V<sub>cp</sub> = 24 hour extended detention of post-development 1-yr 24-hr storm event | ||
| + | |||
*Calculate [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Overbank Flood Protection Volume] (V<sub>p10</sub>) | *Calculate [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Overbank Flood Protection Volume] (V<sub>p10</sub>) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :V<sub>p10</sub> = peak discharge from the 10-yr storm to 10-yr predevelopment rates | ||
| + | |||
*Calculate [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Extreme Flood Volume] (V<sub>p100</sub>). | *Calculate [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Extreme Flood Volume] (V<sub>p100</sub>). | ||
| − | + | :Vp100 = peak discharge from the 100-yr storm to 100-yr predevelopment rates | |
| + | |||
| + | '''2. Once the runoff control volume is determined for design, compute the following design parameters to determine the swale size required.''' | ||
| − | A. Calculate the maximum discharge loading per foot of swale width | + | :A. Calculate the maximum discharge loading per foot of swale width |
<math>q = (0.00236/n) · Y · 1.67 · S · 0.5 </math> | <math>q = (0.00236/n) · Y · 1.67 · S · 0.5 </math> | ||
| Line 223: | Line 277: | ||
:n = Manning’s “n” roughness coefficient (use 0.15 for short prairie grass, 0.25 for dense grasses such as bluegrass, buffalo grass, blue grama grass and other native grass mixtures). | :n = Manning’s “n” roughness coefficient (use 0.15 for short prairie grass, 0.25 for dense grasses such as bluegrass, buffalo grass, blue grama grass and other native grass mixtures). | ||
| − | B. Use a recommended hydrologic model to compute Q<sub>wq</sub> | + | :B. [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Available_stormwater_models_and_selecting_a_model Use a recommended hydrologic model] to compute Q<sub>wq</sub> |
| − | C. Minimum swale length (in feet) = Q<sub>wq</sub> / q | + | :C. Minimum swale length (in feet) = Q<sub>wq</sub> / q |
Where: | Where: | ||
:Q<sub>wq</sub> = the water quality peak discharge (cubic feet per second) | :Q<sub>wq</sub> = the water quality peak discharge (cubic feet per second) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''3.The water quality volume (V<sub>wq)</sub> achieved behind each check dam (instantaneous volume) is given by''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> V_{wq} = h^2 * (h * H + B_w)]/(2S) </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | :h = check dam height (inches) | ||
| + | :H = horizontal component of the swale side slope (1 vertical : H horizontal)(inches) | ||
| + | :S = slope (unitless); and | ||
| + | :Bw = channel bottom width (inches) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add the V<sub>wq</sub> for each check dam together to obtain the cumulative water quality volume for the swale. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For information on check dams, [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Check_dams_for_stormwater_swales link here]. For an example calculation of volume, [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Check_dams_for_stormwater_swales#Sample_calculation link here]. | ||
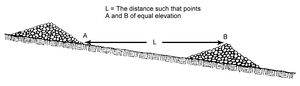
===Step 6. Compute number of check dams=== | ===Step 6. Compute number of check dams=== | ||
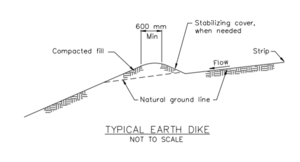
| − | + | [[File:Profile of swale with structural check dams.png|300px|thumb|alt=schematic of swale with check dams|<font size=3>Profile of swale with structural check dams (not to scale). Source: [http://www.virginiadot.org/business/locdes/bmp_designmanual.asp Virginia DOT BMP Design Manual], Chapter 6. Click on image to enlarge.</font size>]] | |
| − | + | [[File:Space check dams in a channel so the crest of the downstream dam is at the elevation of the toe of the upstream dam.jpg |right|thumb|300 px|alt=This image shows space check dams in a channel so the crest of the downstream dam is at the elevation of the toe of the upstream dam|<font size=3>Space check dams in a channel so the crest of the downstream dam is at the elevation of the toe of the upstream dam. Click on image to enlarge.</font size>]] | |
| + | [[File:Profile of Swale with earthern check dams.png|300px|thumb|alt=schematic earthen check dams|<font size=3>Profile of Swale with earthern check dams (not to scale). Source: Oregon Department of Environmental Quality Erosion and Sediment Control Manual. </font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The number of [[Check dams for stormwater swales|check dams]] should be computed based on swale slope, length, and treatment objectives. For example, a swale designed to contain the entire V<sub>wq</sub> may require more check dams than a swale that only contains a portion of the V<sub>wq</sub>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Channel slopes between 0.5 and 2 percent are recommended unless topography necessitates a steeper slope, in which case 6- to 12-inch drop structures can be placed to limit the energy slope to within the recommended 0.5 to 2 percent range. Energy dissipation will be required below the drops. Spacing between the drops should not be closer than 50 feet. Depth of the V<sub>wq</sub> at the downstream end should not exceed 18 inches. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For an example calculation of number of check dams to employ, [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Check_dams_for_stormwater_swales#Sample_calculation link here]. | ||
===Step 7. Calculate drawdown time=== | ===Step 7. Calculate drawdown time=== | ||
Filtration swales (swales with an underdrain) include a bed consisting of a permeable soil layer at least 30 inches in depth, above a 6-inch diameter perforated PVC pipe (AASHTO M 252) longitudinal underdrain in a 12-inch gravel layer. The soil media should have an infiltration rate of at least 0.25 inches per hours with a maximum of 1.5 inches per hour and contain organic material to facilitate pollutant removal but [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Addressing_phosphorus_leaching_concerns_with_media_mixes not contribute to phosphorus leaching]. A permeable filter fabric is placed between the gravel layer and the overlying soil. Dry swale channels are sized to store and filter the entire V<sub>wq</sub> and allow for full filtering through the permeable soil layer. | Filtration swales (swales with an underdrain) include a bed consisting of a permeable soil layer at least 30 inches in depth, above a 6-inch diameter perforated PVC pipe (AASHTO M 252) longitudinal underdrain in a 12-inch gravel layer. The soil media should have an infiltration rate of at least 0.25 inches per hours with a maximum of 1.5 inches per hour and contain organic material to facilitate pollutant removal but [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Design_criteria_for_bioretention#Addressing_phosphorus_leaching_concerns_with_media_mixes not contribute to phosphorus leaching]. A permeable filter fabric is placed between the gravel layer and the overlying soil. Dry swale channels are sized to store and filter the entire V<sub>wq</sub> and allow for full filtering through the permeable soil layer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dry swales with no underdrain will have infiltration occurring. The drawdown time will be equal to the maximum pool depth behind a check dam divided by the soil infiltration rate. See [[Design infiltration rates|design infiltration rates]] for different soil groups. For example, considering a swale with a 1 foot pool depth behind a swale, the drawdown time for a B(SM) soil with an infiltration rate of 0.45 inches per hour will be 26.7 hours, while the drawdown time for an A(SP) soil with an infiltration rate of 0.8 inches per hour will be 15 hours. | ||
