Difference between revisions of "Planning green stormwater infrastructure projects and practices"
m (→Equity) |
|||
| Line 202: | Line 202: | ||
===Equity=== | ===Equity=== | ||
| − | [[File:Environmental justice locator.png|500px|thumb|alt=Environmental justice map tool image|<font size=3>Screen shot of [ | + | [[File:Environmental justice locator.png|500px|thumb|alt=Environmental justice map tool image|<font size=3>Screen shot of [https://ceed.org/resource/twin-cities-environmental-justice/ Twin Cities Environmental Justice Mapping Tool].</font size>]] |
When planning for GSI, equity issues may arise. For example, GSI initiatives tend to favor locations where open space or vegetation already exists, or in affluent neighborhoods. The planning phase of GSI can be used to assess where GSI is most needed and prioritize GSI in <span title="Environmental justice is the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people, regardless of race, color, national origin, or income, with respect to the development, implementation, and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations, and policies."> '''environmental justice'''</span> (EJ) areas. Also consider linking GSI incentives to flood mitigation programs and focus on locations already experiencing flooding and extreme temperatures, which typically coincide with EJ areas. | When planning for GSI, equity issues may arise. For example, GSI initiatives tend to favor locations where open space or vegetation already exists, or in affluent neighborhoods. The planning phase of GSI can be used to assess where GSI is most needed and prioritize GSI in <span title="Environmental justice is the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people, regardless of race, color, national origin, or income, with respect to the development, implementation, and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations, and policies."> '''environmental justice'''</span> (EJ) areas. Also consider linking GSI incentives to flood mitigation programs and focus on locations already experiencing flooding and extreme temperatures, which typically coincide with EJ areas. | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 21 February 2023
This green stormwater infrastructure (GSI) planning guidance was created to
- help practitioners plan for incorporating green stormwater infrastructure into their communities,
- help make the case for green stormwater infrastructure,
- provide resources on how to fund and finance green stormwater infrastructure, and
- provide information on how to include green stormwater infrastructure into ordinances and policy.
Much of the information presented here is geared towards practitioners who are new to GSI planning and is intended to provide an overview of the topics and questions that are relevant in the GSI planning process.
Contents
- 1 Key questions to consider during the planning phase
- 2 How to plan for Green Infrastructure in your community
- 2.1 Defining goals and objectives, including potential multiple benefits of GSI
- 2.2 Consider the scale of GSI planning
- 2.3 Sequence events for GSI planning
- 2.4 Determine length of time needed for GSI planning
- 2.5 Determine technical approach and resource needs
- 2.6 Financial considerations
- 2.7 Identify permitting and approval requirements
- 2.8 Establish partnerships
- 2.9 Conduct public outreach and communication
- 2.10 Potential roadblocks and barriers
- 3 How to make the case for Green Stormwater Infrastructure
- 4 How to fund and finance Green Stormwater Infrastructure
- 5 How to include Green Stormwater Infrastructure into ordinances and policy
- 6 Examples of planning for GI and GSI
- 7 Resources
- 8 References
Key questions to consider during the planning phase
There are a lot of questions to be answered during the planning phase of the GSI project, particularly in the early stages. Even if a planning team is experienced, the total unknown information may be a roadblock itself. The table below is intended to categorize the key questions and topics that should be asked and considered throughout the design process. The following section discusses many of these questions in greater detail.
Key questions to consider during the planning phase for green stormwater infrastructure.
Link to this table
| Topic | Key questions |
|---|---|
| Ownership | Should the GSI practices be owned by the community government, by individual property owners, or by another entity (such as a conservancy or port authority)? |
| Maintenance | What are the recommended maintenance frequencies and practices? How often is the community willing to maintain their GSI practices? Should there be shared responsibility for maintenance? |
| Performance | How much stormwater needs to be treated? What contaminants should be targeted? |
| Cost | What is the available budget range? Are higher cost options acceptable if they provide additional community services? |
| Funding | What are the available funding sources: tax revenue, grants, donors, developers? |
| Technical resources | How will in-house and consultant resources be coordinated? |
| Community support | Are there individuals or groups willing to provide volunteer maintenance? |
| Community outreach | Is the outreach goal to inform people of the project, or is the goal to solicit public input? Who is best positioned to effectively lead community outreach efforts? |
| Exploration | Is the community interested in newer techniques that may require more interventions or would they prefer to stick with the “tried and true” techniques? |
| Ammenities | Should the GSI practices serve as community amenities beyond stormwater management?
What ancillary benefits should the GSI practices provide? |
| Ordinances | Is the community interested in using ordinances as a vehicle for implementing GSI? Are GSI ordinances an option for the community? |
| Permitting | Which permits and regulatory approvals are needed? |
| potential roadblocks | Who may benefit from the GSI project? Who may be adversely impacted by the GSI project? |
| Climate change and resilience | To what extent are we willing to adaptively manage the GSI product in the future to accommodate climate change? Are options designed into the product for future implementation? |
| Canopy cover preservation | Is there existing canopy cover in place that would be removed by the GSI? Can the existing canopy cover be preserved to retain the site’s pre-existing, natural pollutant removal, rainfall interception, evapotranspiration, and shading capabilities? |
How to plan for Green Infrastructure in your community
This section provides information on considerations when planning green stormwater infrastructure in your community.
Defining goals and objectives, including potential multiple benefits of GSI
When planning GSI for your community, an important first step is to define the community’s goals and objectives. Every community is unique and therefore every GSI plan also unique. Goals and objectives should be defined with as broad a partnership or stakeholder group as practical. Stakeholders ultimately judge the success or failure of a project, so engaging them early and often will help ensure a successful outcome. Link here to see a discussion of potential stakeholders.
Example goals and objectives are illustrated in the accompanying table.
Example goals and objectives when planning green infrastructure. Also see Multiple benefits of green stormwater infrastructure.
