Difference between revisions of "Calculating credits for permeable pavement"
m |
m |
||
| Line 245: | Line 245: | ||
<math> 2.72 (2.3446) (1) (0.3) = 1.91 </math> | <math> 2.72 (2.3446) (1) (0.3) = 1.91 </math> | ||
| − | If the depth below the underdrain was 0.5 feet instead of 1 foot, only half of the 1 inch performance goal is infiltrated, corresponding to an annual infiltration volume of 1. | + | If the depth below the underdrain was 0.5 feet instead of 1 foot, only half of the 1 inch performance goal is infiltrated, corresponding to an annual infiltration volume of 1.60 acre-feet. Note that the relationship between infiltration performance goal and annual volume infiltrated is not linear. The first step is to calculate the infiltration and filtered fractions of total volume captured by the BMP. The infiltrated fraction is 1.60/2.3446 or 0.68, leaving a filtered fraction of 0.32. |
Annual TSS removal, in pounds, is given by | Annual TSS removal, in pounds, is given by | ||
| Line 253: | Line 253: | ||
The first term in parenthesis corresponds with the infiltrated portion and equals about 236.3 pounds. The second term in parenthesis corresponds with the filtered portion, having a removal efficiency of 0.74 (74 percent), for a total removal of about 82.3 pounds. | The first term in parenthesis corresponds with the infiltrated portion and equals about 236.3 pounds. The second term in parenthesis corresponds with the filtered portion, having a removal efficiency of 0.74 (74 percent), for a total removal of about 82.3 pounds. | ||
| − | Annual TP removal is given by | + | Annual TP removal, in pounds, is given by |
| − | <math> (2.72 (2.3446) (0.68) (0.3)) + ((2.72 (2.3446) (0.32) (0.55) (0.82) (0.3)) = 1.58 | + | <math> (2.72 (2.3446) (0.68) (0.3)) + ((2.72 (2.3446) (0.32) (0.55) (0.82) (0.3)) = 1.58 </math> |
The first term in parenthesis corresponds with the infiltrated portion and equals about 1.30 pounds. The second term in parenthesis corresponds with the filtered portion, having a particulate P fraction of 0.55, and a removal efficiency of 0.82 (82 percent) for the particulate fraction, for a total removal of about 0.28 pounds. | The first term in parenthesis corresponds with the infiltrated portion and equals about 1.30 pounds. The second term in parenthesis corresponds with the filtered portion, having a particulate P fraction of 0.55, and a removal efficiency of 0.82 (82 percent) for the particulate fraction, for a total removal of about 0.28 pounds. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Methods for calculating credits== | ==Methods for calculating credits== | ||
Revision as of 15:55, 7 May 2015
This site is under construction. Anticipated completion date is June, 2015.
Credit refers to the quantity of stormwater or pollutant reduction achieved either by an individual BMP or cumulatively with multiple BMPs. Stormwater credits are a tool for local stormwater authorities who are interested in
- providing incentives to site developers to encourage the preservation of natural areas and the reduction of the volume of stormwater runoff being conveyed to a best management practice (BMP);
- complying with permit requirements, including antidegradation (see [1]; [2]);
- meeting the MIDS performance goal; or
- meeting or complying with water quality objectives, including Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) Wasteload Allocations (WLAs).
This page provides a discussion of how permeable pavement practices can achieve stormwater credits. Permeable pavement systems with and without underdrains are both discussed, with separate sections for each type of system as appropriate.
Contents
Overview
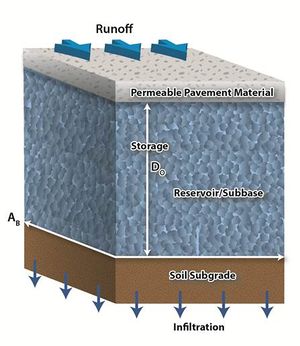
Permeable pavements are a stormwater quality practice that allows runoff to pass through surface voids into an underlying stone reservoir/subbase for temporary storage before being discharged to an underdrain and/or underlying soil via infiltration. The most commonly used types of permeable pavement are pervious concrete, porous asphalt, and permeable interlocking concrete pavers.