===Step 8. Check 2-year and 10-year velocity erosion potential and freeboard=== | ===Step 8. Check 2-year and 10-year velocity erosion potential and freeboard=== | ||
| Line 249: | Line 326: | ||
Follow the design procedures identified in the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Unified Sizing Criteria section of the Manual] to determine the volume control and peak discharge requirements for water quality, recharge (not required), channel protection, overbank flood and extreme storm. | Follow the design procedures identified in the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Unified_sizing_criteria_section Unified Sizing Criteria section of the Manual] to determine the volume control and peak discharge requirements for water quality, recharge (not required), channel protection, overbank flood and extreme storm. | ||
| − | Model the proposed development scenario using a surface water model appropriate for the hydrologic and hydraulic design considerations specific to the site. This includes defining the parameters of the swale practice defined above: ponding elevation and area (defines the ponding volume), infiltration rate and method of application (effective filtration area), and outlet structure and/or flow diversion information. The results of this analysis can be used to determine whether or not the proposed design meets the applicable requirements. If not, the design will have to be re-evaluated. | + | Model the proposed development scenario using a [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Available_stormwater_models_and_selecting_a_model surface water model] appropriate for the hydrologic and hydraulic design considerations specific to the site. This includes defining the parameters of the swale practice defined above: ponding elevation and area (defines the ponding volume), infiltration rate and method of application (effective filtration area), and outlet structure and/or flow diversion information. The results of this analysis can be used to determine whether or not the proposed design meets the applicable requirements. If not, the design will have to be re-evaluated. |
{{alert|The following items are specifically REQUIRED by the MPCA Permit:<br> | {{alert|The following items are specifically REQUIRED by the MPCA Permit:<br> | ||
| Line 259: | Line 336: | ||
*'''Grading plan''': Develop a grading plan based on the preliminary profile and cross-section typical design. | *'''Grading plan''': Develop a grading plan based on the preliminary profile and cross-section typical design. | ||
*'''Dimensions''': Adjust the preliminary profile dimensions to accommodate site specific concerns/impacts. Minimum design parameters for hydraulic, water quality, and quantity management criteria should be rechecked based on adjustments to the dry swale to ensure that safe and adequate conveyance is still maintained. | *'''Dimensions''': Adjust the preliminary profile dimensions to accommodate site specific concerns/impacts. Minimum design parameters for hydraulic, water quality, and quantity management criteria should be rechecked based on adjustments to the dry swale to ensure that safe and adequate conveyance is still maintained. | ||
| − | *'''Check dams''': Adjust the preliminary check dam dimensions to accommodate site specific concerns/impacts. Minimum design parameters for hydraulic and water quality criteria should be rechecked based on adjustments to the check dams to ensure that safe and adequate conveyance is still maintained. | + | *'''Check dams''': Adjust the preliminary [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Check_dams_for_stormwater_swales check dam] dimensions to accommodate site specific concerns/impacts. Minimum design parameters for hydraulic and water quality criteria should be rechecked based on adjustments to the check dams to ensure that safe and adequate conveyance is still maintained. |
| − | *'''Site stabilization''': Course woodchips and compost should be used throughout the limit of disturbance for site stabilization. All areas should be seeded and planted as well as blanketed/matted. | + | *[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Erosion_prevention_practices '''Site stabilization''']: Course woodchips and compost should be used throughout the limit of disturbance for site stabilization. All areas should be seeded and planted as well as blanketed/matted. An appropriate erosion control blanket with biodegradable neeting should be used within the swale bottom and side slopes. |
*'''Excess materials''': It is advisable that excess materials, i.e., cobbles and boulders, be placed at the edge of the cross-section for use during the maintenance phase to correct any physical instability. | *'''Excess materials''': It is advisable that excess materials, i.e., cobbles and boulders, be placed at the edge of the cross-section for use during the maintenance phase to correct any physical instability. | ||
===Step 13. Prepare vegetation and landscaping plan=== | ===Step 13. Prepare vegetation and landscaping plan=== | ||
| − | A landscaping plan for a swale should be prepared to indicate how the enhanced swale system will be stabilized and established with vegetation. Landscape design should specify proper species and be based on specific site, soils, sun exposure and hydric conditions present along the swale. Further information on plant selection and use can be found in the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title= | + | A landscaping plan for a swale should be prepared to indicate how the enhanced swale system will be stabilized and established with vegetation. Landscape design should specify proper species and be based on specific site, soils, sun exposure and hydric conditions present along the swale. Further information on plant selection and use can be found in the [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Plants_for_swales swale plant list section]. |