Link to this table
| Example goals | Example objectives |
|---|---|
| Improve water quality, especially in areas with impaired or polluted waterways | Install GSI upland of waterways Preserve buffer zones around waterways |
| Alleviate recurring local flooding issues | Install infiltration-based GSI. Reduce imperviousness through GSI |
| “Green” highly impervious or urban areas to reduce the urban heat island effect | Increase tree canopy Reduce imperviousness through vegetation-based GSI practices like bioretention practice |
| Provide a neighborhood or community amenity | Incorporate GSI as part of a larger neighborhood amenity like a pocket park or playground |
| Increase biodiversity and native habitat | Use native vegetation as part of a GSI project |
| Address socio-environmental issues in the community | Incorporate GSI as part of an overarching strategy to address socio-environmental concerns |
| Reduce costs and/or increasing effectiveness of stormwater management | Select stormwater practices that are most cost cost effective (e.g. have lowest cost per unit of pllutant reduced) |
Defining the potential multiple benefits of GSI will be an important component of the GSI planning process. These can include environment, social, and economic benefits. The following pages provide more information on the benefits of GSI:
- Multiple benefits of green stormwater infrastructure
- Green Infrastructure benefits of bioretention
- Green Infrastructure benefits of tree trenches and tree boxes
- Green Infrastructure benefits of permeable pavement
- Green Infrastructure benefits of infiltration practices
- Green Infrastructure benefits of constructed wetlands
- Green Infrastructure benefits of vegetated swales
- Green Infrastructure benefits of harvest and use/re-use practices
- Green Infrastructure benefits of green roofs
Also see the section on How to make the case for Green Stormwater Infrastructure.
Consider the scale of GSI planning
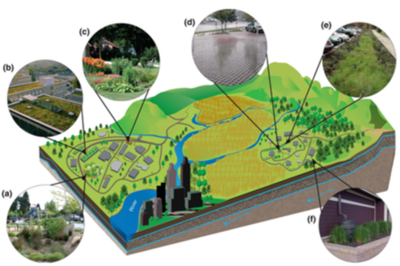
Define the scale of the project and understand whether the objectives of the project meet site-specific improvement goals, local community goals, broader regional goals, or some combination. In addition to local benefits, individual GSI practices contribute to large-scale downstream water quality objectives such as a total maximum daily load (TMDL) or in-stream water quality targets such as phosphorus, nitrogen, sediment, or chloride reduction. Most regional stormwater or water quality goals have their own planning documents (Watershed Restoration and Protection Strategies, TMDL Implementation Plans, etc.) that may help define the need for site-specific GSI.
The table below provides an overview of common plans that could inform the GSI planning process at different scales. These plans do not need to pre-exist or need to be created in order to move forward with the GSI planning process. Rather, these plans, if they exist, can be consulted during the GSI planning process. This table has been adapted from the Credit Valley Conservation and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority and modified to include common Minnesota-specific planning documents (CVA & TRCA, 2010).
Overview of common plans that could inform or be developed during the GSI planning process at various different scales.
Link to this table
| Scale | Planning type | Planning description | Minnesota-specific planning document |
|---|---|---|---|
| Watershed |
|
Major themes and objectives for the municipality’s future growth are established, and challenges and opportunities for growth are identified, such as municipal policy direction for innovative SWM approaches and other climate change initiatives. | |
| Community/subwatershed | Secondary plan | Major elements of the natural heritage system are identified
including terrestrial, aquatic and water resources (hydrology, hydrogeology, fluvial geomorphology, etc.). Stormwater management objectives for surface and groundwater resources. Future drainage boundaries, locations of stormwater management facilities and watercourse realignments are established. |
|
| Block plan | The location of lots, roads, parks and open space blocks, natural heritage features and buffers, and stormwater management facilities are defined. A full range of opportunities to achieve stormwater management objectives are identified, establishing a template for the more detailed resolution of the design of stormwater management facilities at subsequent stages in the planning and design process. | ||
| Neighborhood | Draft Plan of Subdivision/Functional Servicing Plan | Conceptual design is carried out for stormwater management facilities. Consideration should be given to how stormwater management objectives can be achieved and how these objectives influence the location and configuration of each of the components listed above | |
| Registered plan | Detailed design is carried out for stormwater management facilities. | ||
| Site | Site plan | Site-specific opportunities are identified to integrate stormwater management facilities into all of the components of a development including landscaped areas, parking lots, rooftops, and subsurface infrastructure. Solutions should be considered in the context of the overall stormwater management strategy for the block or secondary plan area to ensure that functional requirements are achieved | |
| Site | Permits and other Approvals Plan | Detailed design of SWM for the site |
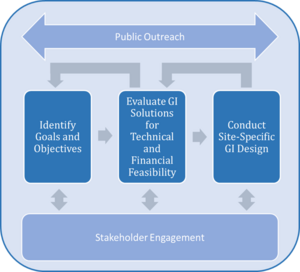
Sequence events for GSI planning
The following steps are typically part of the planning process.
- Determine goals and objectives to meet environmental, social, and economic needs.
- Evaluate possible GSI approaches for technical and financial feasibility.
- Conduct a site-specific GSI design guided by the goals and objectives and the range of technically and financially feasible GSI solutions.
Throughout this process, partnerships with key stakeholders are created, consulted, and used to maximize the chances of successful GSI planning and implementation. Public outreach is typically also conducted throughout the entire process to garner public support of the project.
Determine length of time needed for GSI planning
The length or amount of time needed for GSI planning varies from project to project and is dependent on the type of GSI project.
GSI planning and implementation on land-development projects: These projects (e.g., new development or large redevelopment projects, street reconstruction projects, and master plan development) can take one to several years to realize, depending on the pace of the land development project. This type of GSI planning is often the most successful and cost-efficient since the GSI planning can be incorporated early in the planning and design phase of land-development projects. Ideally, this results in GSI practices that are seamlessly integrated into the landscape and infrastructure of the project.
Retrofit projects: GSI planning and implementation of retrofit projects ((e.g.: adding green stormwater infrastructure to an existing landscape)) can take 6 to 18 months to realize, sometimes longer if unforeseen roadblocks occur. Retrofit projects typically come at a higher cost relative to projects that are integrated into land development projects. Mobilization and other labor costs associated with retrofit costs can be minimized if GSI retrofits are planned to happen in conjunction with other infrastructure improvement projects, such as pavement repairs or regrading. Advanced and comprehensive GSI planning projects are one strategy to save retrofit costs by identifying opportunities to install GSI alongside future capital improvement projects. The Towerside District Stormwater Project, an initiative by the Mississippi Watershed Management Organization, illustrates this concept in this video.
Determine technical approach and resource needs
The technical approach and design process varies from project to project but generally follows a sequence of events described by the Credit Valley Conservation and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority (CVA & TRCA, 2010). The table below shows this sequence and identifies the type of personnel resources that could be used, as well as helpful publicly available technical resources to help GSI planners get started.
Sequence of events and type of personnel resources to help green stormwater infrastructure planners (Credit Valley Conservation and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority, 2010).