Pollutant removal mechanisms
Permeable pavement systems with no underdrains provide stormwater pollutant removal by reducing the volume of runoff from a site and the pollutant mass associated with that volume when infiltration is allowed (Water Environment Federation, 2012). In systems with underdrains most of the water is captured by the underdrain after passing through the subbase. If the underdrain is raised above the underlying soil subgrade, water stored in the reservoir/subbase below the underdrain will infiltrate into the underlying soil. If the underdrain is at the bottom of the reservoir/subbase, a small amount of infiltration may occur. Thus, pollutant removal in a permeable pavement system with an underdrain occurs through filtering of water captured by the underdrain and infiltration for water infiltrating into the underlying soil subgrade.
Location in the treatment train
Stormwater Treatment Trains are comprised of multiple Best Management Practices that work together to minimize the volume of stormwater runoff, remove pollutants, and reduce the rate of stormwater runoff being discharged to Minnesota wetlands, lakes and streams. Under the Treatment Train approach, stormwater management begins with simple methods that prevent pollution from accumulating on the land surface, followed by methods that minimize the volume of runoff generated, and finally by Best Management Practices (BMPs) that reduce the pollutant concentration and/or volume of stormwater runoff.
Permeable pavements are installed near the start of the treatment train as a method that directs the stormwater runoff to a subgrade storage area in order to minimize the volume and pollutant mass of stormwater runoff .
Methodology for calculating credits
This section describes the basic concepts and equations used to calculate credits for volume, Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and Total Phosphorus (TP). Specific methods for calculating credits are discussed later in this article. Permeable pavement is also effective at reducing concentrations of other pollutants including nitrogen, metals, bacteria, and hydrocarbons. This article does not provide information on calculating credits for pollutants other than TSS and TP, but references are provided that may be useful for calculating credits for other pollutants.
Assumptions and approach
In developing the credit calculations, it is assumed the permeable pavement practice is properly designed, constructed, and maintained in accordance with the Minnesota Stormwater Manual. If any of these assumptions is not valid, the BMP may not qualify for credits or credits should be reduced based on reduced ability of the BMP to achieve volume or pollutant reductions. For guidance on design, construction, and maintenance, see the appropriate article within the permeable pavement section of the Manual.
In the following discussion, the water quality volume (VWQ) is assumed to be delivered instantaneously to the BMP. The VWQ is stored within the reservoir/subbase below the bottom of the pavement and above the soil subgrade. The VWQ can vary depending on the stormwater management objective(s). For construction stormwater, the water quality volume is 1 inch off new impervious surface. For MIDS, the VWQ is 1.1 inches. In reality, some water will infiltrate through the bottom and sidewalls of the BMP as a rain event proceeds. The instantaneous method therefore may underestimate actual volume and pollutant losses.
The approach in the following sections is based on the following general design considerations:
- Credit calculations presented in this article are for both event and annual volume and pollutant load removals.
- Stormwater volume credit for permeable pavements equates to the volume of runoff that is fully contained within the stone reservoir/subbase that will ultimately be infiltrated into the soil subgrade.
- TSS and TP credits for permeable pavements are achieved for the volume of runoff that is filtered and captured by an underdrain and the volume of water that is ultimately infiltrated.
Volume credit calculations - no underdrain
Volume credits are calculated based on the capacity of the BMP and its ability to permanently remove stormwater runoff via infiltration into the underlying soil from the existing stormwater collection system. These credits are assumed to be instantaneous values entirely based on the capacity of the BMP to capture, store, and transmit water in any storm event.
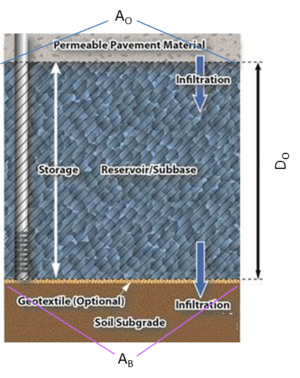
Volume credits for a permeable pavement system are based on the porosity of the subbase and system dimensions, specifically the depth of the reservoir/ subbase, the area of permeable pavement, and the bottom surface area. The volume credit (Vinfb) for infiltration through the bottom of the BMP into the underlying soil, in cubic feet, is given by
\( V_{inf_b} = D_o\ n\ (A_O + A_B)\ / 2 \)
where
- AO = Overflow surface area of the permeable pavement system, in square feet;
- DO = Depth of the reservoir/subbase layer (engineered media), equal to the distance from the bottom of the permeable pavement material to the underlying soil subgrade, in feet; and
- n = Porosity of the reservoir/subbase, in cubic feet per cubic foot.