===Step 14. Prepare operation and maintenance plan=== | ===Step 14. Prepare operation and maintenance plan=== | ||
| Line 270: | Line 347: | ||
===Step 15. Prepare cost estimate=== | ===Step 15. Prepare cost estimate=== | ||
| − | See Cost Considerations section for guidance on preparing a cost estimate that includes both construction and maintenance costs. | + | See [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Cost_considerations_for_dry_swale_(grass_swale) Cost Considerations section] for guidance on preparing a cost estimate that includes both construction and maintenance costs. |
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
| − | |||
==Related pages== | ==Related pages== | ||
| − | *[[Terminology for swales (grass channels)]] | + | *[[Terminology for swales|Terminology for swales (grass channels)]] |
*[[Overview for dry swale (grass swale)]] | *[[Overview for dry swale (grass swale)]] | ||
*[[BMPs for stormwater infiltration|Types of infiltration]] | *[[BMPs for stormwater infiltration|Types of infiltration]] | ||
| Line 284: | Line 360: | ||
*[[Assessing the performance of dry swale (grass swale)]] | *[[Assessing the performance of dry swale (grass swale)]] | ||
*[[Calculating credits for dry swale (grass swale)]] | *[[Calculating credits for dry swale (grass swale)]] | ||
| + | *[[Cost considerations for dry swale (grass swale)]] | ||
| + | *[[Case studies for dry swale (grass swale)]] | ||
*[[Plants for swales]] | *[[Plants for swales]] | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Check dams for stormwater swales]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[External resources for swales|External resources for dry swale (grass swale)]] |
| − | |||
*[[References for dry swale (grass swale)]] | *[[References for dry swale (grass swale)]] | ||
*[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Requirements,_recommendations_and_information_for_using_swale_without_an_underdrain_as_a_BMP_in_the_MIDS_calculator Requirements, recommendations and information for using dry swale (grass swale) without an underdrain in the MIDS calculator] | *[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Requirements,_recommendations_and_information_for_using_swale_without_an_underdrain_as_a_BMP_in_the_MIDS_calculator Requirements, recommendations and information for using dry swale (grass swale) without an underdrain in the MIDS calculator] | ||
*[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Requirements,_recommendations_and_information_for_using_swale_with_an_underdrain_as_a_BMP_in_the_MIDS_calculator Requirements, recommendations and information for using dry swale (grass swale) with an underdrain in the MIDS calculator] | *[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Requirements,_recommendations_and_information_for_using_swale_with_an_underdrain_as_a_BMP_in_the_MIDS_calculator Requirements, recommendations and information for using dry swale (grass swale) with an underdrain in the MIDS calculator] | ||
*[[Requirements, recommendations and information for using swale side slope as a BMP in the MIDS calculator]] | *[[Requirements, recommendations and information for using swale side slope as a BMP in the MIDS calculator]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Specifications and details/Design criteria]] |
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:08, 29 December 2022
This page provides a discussion of design elements and design steps for dry swales, which are often called grass swales. The following discussion includes dry swales used as filtration or infiltration practices, with the distinction being the presence of an underdrain for filtration practices.
Contents
- 1 Terminology
- 2 Details and CADD images
- 3 Design phase maintenance considerations
- 4 Major design elements - Physical feasibility initial check
- 5 Major design elements - Practice and site considerations
- 6 Materials specification
- 7 Design procedure – design steps
- 7.1 Step 1. Make a preliminary judgment - consider basic issues for initial suitability screening
- 7.2 Step 2. Confirm design criteria and applicability
- 7.3 Step 3. Perform field verification of site suitability
- 7.4 Step 4. Select design variant based on physical suitability evaluation
- 7.5 Step 5. Compute runoff control volumes and other key design parameters
- 7.6 Step 6. Compute number of check dams
- 7.7 Step 7. Calculate drawdown time
- 7.8 Step 8. Check 2-year and 10-year velocity erosion potential and freeboard
- 7.9 Step 9. Design low flow control at downstream headwalls and checkdams
- 7.10 Step 10. Design inlets, sediment forebay(s), and underdrain system
- 7.11 Step 11. Check volume, peak discharge rates and drawdown time against state, local, and watershed organization requirements (NOTE: steps are iterative)
- 7.12 Step 12. Finalize the cross-section and profile design for the project
- 7.13 Step 13. Prepare vegetation and landscaping plan
- 7.14 Step 14. Prepare operation and maintenance plan
- 7.15 Step 15. Prepare cost estimate
- 8 Related pages
Terminology
The following terminology is used throughout this design page.
HIGHLY RECOMMENDED - Indicates design guidance that is extremely beneficial or necessary for proper functioning of the practice, but not specifically required by the MPCA CGP.
RECOMMENDED - Indicates design guidance that is helpful for practice performance but not critical to the design.
Details and CADD images
Use this link to access .pdf diagrams of CADD drawings. To see all filtration CADD images in a combined pdf, click here.
- Links to .dwg files for swales
- Swale layout: File:Swale Layout2 (1).pdf
- Typical dry swale profile section with check dams and draintile: File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 2.pdf
- File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 2 (2).pdf
- Typical grass channel cross-section without soil amendment: File:MIDS Dry Swale Sections-SHEET 1.pdf
- Typical wet swale check dam cross section, profile section with check dams, and profile section: File:MIDS WET Swale Sections SHEET 2 (1).pdf
- Cascade profile, riffle pool sequence profile, riffle weir cross-section: File:Stormwater-Step-Pool.pdf
- typical earthen, rock, structural check dams; profile and cross-section: File:VARIOUS CHECK DAMS Layout1 (1).pdf
- Typical wet and dry swale cross-sections: File:Wet and dry swales Layout2 (1).pdf
Design phase maintenance considerations
Implicit in the design guidance is the fact that many design elements of infiltration and filtration systems can minimize the maintenance burden and maintain pollutant removal efficiency. Key examples include
- limiting drainage area;
- providing easy site access (REQUIRED);
- providing pretreatment (REQUIRED); and
- utilizing native plantings (see Plants for Stormwater Design).
For more information on design information for individual infiltration and filtration practices, link here.