Link to this table
| Planning and design step | Examples of Helpful Personnel Resources | Helpful Publicly Available Technical Resources (Non-Exhaustive) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.Use available information from regional, watershed and subwatershed scale studies to develop an understanding of the environmental contexts in which the site is located and the watershed management objectives and targets relevant to the site (e.g., stormwater management, natural heritage system and aquatic community objectives/targets). | Engineer or scientist familiar with the area and its environmental context, and who has GSI expertise | |
| 2.Undertake a comprehensive inventory of the biophysical, ecological, and hydrological characteristics of the site. | Biologist, ecologist, hydrologist, or similar | |
| 3.Identify existing terrestrial and aquatic natural heritage features and functions that require protection as the basis for a natural heritage system. | Biologist or ecologist with terrestrial and aquatic expertise | |
| 4.Identify opportunities to enhance features, connectivity, and functional integrity of the natural heritage system. | Engineer or scientist | |
| 5.Identify soil and hydrogeologic conditions that are well-suited for stormwater infiltration practices. | Hydrologist, geologist, soil scientist, geotechnical engineer, or similar | |
| 6.Identify patterns of shallow groundwater flow and locations of discharge to receiving watercourses or wetlands within or adjacent to the limits of the site. | Hydrologist, geologist, or similar | |
| 7.Identify strategic and desirable locations for stormwater management practices (SWMPs) and the nature and function of facilities (e.g., attenuation, infiltration, filtration, evapotranspiration, harvesting, etc.). | Engineer or scientist with GSI expertise | EPA GSI Modeling Toolkit |
| 8.Identify a long list of opportunities to integrate desirable SWMPs into components of the community or built form. | Planner or landscape architect with GSI expertise | |
| 9.Explore a full range of design options for the community that can achieve stormwater management objectives in conjunction with other community design objectives. | Planner or landscape architect with GSI expertise | |
| 10.Develop the community design plan | Planner or landscape architect with GSI expertise | |
| 11.Resolve the design of the stormwater management strategy including defining the SWMPs to be incorporated into the design of specific components of the development and establish specific design and performance criteria for each practice. | Engineer or scientist with GSI expertise |
GSI practices need to be designed by duly licensed professionals, such as a professional engineer or landscape architect. In addition to the personnel resources listed in the table above, additional types of personnel that could be consulted include
- easement and realty specialists,
- financial planners and/or accountants,
- meeting facilitators,
- regulatory & permitting specialists,
- zoning planners,
- legal counsel specializing in drafting ordinances,
- arborist or restoration specialists,
- marketing specialists,
- GSI Installers, and
- surveyors.
Communities should determine which of these personnel resources they have “in-house,” and which could be provided by consultants. Ideally a planning team would include both in-house resources who have an intimate understanding of the community priorities and resources and consultants who can bring a range of experiences and skills from other projects and communities.
Financial considerations
Financial considerations will be a foundational topic for GSI planning efforts. Based on the stated goals, objectives, and available community resources, the financial priorities and strategies can look quite different for each community.
The three key financial considerations are cost, return on investment (value assessment), and funding.
- Cost: Cost considerations include planning, design, installation, and operations & maintenance costs. These costs can be assessed by the design and planning teams.
- Return on Investment: A value assessment factors in both the direct performance benefits of GSI practices and the ancillary community benefits of such practices. Direct performance benefits can be measured or estimated and include volume of runoff managed, pollutant load reduction achieved, or carbon reduction. These can be measured via monitoring or sampling programs, or estimated via engineering tools and models. Ancillary benefits are harder to measure directly and include improved air quality, impact on pollinators, climate change resiliency, and traffic calming. Because these benefits are more difficult to quantify directly, a relative ranking/scoring strategy is typically used. This assessment is best conducted by all of the planning partners so as not to skew the results. For more information see Multiple benefits of green stormwater infrastructure.
- Funding: Funding is a universal and continuously evolving challenge for GSI projects. There are many funding strategies which can be considered. These are discussed in the How to Fund and Finance GSI section. Funding considerations are best assessed by the GSI management team with support from the design team.
Community priorities are as unique as the communities themselves. Most communities and stakeholders prefer funding GSI projects that provide direct and ancillary amenities. For example, funding a bioretention practice that is also a sidewalk pocket flower garden may be more attractive to the community than replacing the impervious pavement of an alley with permeable pavement, even though both the bioretention and permeable pavers provide similar direct stormwater-related benefits. With this in mind, consider pairing GSI projects to community amenity projects to increase the likelihood of funding and community support. Pairing or grouping projects can also increase the overall cost-effectiveness.
The following resources provide more information on financial cost considerations related to GSI planning.
- Community-enabled Lifecycle Analysis of Stormwater Infrastructure Costs (CLASIC). CLASIC is a user-informed screening tool that utilizes a life cycle cost framework to support implementation of stormwater infrastructure, including green, hybrid green-gray, and gray infrastructure practices. The CLASIC tool integrates Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA), which enables consideration of co-benefits for green infrastructure. There are three integrated components in the CLASIC tool: life cycle cost; performance; and co-benefits.
- NOAA Guide to Assessing Green Infrastructure Costs and Benefits for Flood Reduction. The purpose of this guide is to provide a process that communities can use to assess the costs and benefits of green infrastructure to reduce flooding. The guide takes a step-by-step, watershedbased approach to documenting the costs of flooding; projecting increased flooding and associated costs under future land use and climate conditions; and calculating benefits and costs of reducing flooding with green infrastructure over the long term.
- The National Academies Press Long-Term Performance and Life-Cycle Costs of Stormwater Best Management Practices, NCHRP Report 792. Provides tools and guidance to help optimize the best management practices (BMP) portion of a transportation department’s stormwater program. The report is accompanied by a CD-ROM containing a BMP evaluation tool in a spreadsheet format as a computational aid that provides average annual performance and whole life costs for treatment BMPs.
- USEPA Green Infrastructure Cost-Benefit Resources. Describes how other communities have estimated the costs and benefits of their green infrastructure programs as well as tools to inform cost-benefit analysis.
Identify permitting and approval requirements
Like most infrastructure and construction projects, there is typically a permitting and approval aspect to installing GSI. Permitting and approval authorities vary depending upon the location and extent of the project, but may include
- stormwater utility (e.g., municipality or watershed district),
- watershed districts or watershed management organization,
- gas and electric utility (approval from utilities is required if digging is involved),
- zoning and homeowners associations,
- departments of transportation (if the public right of way is involved), and
- city or county.
Include key people from these organizations as planning partners to help obtain the right permits and approvals when implementing green stormwater infrastructure. Contacting the city, county, or watershed district can be an effective place to begin the permitting process.
The permitting and approval process can be lengthy, so it is helpful to begin the permitting process early. For authorities in which there is an overlap in their permitting processes, it is beneficial for communities to work with these authorities concurrently.