Note that that entire porosity of the subbase layer is used to calculate the volume credit. This slightly overestimates the actual volume infiltrated since some water is held by the media after the runoff infiltrates. The water content after gravity drainage, called field capacity, is less than 5 percent of total porosity for a permeable pavement system.
The annual volume captured and infiltrated by the BMP can be determined with appropriate modeling tools, including the MIDS calculator. Example values are shown below for a scenario using the MIDS calculator. For example, a permeable pavement system designed to capture 1 inch of runoff from impervious surfaces will capture 89 percent of annual runoff from a site with B (SM) soils.
Annual volume, expressed as a percent of annual runoff, treated by a BMP as a function of soil and Water Quality Volume. See footnote1 for how these were determined.
Link to this table
| Soil | Water quality volume (VWQ) (inches) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.50 | |
| A (GW) | 84 | 92 | 96 | 98 | 99 |
| A (SP) | 75 | 86 | 92 | 95 | 97 |
| B (SM) | 68 | 81 | 89 | 93 | 95 |
| B (MH) | 65 | 78 | 86 | 91 | 94 |
| C | 63 | 76 | 85 | 90 | 93 |
1Values were determined using the MIDS calculator. BMPs were sized to exactly meet the water quality volume for a 2 acre site with 1 acre of impervious, 1 acre of forested land, and annual rainfall of 31.9 inches.
Volume calculations - underdrain
In a permeable pavement system with an underdrain, the position of the underdrain determines the amount of water that will infiltrate into the underlying soil. If the underdrain is raised above the bottom of the BMP (i.e. above the interface between the reservoir/subbase and underlying soil subgrade), water stored below the underdrain will infiltrate. The infiltrating volume (Vinfb), in cubic feet, is given by
\( V_{inf_b} = D_o\ n\ (A_U + A_B)\ / 2 \)
where
- DU is the area at the bottom of the underdrain, in square feet.
If the underdrain is at the bottom of the permeable pavement system (i.e. at the reservoir-subgrade interface), some infiltration will occur. This is a function of the infiltration rate of the underlying soil and the time it takes for the water quality volume (VWQ) to drain. Most of the water will be captured by the underdrain. For example, if the VWQ drains in 48 hours and the underlying soil is a D soil with an infiltration rate of 0.06 inches per hour, about 12 percent of the VWQ will infiltrate into the underlying soil. Note the MIDS calculator does not provide a volume credit for a permeable pavement system with an underdrain at the bottom.
Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
The TSS credits available for installation of permeable pavement depend on the design of the storage volume below the pavement and whether the runoff is filtered (through an underdrain), infiltrated, or both. Designs that filter runoff with an underdrain at the bottom of the storage layer are less effective in removing pollutants than infiltration designs. Runoff is filtered while flowing through the permeable pavement and the storage layer and out the underdrain. TSS removal credit of 100 percent is assumed for the infiltrated water. The recommended removal rate for filtered water is 74 percent, based on review of literature.
Removal of TSS by permeable pavement (MTSS), in pounds per event or pounds per year, is given by
\( M_{TSS} = M_{TSS_I}\ + M_{TSS_F} \)
where
- MTSSI = mass of TSS removed by infiltration (pounds per event or pounds per year); and
- MTSSF = mass of TSS removed by filtration (pounds per event or pounds per year).
The annual TSS credit (MTSSI) for infiltrated runoff is given by
\( M_{TSS_I} = 2.72\ V_{_{Annual}}\ F_I\ EMC_{_{TSS}} \)
where
- VAnnual is the annual volume treated by the BMP, in acre-feet;
- FI is the fraction of the total annual volume treated by the BMP that is infiltrated;
- EMCTSS = event mean concentration of TSS in the runoff, in mg/L; and
- Factor of 2.72 used for conversion to pounds.
In a permeable pavement system with an underdrain, some of the water captured by the BMP will enter the underdrain while some will infiltrate below the underdrain. The amount infiltrating depends on several factors, including whether the underdrain is raised above the soil subgrade, the infiltration rate of the underlying soil, and size and spacing of the underdrains. Pollutants in water that enters the underdrain are filtered. The Annual TSS credit for filtered runoff (MTSSF) is given by
\( M_{TSS_F} = 2.72\ R_{_{TSS}}\ V_{_{Annual}}\ (F_F)\ EMC_{_{TSS}} \)
where
- FF is the fraction of the total volume treated by the BMP that is filtered; and
- RTSS is the pollutant removal fraction for filtered water. A value of 0.74 is recommended.