Major design elements - Physical feasibility initial check
Before deciding to use a dry swale practice for stormwater management, it is helpful to consider several items that bear on the feasibility of using such a device at a given location. This section describes considerations in making an initial judgment as to whether or not a dry swale is the appropriate BMP for the site.
Infiltration constraints
If a dry swale is being considered for infiltration, the following links provide additional information on specific constraints to infiltration (applicable to dry swales without an underdrain). The Construction Stormwater General Permit prohibits infiltration under certain conditions, which are summarized and discussed in detail at this link.
- Karst
- Shallow soils and shallow depth to bedrock
- Shallow groundwater
- Soils with low infiltration capacity
- Separation distances
- Potential stormwater hotspots
- Wellhead protection
- Contaminated soils and groundwater
- Procedures for investigating sites with potential constraints
Contributing drainage area
The RECOMMENDED maximum drainage area is typically 5 acres. Dry swales can be designed to convey runoff from larger drainage areas. However, volume reduction, water quality function, and ability to meet the MPCA CGP requirements is diminished.
Site topography and slopes
Unless slope stability calculations demonstrate otherwise (for guidance on calculating slope stability, see [1], [2]) it is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that swales be located a minimum horizontal distance of 200 feet from down-gradient slopes greater than 20 percent, and that slopes in contributing drainage areas be limited to 15 percent.
Site location/minimum setback
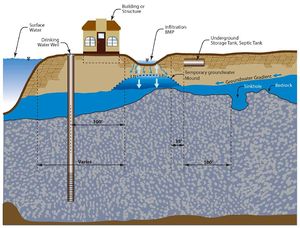
If the swale is constructed as an infiltration practice, the following table summarizes required and recommended minimum horizontal and vertical setback distances from an infiltration practice to an above-ground or underground structure. It will be necessary to consult local ordinances for further guidance on siting infiltration practices.
Required and recommended minimum vertical and horizontal separation distances. This represents the minimum distance from the infiltration practice to the structure of concern. If the structure is above-ground, the distance is measured from the edge of the BMP to the structure. If the structure is underground, the vertical separation distance represents the distance from the point of infiltration through the bottom of the system to the structure, while the horizontal separation (often called setback) distance is the shortest distance from the edge of the system to the structure.
Link to this table
| Structure | Distance (feet) | Requirement or recommendation | Note(s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Saturated soil | 3 | Requirement1 | |
| Bedrock | 3 | Requirement1 | ||
| Horizontal | Public supply well | 100 for sensitive wells; 50 for others3 | Requirement | |
| Building/structure/property line2 | 10 | Recommended | ||
| Surface water | none unless local requirements exist | If nearby stream is impaired for chloride, see [3] | ||
| Septic system | 35 | Recommended | ||
| Contaminated soil/groundwater | No specific distance. Infiltration must not mobilize contaminants. | |||
| Slope | 200 | Recommended | from toe of slope >= 20% | |
| Karst | 1000 up-gradient 100 down-gradient | Requirement1 | active karst | |
1 Required under the Construction Stormwater General Permit
2 Minimum with slopes directed away from the building
3If treating an average of 10,000 gallons per day; otherwise separation distance is 300 feet
Depth to groundwater and bedrock
A separation distance of at least 3 feet is REQUIRED under the MPCA CGP between the bottom elevation of infiltration swales and the elevation of the seasonally high water table. Shallow bedrock areas should be avoided for dry swales with a minimum separation distance of 3 feet.
A field soil properties investigation is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED.
Karst topography
It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that underdrains and an impermeable liner be used for dry swales with filter media in active karst terrain because infiltration is typically not allowed in karst areas.. Geotechnical investigations are HIGHLY RECOMMENDED in karst areas.
Wellhead protection areas
See stormwater and wellhead protection for guidance and recommendations for determining the appropriateness of infiltrating stormwater in a Drinking Water Supply Management Area (DWSMA). For more information on source water protection see Minnesota Department of Health.
- in an Emergency Response Area (ERA) within a DWSMA classified as having high or very high vulnerability as defined by the Minnesota Department of Health; or
- in an ERA within a DWSMA classified as moderate vulnerability unless a regulated MS4 Permittee performed or approved a higher level of engineering review sufficient to provide a functioning treatment system and to prevent adverse impacts to groundwater; or
- outside of an ERA within a DWSMA classified as having high or very high vulnerability, unless a regulated MS4 Permittee performed or approved a higher level of engineering review sufficient to provide a functioning treatment system and to prevent adverse impacts to groundwater
Soils hydrologic soil group mapping (see Design infiltration rates)
See NRCS Web Soil Survey for hydrologic soil descriptions for the swale location. A and B soils are potentially suitable for a dry swale without an underdrain (infiltration swale). C and D soils are potentially suitable for a dry swale with an underdrain (filtration practice). The maximum allowed field-measured infiltration rate shall not exceed 8.3 inches per hour for an infiltration swale.
Major design elements - Practice and site considerations
Several considerations are made in this section for the conceptual design of dry swales. Further design guidance and specifications are made in the following sections.
Conveyance
It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that the design provide non-erosive flow velocities within the swale and at the outlet point to reduce downstream erosion. During the 10-year or 25-year storm (depending on local drainage criteria), discharge velocity should be kept below 4 feet per second for established grassed channels. Erosion control matting or rock should be specified if higher velocities are expected. See Erosion prevention practices for more information on erosion prevention practices.
Pretreatment
Pretreatment prior to the dry swale such as vegetated filter strips or side slopes, small sedimentation basins, water quality inlets, or other pretreatment BMPs should be evaluated. If the dry swale is being used to meet the Construction Stormwater General Permit, pretreatment is required.
Anticipated flow
Although local drainage criteria may require a certain frequency event be used in the design, it is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that larger events be considered depending on the adjacent property and associated risks.
Grading
- Slope of swale: The longitudinal slope of a dry swale may vary from 0.5 to 2 percent and will affect the selection of swale type. It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that the design engineer consider the expected watershed flow to be conveyed by the swale in making the preliminary determination of design type.