Establish partnerships
The most effective way to plan and implement a GSI project is to create a diverse group of partners. Partnerships help increase community involvement, provide technical expertise required to meet goals, and can help create a maintainable GSI system. Partnerships can sometimes augment the available funding and resources through in-kind contributions or additional funding. GSI partners can be loosely grouped into three categories: managers, design teams, and stakeholders. GSI planning efforts should include representatives from all three categories.
- GSI managers may include owners, maintenance personnel, planners, developers, and regulators. GSI managers may be part of private, government, or non-government organizations.
- GSI designers may include engineers, scientists, and landscape architects that are specialized in GSI and natural restoration practices. If one of the GSI goals is to use GSI practices to provide community amenities, then the inclusion of a landscape architect is strongly encouraged. Landscape architects are trained to identify end user needs and design infrastructure to provide a desirable user experience while achieving the technical goals of a design. Designers may be municipal staff or outside consultants.
- GSI stakeholders may include adjacent property owners, adjacent infrastructure managers, community organizations, government leaders and officials, and anyone who may access or see the GSI. The role of stakeholders in the GSI planning process is integral as they will ultimately judge the success of the GSI, so stakeholder engagement should be prioritized in the early planning phases. To cultivate an effective relationship with stakeholders, a stakeholder engagement plan should be developed and may include
- identification of audiences,
- stakeholder roles and responsibilities,
- communication strategies, and
- timing of engagement for individual stakeholders based on roles and responsibilities.
Conduct public outreach and communication

Stakeholders ultimately judge the success or failure of a project, so engaging them early and often helps ensure a successful outcome. Public outreach is particularly important when defining community goals and priorities.
Outreach activities can be done in-house or via a consultant. The role of public outreach is often undervalued, and the effort required is often underestimated. When in doubt, a professional specialist, such as a communications or public relations expert, is recommended to support public outreach.
Many communities have existing resources and strategies for public outreach. Surveys, council meetings, mass mailings, newspapers and print media, social media, public bulletins, and public meetings are common outreach strategies. Most communities and neighborhoods may have one or several primary mechanisms for community notification which can be leveraged. Note that GSI may be unfamiliar to many, so use language that is accessible, clear, and jargon-free when discussing GSI and its challenges and benefits.
The outreach materials are equally as important as the outreach strategies. Interactive communications materials can be highly effective to support outreach strategies, are increasingly common and relatively easy to do, and keeps the public interested and engaged. Examples of interactive communications materials include
- storyboards (e.g.: USACE Engineering With Nature storyboards),
- online story maps (e.g.: City of Atlanta GSI Program storymap),
- online web maps (e.g.: NYC DEP Green Infrastructure Program Map),
- website content (e.g.: Philadelphia GSI webpage),
- targeted priorities boards,
- commenting on maps using post-its,
- public interviews and surveys,
- video booths, and
- interactive physical models.

In addition to well-crafted media content and notification, few techniques are as effective at communicating the benefits of GSI as having the public walk by and through a built example of GSI. Creating high-visibility GSI pilot projects at public facilities such as government offices, schools, or libraries, is an effective means of engaging and educating the public on GSI. Pilot projects can include educational signage about the function and benefits of GSI and allows the public to see GSI under different weather conditions and seasons. GSI pilot projects at schools can also be incorporated into the educational curriculum.
Some useful links providing information on stakeholder involvement and perceptions are illustrated below.
- Stakeholders’ Engagement on Nature-Based Solutions: A Systematic Literature Review
- Using green infrastructure to stimulate discourse with and for planning practice: experiences with fuzzy concepts from a pan-European, a national and a local perspective
- Stakeholders’ Perceptions on the Role of Urban Green Infrastructure in Providing Ecosystem Services for Human Well-Being
- NEW YORK CITY’S GREEN INFRASTRUCTURE PLAN’S EXECUTION: A LOOK AT STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT THROUGH AN ADAPTIVE MANAGEMENT APPROACH
- ENHANCING SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES WITH GREEN INFRASTRUCTURE
- The Role of Stakeholders in Improving Management Practices of Urban Green Infrastructure in Southern Ethiopia
Potential roadblocks and barriers

There are several potential roadblocks and barriers to GSI implementation, but in many cases, these can be anticipated and managed. Below is a list of common roadblocks experienced by GSI planners and suggested ways of addressing or managing these roadblocks.
- Lack of community buy-in: The value and benefit of green stormwater infrastructure is not always readily perceived or understood by community members or stakeholders, which sometimes prevents acceptance or support of GSI efforts. Communicating the benefits of GSI beyond stormwater management, and focusing more on ancillary benefits of GSI, is an effective method for overcoming this particular challenge. Incomplete or inadequate representation of these benefits may leave stakeholders unhappy with value gained from the GSI. Plain language should be used when describing the benefits and mechanisms of stormwater management to community members. Using visuals and graphics can also be an effective means of communicating with community members. Examples of interactive techniques that can be used to communicate with the public are shown in the Public Outreach section.
- GSI costs are deemed too expensive: Costs are a clear roadblock when planning and implementing GSI. Early in the planning process, planners and partners should provide rough cost estimates to set expectations and allow for funding and financing options to be explored as soon as possible. Clear communication on all the benefits of GSI can also help demonstrate and justify the cost of GSI and can help alleviate cost concerns from partners and stakeholders.
- Unclear operations and maintenance responsibilities: Ongoing maintenance is necessary for GSI to operate properly and provide all intended benefits. Failure to properly maintain GSI can lead to expensive repairs. GSI operation and maintenance (O&M) can add a continued expense over the lifetime of the GSI practices; however, these costs can be less than maintenance of traditional gray infrastructure. Ongoing maintenance agreements are always recommended and, in some cases, necessary. More information on GSI operation and maintenance can be found in the O&M of GSI BMPs page of the Minnesota Stormwater Manual.
- Uninterested owner: Occasionally, a land or building owner may not be interested in participating in a GSI project. Landowner approval or buy-in should be sought as early as possible during the planning process so that alternatives can be identified if necessary. Clear communication on all the benefits of GSI can also be helpful. Some landowners may be interested in participating in water quality trading.
- Lack of commitment after design stage of project: Sometimes design components that are included in early project renderings are dropped after the project has been approved and permitted. Consider retaining commitments to the design through the approval process and beyond.
- Competing resources and priorities: In addition to monetary resources, available time from those stakeholders and partners with critical skillsets can derail progress on GSI planning. To the extent possible, only partners that have the time and capacity to stay actively and sufficiently engaged throughout the entire planning process should be selected. Timelines should be developed to accommodate competing priorities so that delays are avoided, and expectations are set appropriately.