If the permeable pavement is not the upstream most BMP in the treatment train, EMCTSS should be dependent on the MTSS effluent (mg/L) from the next upstream tributary BMP.
The annual volume treated by the BMP can be determined with appropriate modeling tools, including the MIDS calculator. Example values are shown below for a scenario using the MIDS calculator. For example, a permeable pavement system designed to capture 1 inch of runoff from impervious surfaces will capture 89 percent of annual runoff from a site with B (SM) soils. If an underdrain is in the system, this volume will have to be divided into the portion that infiltrates and the portion that is captured by the underdrain. The MIDS calculator can be used to determine these values.
Annual volume, expressed as a percent of annual runoff, treated by a BMP as a function of soil and Water Quality Volume. See footnote1 for how these were determined.
Link to this table
| Soil | Water quality volume (VWQ) (inches) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.50 | |
| A (GW) | 84 | 92 | 96 | 98 | 99 |
| A (SP) | 75 | 86 | 92 | 95 | 97 |
| B (SM) | 68 | 81 | 89 | 93 | 95 |
| B (MH) | 65 | 78 | 86 | 91 | 94 |
| C | 63 | 76 | 85 | 90 | 93 |
1Values were determined using the MIDS calculator. BMPs were sized to exactly meet the water quality volume for a 2 acre site with 1 acre of impervious, 1 acre of forested land, and annual rainfall of 31.9 inches.
The event (storm) event based TSS credit (MTSSI) for infiltrated runoff is given by
\( M_{TSS_I} = 2.72\ V_I\ EMC_{_{TSS}}\ / 43,560 \)
where
- VI is the event-based volume infiltrated by the BMP, in cubic feet, and
- a factor of 43,560 is used for conversion of volume from cubic feet to acre-ft.
The storm event based TSS credit (MTSS-F) for filtered runoff is given by
\( M_{TSS_F} = R_{_{TSS}}\ 2.72\ V_F\ EMC_{_{TSS}}\ / 43560 \)
where
- VF is the event-based volume filtrated by the BMP, in cubic feet.
Total phosphorus (TP) credit calculations
Similar to TSS, TP reduction credits correspond directly with volume reduction through infiltration and filtration of captured stormwater. The water quality credits available for a permeable pavement system depend on the design of the storage volume below the pavement and whether or not the runoff is filtered (through underdrain) or infiltrated. TP credit is divided into particulate phosphorus (PP) and dissolved phosphorus (DP) removal, respectively making up 55 percent and 45 percent of the total TP credit. Because the volume of infiltrated water (calculated above) is completely removed from the existing system, 100 percent TP credit is assumed for all infiltrated stormwater. Filtered stormwater only receives credit for PP credit, and no credit is given for DP. This approach is consistent with the approach used in the MIDS calculator.
Removal of TP by permeable pavement is given by
\( M_{TP} = M_{TP_I}\ + M_{TP_F}\)
where
- MTP is the annual or event TP removal (lb/yr or lb/event);
- MTPI is the annual or event TP removal from infiltrated runoff (lb/yr or lb/event); and
- MTPF is the annual or event TP removal from filtered water (lb/year or lb/event).
The total annual TP removal for infiltrated runoff is given by
\( M_{TP_I} = 2.72\ V_{annual}\ F_I\ EMC_{_{TP}} \)
where
- Vannual is the annual volume treated by the BMP, in acre-feet,
- FI is the fraction of the total annual volume treated by the BMP that is infiltrated,
- EMCTP = event mean concentration of TP in the runoff, in mg/L, and
- a factor of 2.72 used for conversion to pounds.
In a permeable pavement system with an underdrain, some of the water captured by the BMP will enter the underdrain while some will infiltrate below the underdrain. The amount infiltrating depends on several factors, including whether the underdrain is raised above the soil subgrade, the infiltration rate of the underlying soil, and size and spacing of the underdrains. Pollutants in water that enters the underdrain are filtered. The Annual TP credit for filtered runoff (MTPF) is given by
\( M_{TP_F} = 2.72\ R_{_{TP}}\ V_{_{Annual}}\ F_F\ EMC_{_{TP}} \)
where
- FF is the fraction of the total volume treated by the BMP that is filtered; and
- RTP is the pollutant removal fraction for filtered water.