- Swale bottom: It is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that the swale bottom be no less than 3 feet wide and should be adjusted with the cross-sectional area to be able to contain the expected range of flows within the swale. See additional design information on the cross-sectional area under the Swale Depth section.
- Side slopes: It is RECOMMENDED that the maximum side slopes within a swale do not exceed 3H:1V and be designed based on the relative stage-dependent flow driven cross-sectional area.
- Swale depth: Swale depth (pooled water depth) will be estimated based on the relative stage-dependent flow driven cross-sectional area to keep the swale from over topping.
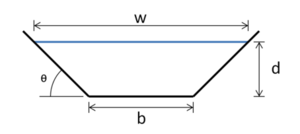
The schematic at the right illustrates hydraulic parameters of a channel section. The area (A) is given by
A=((b+d/tan(θ))d
the wetted perimeter (P) is given by
P=b+2(d/sin(θ))
the hydraulic radius (R) is given by
R=(bdsin(θ)+d2cos(θ))/(bsin(θ)+2d)
and the flow quantity is given by Manning's Formula for swale sizing
Q=vA=1.49/nAR0.67S0.5
where
- Q = Flow Quantity (ft3/sec),
- v = Velocity (ft/sec),
- n = manning’s coefficient,
- S = Slope (ft/ft), and
- the other dimensions are shown in the schematic to the right.
- Infiltration and filtration considerations: The design engineer should review the results of the feasibility check to assist in the selection of swale type. An additional consideration includes watershed soil transport to the site. Watersheds with unstable soils or lack of vegetative cover (e.g., construction, farmland and highly impervious surfaces) can generate and transport excessive sediments to the swale that may affect both infiltration and filtration capacity. In these situations, pretreatment via sedimentation processes is REQUIRED. Another consideration is the level of compaction and structure of in-situ soils, when considering dry swales. Construction of developments and roads, for example, significantly alter the parent state of native soils and therefore their hydrologic soil classification should be downgraded for feasibility study purposes.
Filter media
Swales designed for filtration (i.e. swales that have an underdrain) typically have bioretention engineered media. The media is comprised of a combination of sand and organic material on top of a pea gravel bed that encases a perforated drain pipe. The media assists in the removal of fine particulate and dissolved pollutants, improving on the overall performance of swale systems. See design specifications for media. If the filtered water is eventually discharged to a receiving water impaired for phosphorus, the practice should be designed to minimize phosphorus loss.
Soils with high infiltration rates (A and B soils) typically do not utilize engineered media. Swales constructed on these soils are suitable for infiltration and underdrains are not needed.
Underdrains
Underdrains are used when drawdown requirements cannot be me (e.g. C and D soils) or when there are other constraints to infiltration (see constraints to infiltration). Underdrains are comprised of a perforated, PVC pipe laid within filter media to convey runoff to either a stable day-lit area, a second form of treatment, or the storm sewer. A solid-walled PVC section of piping should be connected to the perforated drain pipe with a “tee” junction piece and extended to the swale’s surface to serve as an inspection and cleanout access point. These observation/maintenance ports are spaced throughout the system. See specifications for underdrains.
Treatment
Stormwater treatment in dry swales varies by design. For swales designed as infiltration practices, pollutants are attenuated through settling of sediment and adsorption of pollutants on soil media. Pollutants not attenuated by these processes will infiltrate deeply into the vadose zone, where they may be adsorbed, undergo chemical change, or leach to groundwater.
For swales designed as filtration practices, pollutants are attenuated through settling of sediment and adsorption of pollutants. Engineered media, which typically has a relatively organic matter content, is effective in attenuating metals, most organics, and bacteria. Soluble pollutants, such as nitrate, dissolved phosphorus, and chloride, may be taken up by vegetation but will largely be captured by the underdrain and returned to the stormwater drainage system. Unless lined, some infiltration will occur below the underdrain in filtration systems.
The use of impermeable check dams or weirs can enhance treatment by increasing the volume of water retained and increasing the contact time between soil or media and runoff water.
Vegetation
Vegetation plays a crucial role in dry swale treatment capacity, flow attenuation and stabilization of the swale itself (i.e., erosion control). It is HIGHLY RECEOMMENDED that preference is given to robust native, non-clump forming grasses as the predominant plant type within the swale flow area. Care must also be taken to consider species selection in light of sun exposure duration/timing as well as soil moisture, ponding depth and ponding duration.
For more information, see the section Plants for swales.
Landscaping
Swales can be effectively integrated into the site planning process and aesthetically designed as attractive green spaces planted with native vegetation. Because vegetation is fundamental to the performance and function of the swale, aesthetically chosen vegetation may only be possible on the surface of the swales.
Snow considerations
Considering management of snow, the following are recommended
- Plan a plow path during design phase and tell snowplow operators where to push the snow. Plan trees around (not in) plow path, with a 16 foot minimum between trees.
- Plan for snow storage (both temporary during construction and permanent). Don’t plow into dry swales routinely. Dry swales should be a last resort for snow storage (i.e. only for very large snow events as “emergency overflow”.
- Snow storage could be, for example, a designed pretreatment area.
For more information and example photos, see the section on snow and ice management.
Safety
Swales do not pose any major safety hazards. Potential hazards could occur from the steep side slope and checks of the swales if they are close to pedestrian traffic or roadways with no shoulders.
Materials specification
Erosion control (MNDOT Standard Specifications 2575, 3861-3898)
The use of temporary erosion control materials is REQUIRED in the design and construction of all swale types to allow for the establishment of firmly-rooted, dense vegetative cover. The dry swale bottom and side slopes up to the 10 year event should use robust erosion control matting that can resist the expected shear stresses associated with channelized flows. The matting should have a minimum life expectancy of three years. Upper banks of the swale slope should be protected by either similar matting or a straw/coconut blend erosion control blanket. See MNDOT specifications for guidance on selection of erosion control products.