- Concerns about GSI aesthetics: Certain GSI may not meet the aesthetic preferences of all stakeholders, particularly those who may interact with a practice. The end user should always be considered, and design features should incorporate their feedback and preferences. Alternative GSI types may help offset aesthetic concerns, but not always. Early buy-in from stakeholders can also minimize this roadblock.
- Concerns about GSI effectiveness: Stakeholders may question the effectiveness of GSI related to stormwater volume or pollutant load reductions. This may be a general concern (uncertainty in the literature values) or due to site-specific modeling that shows GSI may not achieve the desired objectives. In both situations, open communication between all partners, and particularly the design team and managers, should be encouraged. The team as a whole should reach a consensus based on the best available information. Proper installation is critical to GSI effectiveness. Third party oversight and inspection are helpful to ensure proper installation of GSI, which will help achieve maximum potential efficiency.
- Regulatory hurdles: Regulatory hurdles may slow down or derail the GSI planning, and as such can be disincentive to certain stakeholders. Experienced engineers, planners, and other partners should be included from the onset of planning to make the regulatory process as streamlined as possible. Clear communication between the party that owns or is implementing the regulatory process and the regulator is encouraged. The permitting and approvals section has additional information on potential permitting and approval requirements for GSI.
Additional information on overcoming barriers to green stormwater infrastructure is available on the following websites.
- Overcoming Barriers to Green Infrastructure (EPA)
- Overcoming Barriers to Green Infrastructure (New Hampshire)
- TACKLING BARRIERS TO Green Infrastructure
- Research Spotlight: Overcoming Barriers to Green Infrastructure Solutions
- Barriers and Gateways to Green Infrastructure
- Challenges of mainstreaming green infrastructure in built environment professions
How to make the case for Green Stormwater Infrastructure
Planners and engineers who would like to integrate GSI into landscapes and projects sometimes find themselves having to “make the case” for GSI. This may include presenting on the multiple benefits of GSI (social, economic, and environmental), describing the equity and environmental justice aspects of GSI, and discussing cost related topics such as life cycle costs, triple bottom line, and cost-benefit analysis. Different outreach and communications strategies can be used to help “make the case”.
Presenting the multiple benefits of GSI

Green infrastructure should be presented as not only providing stormwater benefits, but also as providing multiple social, economic, and environmental benefits (see Multiple benefits of green stormwater infrastructure). Considering and presenting these benefits together rather than separately, and highlighting the interactions between benefits, is important in making a better business case for implementing green stormwater infrastructure.
Social benefits of GSI: The social benefits of GSI are numerous. Green infrastructure can be integrated into the creation of public amenities such as pocket parks or micro green spaces. GSI can also improve overall public health by reducing air temperatures in the summer (counteracting the urban heat island effect), improving air quality, and decreasing asthma incidences, and stimulate a more inviting and walkable environment (USEPA, 2017). Secondary cascading impacts such as transportation delays, utility service disruptions, and even pandemics are also times when GSI can have a positive effect: waiting for a late bus under the shade of street trees on a 95℉ day or a stroll through a city park for moments of socially distanced relief during the recent Covid pandemic are relatable moments. Social equity challenges are highlighted in low- to moderate-income communities and urban neighborhoods, which often have more impervious areas than tree cover (New York Times, 2020) and older, traditional stormwater management infrastructure. Deploying GSI in the form of street trees, urban forests, and integrated stormwater management can provide traditional infrastructural service benefits while also satisfying the innate human instinct to connect with nature. Placing GSI in urban areas increases the likelihood that a greater diversity of people gets time in and around natural systems. If planned properly, strategic GSI placement can help provide socially equitable access to green spaces for all residents. In identifying the social benefits of GSI, a community should also address the role GSI plays in gentrification and should consider these unintended social consequences in the design and placement of GSI. Refer to the Equity Section for further information on the role of GSI in gentrification and tools for addressing it.
Economic benefits of GSI: Economic benefits of GSI include reduction of O&M costs relative to traditional infrastructure, reducing the initial capital outlay costs of large traditional (gray) infrastructure, preserving property values, supporting local workforces, and even agri/eco-tourism. While GSI does require careful maintenance as discussed in the Potential Roadblocks and Barriers section, GSI tends to appreciate in value over time as the ecosystems protected or created, such as rain gardens, bioswales, and constructed stormwater wetlands, increase in functionality. This is an advantage over traditional gray infrastructure, which tends to depreciate over its lifetime (The Nature Conservancy / AECOM, 2021), resulting in the need for major repairs or replacement. Green roofs are an example of building-integrated GSI which can minimize traditional building component replacement cycles and extend the life of components - in this case sheltering roofing membranes by limiting exposure to damaging ultraviolet rays. Other examples include GSI techniques such as onsite stormwater capture and infiltration with rain gardens, bioswales, and constructed wetlands which can reduce the need for large, complex, costly, and often unattractive traditional stormwater management structures such as concrete detention basins, hardscaped bypass channels, and below-grade catchment tanks which require expensive excavation and relocation of utilities to install (Conservation International, 2019). Planting chloride-tolerant species reduces the replacement costs from deicing salts. Maintaining or increasing property values have been shown to be a positive secondary benefit of GSI related to social benefits listed above. People and businesses value being located in and near vegetation and green areas. Designing, building, operating, and maintaining GSI cannot be outsourced. These are local jobs done by local people, keeping dollars in the community (FEMA, 2021). Finally, treating agricultural, preservation, and reservation lands as green stormwater infrastructure extends the possibility of economic benefits of agri/eco-tourism into non-urban areas.