The pollutant removal fraction applies only to particulate phosphorus (PP), which is assumed to be 55 percent of total phosphorus (TP). The recommended removal efficiency for PP is 82 percent. Thus, the recommended value for RTP is 0.55 * 0.82 or 0.45.
If the permeable pavement is not the upstream most BMP in the treatment train, EMCTP should be dependent on the MTP effluent (mg/L) from the next upstream tributary BMP.
The annual volume treated by the BMP can be determined with appropriate modeling tools, including the MIDS calculator. Example values are shown below for a scenario using the MIDS calculator. For example, a permeable pavement system designed to capture 1 inch of runoff from impervious surfaces will capture 89 percent of annual runoff from a site with B (SM) soils. If an underdrain is in the system, this volume will have to be divided into the portion that infiltrates and the portion that is captured by the underdrain. The MIDS calculator can be used to determine these values.
Annual volume, expressed as a percent of annual runoff, treated by a BMP as a function of soil and Water Quality Volume. See footnote1 for how these were determined.
Link to this table
| Soil | Water quality volume (VWQ) (inches) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.50 | |
| A (GW) | 84 | 92 | 96 | 98 | 99 |
| A (SP) | 75 | 86 | 92 | 95 | 97 |
| B (SM) | 68 | 81 | 89 | 93 | 95 |
| B (MH) | 65 | 78 | 86 | 91 | 94 |
| C | 63 | 76 | 85 | 90 | 93 |
1Values were determined using the MIDS calculator. BMPs were sized to exactly meet the water quality volume for a 2 acre site with 1 acre of impervious, 1 acre of forested land, and annual rainfall of 31.9 inches.
The event (storm) event based TP credit (MTPI) for infiltrated runoff is given by
\( M_{TP_I} = 2.72\ V_I\ EMC_{_{TP}}\ / 43,560 \)
where
- VI is the event-based volume infiltrated by the BMP, in cubic feet; and
- a factor of 43,560 is used for conversion of volume from cubic feet to acre-ft.
The storm event based TP credit (MTP-F) for filtered runoff is given by
\( M_{TP - F} = R_{_{TP}}\ 2.72\ V_F\ EMC_{_{TP}}\ / 43560 \)
where
- VF is the event-based volume filtered by the BMP, in cubic feet
Example calculations for TSS and TP
NOTE: The MIDS calculator was used for the following examples. The performance goal was changed from the MIDS default of 1.1 inches to 1 inch.
Assume a permeable pavement system is designed to capture and treat 1 inch of runoff from a 1 acre impervious area. Note that in these calculations, the permeable pavement is considered part of the impermeable surface.
For this example, assume a 9000 square foot surface area at the top of the reservoir/subbase, a 9000 square foot area at the reservoir/soil subgrade, an underlying B soil with an infiltration rate of 0.45 inches per hour, a porosity of 0.4 cubic feet per cubic foot, a depth below the underdrain of 1 foot, a TSS EMC of 54.5 milligrams per liter, and a TP EMC of 0.3 milligrams per liter. With this depth below the underdrain, all the water can be infiltrated (3600 cubic feet per event; 2.3446 acre-feet per year). Annual TSS removal, in pounds, is given by
\( 2.72 (2.3446) (1) (54.5) = 347 \)
Annual TP removal is given by
\( 2.72 (2.3446) (1) (0.3) = 1.91 \)
If the depth below the underdrain was 0.5 feet instead of 1 foot, only half of the 1 inch performance goal is infiltrated, corresponding to an annual infiltration volume of 1.60 acre-feet. Note that the relationship between infiltration performance goal and annual volume infiltrated is not linear. The first step is to calculate the infiltration and filtered fractions of total volume captured by the BMP. The infiltrated fraction is 1.60/2.3446 or 0.68, leaving a filtered fraction of 0.32.
Annual TSS removal, in pounds, is given by
\( (2.72 (2.3446) (0.68) (54.5)) + ((2.72 (2.3446) (0.32) (0.74) (54.5)) = 319 \)
The first term in parenthesis corresponds with the infiltrated portion and equals about 236.3 pounds. The second term in parenthesis corresponds with the filtered portion, having a removal efficiency of 0.74 (74 percent), for a total removal of about 82.3 pounds.