Filter media
Filter media used in dry swale designs should follow guidance on material specifications within the bioretention section of the MN Stormwater Manual.
Underdrains (MNDOT Specifications 3245, 3247, 3248, 3278)
The following are RECOMMENDED for infiltration practices with underdrains.
- The minimum pipe diameter is 4 inches.
- Install 2 or more underdrains for each infiltration system in case one clogs. At a minimum provide one underdrain for every 1,000 square feet of surface area.
- Include at least 2 observation/cleanouts for each underdrain, one at the upstream end and one at the downstream end. Cleanouts should be at least 4 inches diameter vertical non-perforated schedule 40 PVC pipe, and extend to the surface. Cap cleanouts with a watertight removable cap.
- Construct underdrains with Schedule 40 or SDR 35 smooth wall PVC pipe.
- Install underdrains with a minimum slope of 0.5 percent, particularly in hydrologic soil group D soils (Note: to utilize Manning’s equation the slope must be greater than 0).
- Include a utility trace wire for all buried piping.
- For underdrains that daylight on grade, include a marking stake and animal guard;
- For each underdrain have an accessible knife gate valve on its outlet to allow the option of operating the system as either an infiltration system, filtration system, or both. The valve should enable the ability to make adjustments to the discharge flow so the sum of the infiltration rate plus the underdrain discharge rate equal a 48 hour drawdown time.
- Perforations should be 3/8 inches. Use solid sections of non-perforated PVC piping and watertight joints wherever the underdrain system passes below berms, down steep slopes, makes a connection to a drainage structure, or daylights on grade.
- Spacing of collection laterals should be less than 25 feet.
- Underdrain pipes should have a minimum of 3 inches of washed #57 stone above and on each side of the pipe (stone is not required below the pipe). Above the stone, two inches of choking stone is needed to protect the underdrain from blockage.
- Avoid filter fabric .
- Pipe socks may be needed for underdrains imbedded in sand. If pipe socks are used, then use circular knit fabric.
The procedure to size underdrains is typically determined by the project engineer. An example for sizing underdrains is found in the North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources Stormwater BMP Manual. Underdrain spacing can be calculated using the following spreadsheet, which utilizes the vanSchilfgaarde Equation. The spreadsheet includes an example calculation. File:Underdrain spacing calculation.xlsx
Rock
See MNDOT Standard Specification 3601.
Weir
See MNDOT Standard Specifications 2461, 2573, 3137, 3301, 3491, 3601.
Plants
See MNDOT Standard Specifications 2571, 2574, 2575, 3861, 3876, 3878.
Refer to the swales plant list section of the manual for selection of Minnesota native plants to be used in swales. Care must be taken to specify plants for their position in the system (swale bottom, side slopes and buffer). For the bottom of the swale, preference should be given to robust non-clump forming grasses or sedges that can withstand flow forces as well as provide adequate filtration functions. It is also important to understand draw-down time not only within the channel itself, but in either in-situ soils or the filter media, as plants have variable tolerance to the depth and duration of inundation as well as soil moisture period. Lastly, care should be taken to understand sun exposure and salt tolerance requirements of various plants to ensure a robust, dense establishment of vegetative cover.
Dry swale materials specifications
Link to this table
| Parameter | Specification | Size | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | Topsoil per MNDOT 3877 | n/a | Characteristic of local site soils |
| Media sand | ASTM C-33 fine aggregate concrete sand | 0.02” to 0.04” | |
| Check dam (pressure treated) | AWPA Standard C6 | 6” by 6” or 8” by 8” | Do not coat with creosote; embed at least 3’ into side slopes |
| Check Dam (natural wood) | Black Locust, Red Mulberry, Cedars, Catalpa, White Oak, Chestnut Oak, Black Walnut | 6” to 12” diameter; notch as necessary | Do not use the following, as these species have a predisposition towards rot: Ash, Beech, Birch, Elm, Hackberry, Hemlock, Hickories, Maples, Red and Black Oak, Pines, Poplar, Spruce, Sweetgum, Willow |
| Check dam (rock, rip rap) | Per local criteria | Size per requirements based on 10-year design flow | Cannot get water quality volume credit when using a permeable check dam |
| Check dam (earth) | Per local criteria | Size per requirements based on 10-year design flow | Use clayey soils with low permeability |
| Check dam (precast concrete) | Per pre-cast manufacturer | Size per requirements based on 10-year design flow | Testing of pre-cast concrete required: 28 day strength and slump test; all concrete design (cast-in-place or pre-cast) not using previously approved State or local standards requires design drawings sealed and approved by a licensed professional structural engineer. Embed at least 3’ into side slopes |
| Filter Strip sand/gravel pervious berm | sand: per dry swale sand gravel; AASHTO M-43 | sand: 0.02” to 0.04” gravel: 1/2” to 1” | Mix with approximately 25% loam soil to support grass cover crop; see Bioretention planting soil notes for more detail |
| Pea gravel diaphragm and curtain drain | ASTM D 448 | varies (No. 6) or (1/8” to 3/8”) | Use clean bank-run gravel |
| Underdrain gravel | per pre-cast manufacturer | 1.5” to 3.5” | |
| Underdrain | ASTM D-1785 or AASHTO M-278 | 6” rigid Schedule 40 PVC | 3/8” perf. @ 6” o.c.; 4 holes per row |
Design procedure – design steps
It is important to acknowledge that each site has unique and defining features that require site-specific design and analysis. The guidance provided below is intended to provide the fundamentals for designing dry swale systems to meet regulatory requirements but is not intended to substitute engineering judgment regarding the validity and feasibility associated with site-specific implementation. Designers need to be familiar with the hydrologic and hydraulic engineering principles that are the foundation of the design and they should also enlist the expertise of qualified individuals in stormwater management and stream restoration plantings with respect to developing appropriate planting plans and habitat improvement features.