Environmental benefits of GSI: Environmental benefits from GSI include improvements in water quality, air quality, greenhouse gases, ecological habitat, and reduced impacts from flooding, extreme precipitation, extreme heat, wildfire, and other climate stressors such as landslides, mudflows, and subsidence (FEMA, 2021). Integrated stormwater management with GSI retains and treats storm water locally, reduces the need for extensive and often oversized drainage systems, reduces exposure of stormwater to surface pollution like road salts and oils, and can reduce occurrences of localized flooding. GSI can also help mitigate greenhouse gasses and help reach increasingly aggressive state and local targets through carbon sequestration. Carbon sequestration can happen by planting and preserving deep-rooted and woody-stemmed native plants and trees on small urban sites, suburban lots, and in rural forest, wetland, and meadow areas. Regenerative agricultural practices such as crop rotation, conservation tillage (no- or low-till), intercropping, integration of deep-rooted grasses (and other prairie plants), and use of biochar can further extend carbon mitigation potential of agricultural lands (Food, Agriculture, and Land Use Solutions Project Drawdown, 2021). From pollinator gardens to constructed wetlands, GSI not only increases the number and diversity of types of habitats for different species of plants and animals through habitat creation, but it also increases ecological connectivity across urban, suburban, and rural areas through habitat preservation. With elevated annual precipitation and frequency of heavy rains in Minnesota, the risk of flooding is likely to increase (MNDNR, 2021). GSI can manage flood risk by reducing stormwater runoff through infiltration practices (e.g., bioswales) (USEPA, 2022a). NOAA provides A Guide to Assessing Green Infrastructure Costs and Benefits for Flood Reduction. Green infrastructure can include water elements or solar elements to implement blue-green infrastructure and yellow-green stormwater infrastructure, respectively, in a community which can provide additional water quality, energy, and aesthetic benefits.
Social, economic, and environmental benefits should also be considered holistically rather than separately. Consider all benefits categories and set goals to achieve high marks across the board. For example, integrated stormwater management with GSI keeps water onsite locally, provides an attractive landscape (social), reduces the need for oversized traditional water treatment infrastructure (economic), and creates pockets of ecological habitat and shading (environmental). Also consider the interactions between benefits and use the process as an opportunity to innovate. Workforce development and equity are closely linked, for example. Implementing green stormwater infrastructure in disadvantaged communities is critical as discussed above, but the design, installation, operation and maintenance of green stormwater infrastructure also presents further opportunities to reduce barriers for entry for local builders from historically disadvantaged populations. Consider tailoring training programs in GSI for O&M staff, small businesses (especially (MBE / DBE / WBE), trade / vocational schools, and community colleges. Developing training for older staff and contractors familiar only with traditional infrastructure will improve job retention, prioritize continuing education, and encourage broader uptake and acceptance of green stormwater infrastructure.
Equity
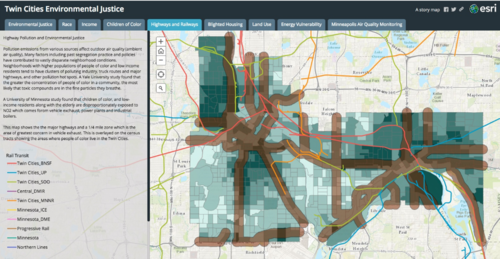
When planning for GSI, equity issues may arise. For example, GSI initiatives tend to favor locations where open space or vegetation already exists, or in affluent neighborhoods. The planning phase of GSI can be used to assess where GSI is most needed and prioritize GSI in environmental justice (EJ) areas. Also consider linking GSI incentives to flood mitigation programs and focus on locations already experiencing flooding and extreme temperatures, which typically coincide with EJ areas.
Another common equity issue is lack of a diverse stakeholder group involvement during the GSI planning stages. Engaging stakeholders from a variety of backgrounds and expertise to maximize potential project benefits and buy-in is critical for the success of GSI (The Nature Conservancy / AECOM, 2021). Involving a diverse group of community members can occur at all GSI stages, including planning, designing, building, and monitoring green stormwater infrastructure. Consider historically disadvantaged populations, income-limited, or other vulnerable groups such as the elderly, small-to-medium enterprises (SME), low-to-medium income (LMI) households, single-parent households, and renters; and populations at increased risk of climate change impacts.
To engage a diverse group of stakeholders, consider the barriers to community engagement, such as work schedules conflicts, limited transportation options, or cost of attendance. Providing incentives such as compensating stakeholders for their time, reimbursing travel costs, or planning engagement opportunities outside of traditional work schedules can be very helpful in attracting a diverse group of stakeholders. Be intentional and considerate when entering relationships with community members and be mindful of mistrust based on historic environmental racism and redlining, as well as the impact of gentrification on the community and the contribution to gentrification by GSI. Meet people where they are, early and often, by conducting outreach in community locations such as libraries, community centers, schools, churches, and parks. Leverage relationships with local groups, partners, and organizers who know the community. Demographic research can also be used to identify the desired composition of a stakeholder group.
Another equity concern is that newer GSI design, construction, installation, and maintenance may present barriers for market-entry for local builders from historically disadvantaged populations and communities without training. This population can be targeted for specific communication on GSI work opportunities for smaller construction firms typically owned and operated by income-limited or vulnerable groups such as small-to-medium enterprises (SME). Consider encouraging local trade schools and career centers to provide training on GSI design, construction, installation, and maintenance training. Communities can also provide incentive and/or subsidy programs to small-to-medium enterprises (SME), low-income homeowners, and landlords for GSI implementation. These incentives could include access to technical assistance and financial incentives, including tax rebates, subsidies, and permit waivers or expedited permitting.
Additional resources for addressing equity and environmental justice in GSI planning include:
- The University of Minnesota toolkit on investing in green stormwater infrastructure as means of improving equity among communities
- EPA Equitable Development and Environmental Justice
Life cycle costs, triple bottom line, cost-benefit analysis
Green infrastructure can be a cost-effective approach to reduce stormwater flows, improve water quality, and help communities stretch their infrastructure investments further by providing multiple environmental, economic, and social benefits also known as the triple bottom line (USEPA, 2022b). Making the case for GSI often entails comparing life cycle costs or cost-benefit analysis between green and grey infrastructure, or between different types of GSI. Cost considerations should include the upfront capital costs as well as the long-term maintenance requirements and replacement costs over the expected life span of the infrastructure.
Many guidance documents and tools exist to assist planners and engineers calculate life cycle costs, assess the triple bottom line, or conduct a cost-benefit analysis, including:
- EPA’s National Stormwater Calculator
- EPA’s Green Infrastructure Cost-Benefit Resources
- The National Academies Press Long-Term Performance and Life-Cycle Costs of Stormwater Best Management Practices, NCHRP Report 792
- Community-enabled Lifecycle Analysis of Stormwater Infrastructure Costs (CLASIC)
It is also worth noting that entities implementing GSI may want to consider collecting their own long-term performance and life-cycle cost data to improve their decision-making process in the future.
How to fund and finance Green Stormwater Infrastructure
Funding GSI can be a considerable roadblock for a planner or community. Financial constraints and funding opportunities should be understood at an early stage of planning. Fortunately, there are many federal, state, and other grant opportunities that can be leveraged to help finance GSI.
Federal funding opportunities are diverse - they come from numerous agencies and target many types of benefits. Given the variety of GSI benefits (e.g., water quality, flood management), GSI is applicable to many opportunities. EPA maintains one such list of applicable funding sources.