Annual TP removal, in pounds, is given by
\( (2.72 (2.3446) (0.68) (0.3)) + ((2.72 (2.3446) (0.32) (0.55) (0.82) (0.3)) = 1.58 \)
The first term in parenthesis corresponds with the infiltrated portion and equals about 1.30 pounds. The second term in parenthesis corresponds with the filtered portion, having a particulate P fraction of 0.55, and a removal efficiency of 0.82 (82 percent) for the particulate fraction, for a total removal of about 0.28 pounds.
Methods for calculating credits
This section provides specific information on generating and calculating credits from permeable pavement for volume, Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and Total Phosphorus (TP). Stormwater runoff volume and pollution reductions ("credits”) may be calculated using one of the following methods:
- Quantifying volume and pollution reductions based on accepted hydrologic models
- The Simple Method and MPCA Estimator
- MIDS Calculator
- Quantifying volume and pollution reductions based on values reported in literature
- Quantifying volume and pollution reductions based on field monitoring
Credits based on models
Users may opt to use a water quality model or calculator to compute volume, TSS and/or TP pollutant removal for the purpose of determining credits. The available models described in the following sections are commonly used by water resource professionals, but are not explicitly endorsed or required by the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. Use of models or calculators for the purpose of computing pollutant removal credits should be supported by detailed documentation, including:
- Model name and version
- Date of analysis
- Person or organization conducting analysis
- Detailed summary of input data
- Calibration and verification information
- Detailed summary of output data
The following table lists water quantity and water quality models that are commonly used by water resource professionals to predict the hydrologic, hydraulic, and/or pollutant removal capabilities of a single or multiple stormwater BMPs. The table can be used to guide a user in selecting the most appropriate model for computing volume, TSS, and/or TP removal by the BMP.
Comparison of stormwater models and calculators. Additional information and descriptions for some of the models listed in this table can be found at this link. Note that the Construction Stormwater General Permit requires the water quality volume to be calculated as an instantaneous volume, meaning several of these models cannot be used to determine compliance with the permit.
Link to this table
Access this table as a Microsoft Word document: File:Stormwater Model and Calculator Comparisons table.docx.
| Model name | BMP Category | Assess TP removal? | Assess TSS removal? | Assess volume reduction? | Comments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constructed basin BMPs | Filter BMPs | Infiltrator BMPs | Swale or strip BMPs | Reuse | Manu- factured devices |
|||||
| Center for Neighborhood Technology Green Values National Stormwater Management Calculator | X | X | X | X | No | No | Yes | Does not compute volume reduction for some BMPs, including cisterns and tree trenches. | ||
| CivilStorm | Yes | Yes | Yes | CivilStorm has an engineering library with many different types of BMPs to choose from. This list changes as new information becomes available. | ||||||
| EPA National Stormwater Calculator | X | X | X | No | No | Yes | Primary purpose is to assess reductions in stormwater volume. | |||
| EPA SWMM | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | User defines parameter that can be used to simulate generalized constituents. | |||
| HydroCAD | X | X | X | No | No | Yes | Will assess hydraulics, volumes, and pollutant loading, but not pollutant reduction. | |||
| infoSWMM | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | User defines parameter that can be used to simulate generalized constituents. | |||
| infoWorks ICM | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| i-Tree-Hydro | X | No | No | Yes | Includes simple calculator for rain gardens. | |||||
| i-Tree-Streets | No | No | Yes | Computes volume reduction for trees, only. | ||||||
| LSPC | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | Though developed for HSPF, the USEPA BMP Web Toolkit can be used with LSPC to model structural BMPs such as detention basins, or infiltration BMPs that represent source control facilities, which capture runoff from small impervious areas (e.g., parking lots or rooftops). | |||
| MapShed | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | Region-specific input data not available for Minnesota but user can create this data for any region. | ||
| MCWD/MWMO Stormwater Reuse Calculator | X | Yes | No | Yes | Computes storage volume for stormwater reuse systems | |||||
| Metropolitan Council Stormwater Reuse Guide Excel Spreadsheet | X | No | No | Yes | Computes storage volume for stormwater reuse systems. Uses 30-year precipitation data specific to Twin Cites region of Minnesota. | |||||
| MIDS Calculator | X | X | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | Includes user-defined feature that can be used for manufactured devices and other BMPs. |