Step 1. Make a preliminary judgment - consider basic issues for initial suitability screening
Make a preliminary judgment as to whether site conditions are appropriate for the use of a dry swale, and identify its function (filtration or infiltration) in the overall treatment system.
A. Consider basic issues for initial suitability screening, including:
- Site drainage area
- Site topography and slopes
- Soil types
- Regional or local depth to ground water and bedrock
- Bottom of facility to be at least three feet above the seasonably high water table
- Site location/minimum setbacks
- Presence of active karst
B. Determine how the swale will fit into the overall stormwater treatment system, including:
- Decide whether the swale is the only BMP to be employed, or if are there other BMPs addressing some of the treatment requirements.
- Decide where on the site the swale will most likely be located.
Step 2. Confirm design criteria and applicability
A. Determine whether the swale must comply with the MPCA CGP. To determine if permit compliance is required, see Permit Coverage and Limitations.
B. Check with local officials, watershed organizations, and other agencies to determine if there are any additional restrictions and/or surface water or watershed requirements that may apply.
Step 3. Perform field verification of site suitability
Consider the following when determining if a swale is suitable:
- The drainage area and area for swale
- The slope to get the drainage to the swale in addition to the swale slope to fully drain to a discharge point
- Any utility conflicts or roadway crossings that will need to be addressed in design
- MnDOT standards for roadway channel slopes and adequate depth for the 10-year drainage without overtopping the roadway
Consider the following when infiltration is desired in the swale design.
- Stormwater infiltration: This page contains links to several pages that address infiltration of stormwater runoff.
- Confirm infiltration rate of in-situ soils
Recommended number of soil borings, pits or permeameter tests for bioretention design. Designers select one of these methods.
Link to this table
| Surface area of stormwater control measure (BMP)(ft2) | Borings | Pits | Permeameter tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 1000 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 1000 to 5000 | 2 | 2 | 10 |
| 5000 to 10000 | 3 | 3 | 15 |
| >10000 | 41 | 41 | 202 |
1an additional soil boring or pit should be completed for each additional 2,500 ft2 above 12,500 ft2
2an additional five permeameter tests should be completed for each additional 5,000 ft2 above 15,000 ft2
Groundwater mounding, the process by which a mound of water forms on the water table as a result of recharge at the surface, can be a limiting factor in the design and performance of infiltration practices. A groundwater mounding analysis is RECOMMENDED to verify separation distances required for infiltration practices. For more information on groundwater mounding, see the following sections in this manual.
- Stormwater infiltration and groundwater mounding
- When should a mounding analysis be conducted?
- How to predict the extent of a mound
- Example mound calculations
Step 4. Select design variant based on physical suitability evaluation
Once the physical suitability evaluation is complete, it is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that the better site design principles be applied in sizing and locating the filtration practice(s) on the development site. Given the drainage area, select the appropriate swale practice for the first iteration of the design process. Note: Information collected during the physical suitability evaluation (see Step 1) should be used to explore the potential for multiple swale practices versus relying on a single facility.
Step 5. Compute runoff control volumes and other key design parameters
1. Calculate the following runoff control volumes.
- Calculate the Water Quality Volume (Vwq): If the swale is being designed to meet the requirements of the MPCA Construction Stormwater General Permit, the REQUIRED treatment volume is the water quality volume of 1 inch of runoff from the new impervious surfaces created from the project. If part of the overall Vwq is to be treated by other BMPs, subtract that portion from the Vwq to determine the part of the Vwq to be treated by the dry swale.
- Vwq = 1 inch x Areaimpervious surface
To calculate the volume behind a check dam, see item 3 below.
- Calculate Channel Protection Volume (Vcp)
- Vcp = 24 hour extended detention of post-development 1-yr 24-hr storm event
- Calculate Overbank Flood Protection Volume (Vp10)
- Vp10 = peak discharge from the 10-yr storm to 10-yr predevelopment rates
- Calculate Extreme Flood Volume (Vp100).
- Vp100 = peak discharge from the 100-yr storm to 100-yr predevelopment rates
2. Once the runoff control volume is determined for design, compute the following design parameters to determine the swale size required.
- A. Calculate the maximum discharge loading per foot of swale width
q=(0.00236/n)·Y·1.67·S·0.5
Where:
- q = discharge per foot of length of the swale, from Manning’s equation (cfs/ft);
- Y = allowable depth of flow (inches);
- S = slope of swale (percent) (0.5 to 2 percent); and
- n = Manning’s “n” roughness coefficient (use 0.15 for short prairie grass, 0.25 for dense grasses such as bluegrass, buffalo grass, blue grama grass and other native grass mixtures).
- B. Use a recommended hydrologic model to compute Qwq
- C. Minimum swale length (in feet) = Qwq / q
Where:
- Qwq = the water quality peak discharge (cubic feet per second)
3.The water quality volume (Vwq) achieved behind each check dam (instantaneous volume) is given by
Vwq=h2∗(h∗H+Bw)]/(2S)
where
- h = check dam height (inches)
- H = horizontal component of the swale side slope (1 vertical : H horizontal)(inches)
- S = slope (unitless); and
- Bw = channel bottom width (inches)
Add the Vwq for each check dam together to obtain the cumulative water quality volume for the swale.
For information on check dams, link here. For an example calculation of volume, link here.
Step 6. Compute number of check dams
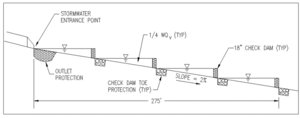
The number of check dams should be computed based on swale slope, length, and treatment objectives. For example, a swale designed to contain the entire Vwq may require more check dams than a swale that only contains a portion of the Vwq.
Channel slopes between 0.5 and 2 percent are recommended unless topography necessitates a steeper slope, in which case 6- to 12-inch drop structures can be placed to limit the energy slope to within the recommended 0.5 to 2 percent range. Energy dissipation will be required below the drops. Spacing between the drops should not be closer than 50 feet. Depth of the Vwq at the downstream end should not exceed 18 inches.