At the state level, MPCA maintains a page devoted to state funding options. MN’s Clean Water Fund has funded over 3,300 projects with the mission of improving and protecting surface water resources.
Local governments also fund projects through stormwater fees or other infrastructure funds. Contact municipal and county governments for local opportunities. Municipal bonds and private financing are other opportunities for funding.
A non-exhaustive list of current funding opportunities is provided in the table below. It should be noted that some of the funding resources provided may be only loosely connected to GSI but may be worthwhile to explore as GSI may be used to accomplish their overarching goals.
List of current funding opportunities for green stormwater infrastructure. Some of the funding resources provided may be only loosely connected to GSI
Link to this table
| Program/funding source | Agency/organization/owner | Federal/state/local/other | Target benefit | Similar program/funding source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Water Fund | State of Minnesota | State | ||
| Clean Water Act - NPS Grant (Section 319) | EPA | Federal | Nonpoint source | |
| Clean Water State Revolving Fund | EPA | Federal/state | General water quality | |
| Drinking Water State Revolving Fund | EPA | Federal/state | Source water quality & quantity | USDA Rural Development Water & Waste Disposal |
| Great Lakes Restoration Initiative | EPA | Federal | Great Lakes focus (i.e., communities along Lake Superior) | |
| Brownfields Grant Program | EPA | Federal (with state and local collaboration) | Brownfields | |
| Superfund Redevelopment Program | EPA | Federal | Superfund sites - flood and erosion risk mitigation | |
| Five Star & Urban Waters Restoration | EPA | Federal | River, wetland, riparian, forest, coastal, and wildlife conservation | USDA National Urban & Community Forestry |
| Environmental Justice Small Grants | EPA | Federal | Water as pertains to public health - focus on NGOs, Tribal organizations | |
| Urban Waters Small Grants | EPA | Federal | WQ in urban communities | |
| Greening America’s Communities | EPA | Federal | All GSI related benefits | |
| Building Blocks Program | EPA | Federal | Pre-concept level planning discussion | |
| Planning Assistance to States | US Army Corps of Engineers | Federal | Development of conservation plans | |
| Weatherization & Intergovernmental Program | DOE | Federal | GSI focused on weather impacts (e.g., green roofs) | |
| Building Resilient Infrastructure & Communities | FEMA | Federal | Natural disaster risk mitigation (e.g., flooding) | NOAA Coastal Resilience Grants |
| Hazard Mitigation Grant Program | FEMA | Federal | Natural disaster risk mitigation (post-disaster relief) | HUD Community Development Block Grant; NOAA Coastal Resilience Grants |
| Flood Mitigation Assistance | FEMA | Federal | Flood mitigation | |
| Community Development Block Grant | HUD | Federal | GSI implementation in concert with affordable housing projects | |
| Sustainable Communities Regional Planning | HUD | Federal | Planning level involvement | |
| Community Development Block Grant | HUD | Federal | Post-disaster recovery | FEMA Hazard Mitigation Grant Program; NOAA Coastal Resilience Grants |
| Community-Based Restoration Program | NOAA | Federal | Aquatic habitat | |
| Coastal Resilience Grants | NOAA | Federal | Pre and Post disaster recovery for coastal communities (for MN this would be Lake Superior) | Program, HUD |
| National Urban & Community Forestry | USDA | Federal | Urban forestry | EPA Five Star & Urban Waters Restoration |
| Rural Development Water and Environment | USDA | Federal | Reliable water supply and disposal | EPA Drinking Water State Revolving Fund; USDA Rural Development Water & Waste Disposal |
| Rural Development Water & Waste Disposal | USDA | Federal | Reliable water supply and disposal | EPA Drinking Water State Revolving Fund; USDA Rural Development Water and Environment |
| BUILD Grant Program | DOT | Federal | Transportation projects featuring GSI | |
| Congestion Mitigation & Air Quality | FHWA | Federal | Bike & pedestrian trails that include GSI | |
| Minnesota’s Lake Superior Coastal Program | MN DNR | State | Lake Superior coastal resources | |
| Metropolitan Council funding | Metropolitan Council | Local | Connection of jobs, housing, and amenities through transit. Increase equitability | |
| Soil and Water Conservation Districts | Board of Water and Soil Resources (BWSR) | Local | Landowner conservation projects | |
| Climate resilience | MN DNR | State | Flood risk and stormwater quality | |
| Funding form | Watershed Districts/Watershed Management Organizations | Local | Improve water quality within the watershed | Capital Region Watershed District |
| Varies |
Companies looking to promote water sustainability (ex. General Mills, BestBuy, major tech companies, food & beverage companies) | Other | Offset company water consumption (conservation, replenish) | |
| Varies | Local private foundations, specifically those with a sustainability focus | Local | Support progression of sustainable practices |
How to include Green Stormwater Infrastructure into ordinances and policy
General overview

Ordinances and policies are effective tools to assist municipalities in implementing green stormwater infrastructure in a consistent and integrated way (EPA, 2021). Green infrastructure and stormwater ordinances are becoming widespread across the United States as communities and the public are realizing the environmental, social, and economic benefits of these ordinances. The Missouri Department of Natural Resources created a flow chart that shows the types of policies and ordinances that can help control stormwater runoff and promote green stormwater infrastructure (see adjacent figure).
Ordinances should clearly identify the objectives and performance goals. Some communities develop ordinances and engineering or design guidelines at the same time. This can help streamline implementation and provide practitioners with the necessary tools to follow the ordinance requirements. The objectives and performance goals of an ordinance can vary widely depending on what a community would like to achieve. Some examples include protection of existing trees, reduction of post-construction stormwater volume and peak flows, promotion of native vegetation, and reduction of impervious surfaces.
Some communities may provide alternatives to ordinances in order to promote green stormwater infrastructure, such as green stormwater infrastructure incentive programs. These typically consist of some kind of monetary rebate to install green stormwater infrastructure. Rebate or incentive programs can be specific and target specific geographic locations, types of buildings, or types of green stormwater infrastructure. Examples of other alternatives include zoning codes or building codes that require green stormwater infrastructure for new construction or renovations.
General process
Developing ordinances typically requires collaboration across multiple city departments. The request for an ordinance can be initiated by an entity who is responsible for green stormwater infrastructure and/or stormwater, or an entity who has authority over the land on which green stormwater infrastructure would be implemented.