| MIKE URBAN (SWMM or MOUSE) | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | User defines parameter that can be used to simulate generalized constituents. | |||
| P8 | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| PCSWMM | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | User defines parameter that can be used to simulate generalized constituents. | |||
| PLOAD | X | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | No | User-defined practices with user-specified removal percentages. | |
| PondNet | X | Yes | No | Yes | Flow and phosphorus routing in pond networks. | |||||
| PondPack | X | [ | No | No | Yes | PondPack can calculate first-flush volume, but does not model pollutants. It can be used to calculate pond infiltration. | ||||
| RECARGA | X | No | No | Yes | ||||||
| SHSAM | X | No | Yes | No | Several flow-through structures including standard sumps, and proprietary systems such as CDS, Stormceptors, and Vortechs systems | |||||
| SUSTAIN | X | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | Categorizes BMPs into Point BMPs, Linear BMPs, and Area BMPs | |
| SWAT | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | Model offers many agricultural BMPs and practices, but limited urban BMPs at this time. | |||
| Virginia Runoff Reduction Method | X | X | X | X | X | X | Yes | No | Yes | Users input Event Mean Concentration (EMC) pollutant removal percentages for manufactured devices. |
| WARMF | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | Includes agriculture BMP assessment tools. Compatible with USEPA Basins | ||||
| WinHSPF | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | USEPA BMP Web Toolkit available to assist with implementing structural BMPs such as detention basins, or infiltration BMPs that represent source control facilities, which capture runoff from small impervious areas (e.g., parking lots or rooftops). | |||
| WinSLAMM | X | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| XPSWMM | X | X | X | Yes | Yes | Yes | User defines parameter that can be used to simulate generalized constituents. | |||
The Simple Method and MPCA Estimator
The Simple Method is a technique used for estimating storm pollutant export delivered from urban development sites. Pollutant loads are estimated as the product of mean pollutant concentrations and runoff depths over specified periods of time (usually annual or seasonal). The method was developed to provide an easy yet reasonably accurate means of predicting the change in pollutant loadings in response to development. Ohrel (2000) states: "In general, the Simple Method is most appropriate for small watersheds (<640 acres) and when quick and reasonable stormwater pollutant load estimates are required". Rainfall data, land use (runoff coefficients), land area, and pollutant concentration are needed to use the Simple Method. For more information on the Simple Method, see The Simple method to Calculate Urban Stormwater Loads or The Simple Method for estimating phosphorus export.
Some simple stormwater calculators utilize the Simple Method (STEPL, Watershed Treatment Model). The MPCA developed a simple calculator for estimating load reductions for TSS, total phosphorus, and bacteria. Called the MPCA Estimator, this tool was developed specifically for complying with the MS4 General Permit TMDL annual reporting requirement. The MPCA Estimator provides default values for pollutant concentration, runoff coefficients for different land uses, and precipitation, although the user can modify these and is encouraged to do so when local data exist. The user is required to enter area for different land uses and area treated by BMPs within each of the land uses. BMPs include infiltrators (e.g. bioinfiltration, infiltration basin, tree trench, permeable pavement, etc.), filters (biofiltration, sand filter, green roof), constructed ponds and wetlands, and swales/filters. The MPCA Estimator includes standard removal efficiencies for these BMPs, but the user can modify those values if better data are available. Output from the calculator is given as a load reduction (percent, mass, or number of bacteria) from the original estimated load.
Because the MPCA Estimator does not consider BMPs in series, makes simplifying assumptions about runoff and pollutant removal processes, and uses generalized default information, it should only be used for estimating pollutant reductions from an estimated load. It is not intended as a decision-making tool.
Download MPCA Estimator here: File:MPCA Estimator.xlsx
A quick guide for the estimator is available Quick Guide: MPCA Estimator tab.
MIDS Calculator

The Minimal Impact Design Standards (MIDS) best management practice (BMP) calculator is a tool used to determine stormwater runoff volume and pollutant reduction capabilities of various low impact development (LID) BMPs. The MIDS calculator estimates the stormwater runoff volume reductions for various BMPs and annual pollutant load reductions for total phosphorus (including a breakdown between particulate and dissolved phosphorus) and total suspended solids (TSS). The calculator was intended for use on individual development sites, though capable modelers could modify its use for larger applications.