For an example calculation of number of check dams to employ, link here.
Step 7. Calculate drawdown time
Filtration swales (swales with an underdrain) include a bed consisting of a permeable soil layer at least 30 inches in depth, above a 6-inch diameter perforated PVC pipe (AASHTO M 252) longitudinal underdrain in a 12-inch gravel layer. The soil media should have an infiltration rate of at least 0.25 inches per hours with a maximum of 1.5 inches per hour and contain organic material to facilitate pollutant removal but not contribute to phosphorus leaching. A permeable filter fabric is placed between the gravel layer and the overlying soil. Dry swale channels are sized to store and filter the entire Vwq and allow for full filtering through the permeable soil layer.
Dry swales with no underdrain will have infiltration occurring. The drawdown time will be equal to the maximum pool depth behind a check dam divided by the soil infiltration rate. See design infiltration rates for different soil groups. For example, considering a swale with a 1 foot pool depth behind a swale, the drawdown time for a B(SM) soil with an infiltration rate of 0.45 inches per hour will be 26.7 hours, while the drawdown time for an A(SP) soil with an infiltration rate of 0.8 inches per hour will be 15 hours.
Step 8. Check 2-year and 10-year velocity erosion potential and freeboard
Check for erosive velocities and modify design as appropriate based on local conveyance regulations. Provide a minimum of 6 inches of freeboard.
Step 9. Design low flow control at downstream headwalls and checkdams
Design control to pass Vwq in 48 hours.
Step 10. Design inlets, sediment forebay(s), and underdrain system
Inlets to swales must be provided with energy dissipaters such as riprap or geotextile reinforcement. Pretreatment of runoff is typically provided by a sediment forebay located at the inlet. Enhanced swale systems that receive direct concentrated runoff may have a 6-inch drop to a pea gravel diaphragm flow spreader at the upstream end of the control. A pea gravel diaphragm and gentle side slopes should be provided along the top of channels to provide pretreatment for lateral sheet flows. The underdrain system should discharge to the storm drainage infrastructure or a stable outfall.
Step 11. Check volume, peak discharge rates and drawdown time against state, local, and watershed organization requirements (NOTE: steps are iterative)
Follow the design procedures identified in the Unified Sizing Criteria section of the Manual to determine the volume control and peak discharge requirements for water quality, recharge (not required), channel protection, overbank flood and extreme storm.
Model the proposed development scenario using a surface water model appropriate for the hydrologic and hydraulic design considerations specific to the site. This includes defining the parameters of the swale practice defined above: ponding elevation and area (defines the ponding volume), infiltration rate and method of application (effective filtration area), and outlet structure and/or flow diversion information. The results of this analysis can be used to determine whether or not the proposed design meets the applicable requirements. If not, the design will have to be re-evaluated.
A. Volume: Swale systems shall be sufficient to infiltrate a water quality volume of 1 inch of runoff from the new impervious surfaces created by the project. If this criterion is not met, increase the storage volume of the practice or treat excess water quality volume (Vwq) in an upstream or downstream BMP (see Step 5). If this requirement cannot be met, infiltrate to the extent possible and ensure that the remaining volume is treated through filtration.
B. Drawdown: Dry swales shall discharge through the soil or filter media in 48 hours or less. Additional flows that cannot be infiltrated or filtered in 48 hours should be routed to bypass the system through a stabilized discharge point.
Step 12. Finalize the cross-section and profile design for the project
- Grading plan: Develop a grading plan based on the preliminary profile and cross-section typical design.
- Dimensions: Adjust the preliminary profile dimensions to accommodate site specific concerns/impacts. Minimum design parameters for hydraulic, water quality, and quantity management criteria should be rechecked based on adjustments to the dry swale to ensure that safe and adequate conveyance is still maintained.
- Check dams: Adjust the preliminary check dam dimensions to accommodate site specific concerns/impacts. Minimum design parameters for hydraulic and water quality criteria should be rechecked based on adjustments to the check dams to ensure that safe and adequate conveyance is still maintained.
- Site stabilization: Course woodchips and compost should be used throughout the limit of disturbance for site stabilization. All areas should be seeded and planted as well as blanketed/matted. An appropriate erosion control blanket with biodegradable neeting should be used within the swale bottom and side slopes.
- Excess materials: It is advisable that excess materials, i.e., cobbles and boulders, be placed at the edge of the cross-section for use during the maintenance phase to correct any physical instability.
Step 13. Prepare vegetation and landscaping plan
A landscaping plan for a swale should be prepared to indicate how the enhanced swale system will be stabilized and established with vegetation. Landscape design should specify proper species and be based on specific site, soils, sun exposure and hydric conditions present along the swale. Further information on plant selection and use can be found in the swale plant list section.
Step 14. Prepare operation and maintenance plan
See Operation and Maintenance section for guidance on preparing an O&M plan.
Step 15. Prepare cost estimate
See Cost Considerations section for guidance on preparing a cost estimate that includes both construction and maintenance costs.
Related pages
- Terminology for swales (grass channels)
- Overview for dry swale (grass swale)
- Types of infiltration
- Types of filtration
- Design criteria for dry swale (grass swale)
- Construction specifications for dry swale (grass swale)
- Operation and maintenance of dry swale (grass swale)
- Assessing the performance of dry swale (grass swale)
- Calculating credits for dry swale (grass swale)
- Cost considerations for dry swale (grass swale)
- Case studies for dry swale (grass swale)
- Plants for swales
- Check dams for stormwater swales
- External resources for dry swale (grass swale)
- References for dry swale (grass swale)
- Requirements, recommendations and information for using dry swale (grass swale) without an underdrain in the MIDS calculator
- Requirements, recommendations and information for using dry swale (grass swale) with an underdrain in the MIDS calculator
- Requirements, recommendations and information for using swale side slope as a BMP in the MIDS calculator
This page was last edited on 29 December 2022, at 16:08.