Developing ordinances requires strong stakeholder support in order to be accepted as well as City Council support. Stakeholders can include individuals, trade organizations, or public interest groups. The stakeholder process can be time and resource intensive, but a successful stakeholder program can be helpful in successfully developing ordinances. The entity’s legal team should review any proposed ordinance to make sure the ordinance is aligned with local, state, and national laws. Ordinances may also need approval from municipal councils, boards, or the public. Developing ordinances can be done using in-house resources, although outside expertise can be brought in for technical, outreach, communications, or legal support.
Developing ordinances may take anywhere from several months to several years, depending on the intended reach of the ordinance and the support from the affected community. Common obstacles to implementing ordinances include stakeholder opposition, competing ordinances (e.g.: an ordinance on minimum sidewalk could compete with an ordinance for larger tree boxes), and lack of support from municipal leaders.
Unintentional barriers
Current codes and ordinances may create unintentional barriers to the implementation of GSI due to outdated regulations or unclear language that limit the application of key GSI runoff mitigation measures. Some of these barriers include:
- dimensional standards,
- requirement of sealcoating paved surfaces,
- landscaping buffers, and
- building codes requiring curbs and gutters.
Strategies for overcoming these code and ordinance related barriers include performing an audit of the codes and ordinances, amending codes and ordinances, and developing design guidance for GSI that are acceptable within the bounds of existing codes and ordinances. Resources in addressing code and ordinance barriers to GSI include the following.
- WI Sea Grant Tackling Barriers to Green Infrastructure: An Audit of Municipal Codes and Ordinances
- USEPA Overcoming Barriers to Green Infrastructure
- An Updated Code and Ordinance Worksheet for Improving Local Development Regulations - Center for Watershed Protection
Ordinance resources and guidance documents
Many resources and guidance documents exist for developing ordinances. A non-exhaustive list of these is provided in the table below.
Resources and guidance documents exist for developing green stormwater infrastructure ordinances
Link to this table
| Type | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| General | Georgetown Climate Center Ordinance Resources | [5] |
| Integrating GSI intro ordinances | [6] | |
| WeConservePA ordinance resources | [7] | |
| EPA GSI Policy Guides | [8] | |
| Municipal Online Stormwater Training Center (MOST) | [9] | |
| 3 Rivers Wet Weather | [10] | |
| Integrating Green Infrastructure Into Ordinances | [11] | |
| MIDS-related ordinances | Examples of communities who developed ordinances that use the MIDS performance goals. | [12] |
| Tree ordinances | Examples of tree ordinances from MPCA | [13] |
| Model Floodplain Ordinances | MN Model Floodplain Ordinances | [14] |
| Post Construction Runoff Control Ordinances | Examples provided by the Stormwater Center | [15] |
| Stream buffer ordinances | Examples provided by the Stormwater Center | [16] |
| Open space preservation ordinances | Examples provided by the Stormwater Center | [17] |
| Ordinance barriers | Tackling Barriers to Green Infrastructure: An Audit of Municipal Codes and Ordinances | [18] |
Examples of planning for GI and GSI
- Planning for green infrastructure and mapping synergies and trade-offs: A case study in the Yanshuei River Basin, Taiwan
- Lisbon: Masterplan Vale de Alcantara: A green corridor
- Planning a Green Infrastructure Network from Theory to Practice: The Case Study of Setúbal, Portugal
- Green Infrastructure Planning: Recent Advances and Applications
Resources
- Chapter 3 of the San Mateo Green Infrastructure Design Guide provides information for GSI design and planning
- Community-enabled Lifecycle Analysis of Stormwater Infrastructure Costs (CLASIC)
- Friends of the Greenbelt Foundation and Green Infrastructure Ontario Coalition’s A Green Infrastructure Guide for Small Cities, Towns and Rural Communities identifies specific planning zones and the appropriate GSI to use for each, and includes case studies for each planning zone
- Georgetown Climate Center’s Green Infrastructure Toolkit includes information on integrating GSI into existing infrastructure, funding GSI development, communicating the benefits of GSI, and equity and environmental justice surrounding GSI
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency Stormwater Financial Assistance
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency Water Quality Trading
- Minnesota Clean Water Fund
- New Jersey Green Infrastructure Planning provides a step-by-step guide through the planning process
- NOAA Guide to Assessing Green Infrastructure Costs and Benefits for Flood Reduction
- The National Academies Press Long-Term Performance and Life-Cycle Costs of Stormwater Best Management Practices, NCHRP Report 792
- The University of Minnesota toolkit provides information on investing in green stormwater infrastructure as a means of improving equity among communities
- US EPA Community Solutions for Voluntary Long-Term Stormwater Planning
- US EPA Green Infrastructure Funding Opportunities
- US EPA Integrated Planning for Municipal Stormwater and Wastewater
- US EPA Overcoming Barriers to Green Infrastructure
- USEPA Equitable Development and Environmental Justice
- USEPA National Stormwater Calculator
- USEPA Green Infrastructure Cost-Benefit Resources
- Wisconsin Sea Grant Tackling Barriers to Green Infrastructure: An Audit of Municipal Codes and Ordinances
References
- Conservation International, 2019. Practical Guide to Implementing Green-Gray Infrastructure
- CVC & TRCA, 2010. Credit Valley Conservation and Toronto and Region Conservation Authority. LID-SWM-Guide-v1.0_2010_1_no-appendices.pdf
- FEMA, 2021. Building Community Resilience with Nature-Based Solutions: A Guide for Local Communities
- Franke, 2016. So You Want to Build a Rain Garden?
- MNDNR, 2021. Climate trends
- MODNR, 2012. Integrating Green Infrastructure Into Ordinances
- New York Times, 2020. How Decades of Racist Housing Policy Left Neighborhoods Sweltering
- Prince George’s County Climate Action Commission, 2021. Climate Action Plan (Nov. 2021 revision)
- NOAA, 2015. A Guide to Assessing Green Infrastructure Costs and Benefits for Flood Reduction
- Project Drawdown, 2021. Food, Agriculture, and Land Use Solutions
- The Nature Conservancy / AECOM, 2021, Promoting Nature-Based Hazard Mitigation Through FEMA Mitigation Grants
- University of Minnesota, 2022. Sharing in the Benefits of a Greening City Toolkit
- USDA, Guidelines for Establishing Aquatic Plants in Constructed Wetlands
- USEPA, 2017. Healthy Benefits of Green Infrastructure in Communities
- USEPA, 2021a. Policy Guides
- USEPA, 2021b. Equitable Development and Environmental Justice
- USEPA, 2022a. Manage Flood Risk
- USEPA, 2022b. Green Infrastructure Cost-Benefit Resources
- WI Sea Grant: Tackling Barriers to Green Infrastructure: An Audit of Municipal Codes and Ordinances