The MIDS calculator is designed in Microsoft Excel with a graphical user interface (GUI), packaged as a windows application, used to organize input parameters. The Excel spreadsheet conducts the calculations and stores parameters, while the GUI provides a platform that allows the user to enter data and presents results in a user-friendly manner.
Detailed guidance has been developed for all BMPs in the calculator, including permeable pavement. An overview of individual input parameters and workflows is presented in the MIDS Calculator User Documentation.
Credits based on reported literature values
A simplified approach to computing a credit would be to apply a reduction value found in literature to the pollutant mass load or concentration (EMC) of the biofiltration device. Concentration reductions resulting from treatment can be converted to mass reductions if the volume of stormwater treated is known.
Designers may use the pollutant reduction values reported in this manual or may research values from other databases and published literature. Designers who opt for this approach should
- select the median value from pollutant reduction databases that report a range of reductions, such as from the International BMP Database;
- select a pollutant removal reduction from literature that studied a permeable pavement system with site characteristics and climate similar to the device being considered for credits;
- review the article to determine that the design principles of the studied permeable pavement system are close to the design recommendations for Minnesota, as described in this manual and/or by a local permitting agency; and
- give preference to literature that has been published in a peer-reviewed publication.
The following references summarize pollutant reduction values from multiple studies or sources that could be used to determine credits. Users should note that there is a wide range of monitored pollutant removal effectiveness in the literature. Before selecting a literature value, users should compare the characteristics of the monitored site in the literature against the characteristics of the proposed permeable pavement system, considering such conditions as watershed characteristics, BMP sizing, soil infiltration rates, and climate factors.
- BMP Performance Analysis. Prepared for US EPA Region 1, Boston MA.
- Appendix B provides pollutant removal performance curves
- Provides values for TP, TSS, and Zn.
- Pollutant removal broken down according to land use.
- Applicable to Infiltration Trench, Infiltration Basin, Bioretention, Grass Swale, Wet Pond, and Porous Pavement.
- Brown, Chris; Angus Chu; Bert van Duin; Caterina Valeo. 2009. Characteristics of Sediment Removal in Two Types of Permeable Pavement. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. Volume 44, No. 1, 59-70.
- The Illinois Green Infrastructure Study
- Figure ES-1 summarizes BMP effectiveness
- Provides values for TN, TSS, peak flows / runoff volumes
- Applicable to Permeable Pavements, Constructed Wetlands, Infiltration, Detention, Filtration, and Green Roofs
- International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary Statistical Addendum: TSS, Bacteria, Nutrients, and Metals
- Provides values for TSS removal
- Compilation of BMP performance studies published through 2011.
- Provides values for TSS, Bacteria, Nutrients, and Metals
- Applicable to grass strips, bioretention, bioswales, detention basins, green roofs, manufactured devices, media filters, porous pavements, wetland basins, and wetland channels.
- New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services. 2008. New Hampshire Stormwater Manual. Volume 2 Appendix B.
- Provides values for volume, TSS, TN, and TP removal
- In addition to permeable pavement, includes data for stormwater ponds, stormwater wetlands, infiltration practices, filtering practices, treatment swales, vegetated buffers, and pre-treatment practices
- New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. 2004. New Jersey Stormwater BMP Manual. Standards for Pervious Paving Systems. Chapter 9.7.
- Provides values for TSS removal
- North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources. Water Quality Division. 2012. Stormwater BMP Manual & BMP Forms. Chapter 18. Permeable Pavement.
- Provides values for TSS, TN, and TP removal based on calculations of impervious surface converted to permeable pavement
- Tennis, Paul D.; Michael L. Leming; David J. Akers. 2004. Pervious Concrete Pavements. EB302.02, Portland Cement Association and National Ready Mixed Concrete Association.
- Provides values for TSS, TN, and TP removal
- Tota-Maharaj, K. and Scholz, M. 2010. Efficiency of permeable pavement systems for the removal of urban runoff pollutants under varying environmental conditions. Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy, 29: 358–369. doi: 10.1002/ep.10418
- Provides removal efficiencies for total coliforms, Escherichia coli, and fecal Streptococci, as well as the key nutrients ammonia-nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, and ortho-phosphate phosphorus, and physical variables such as suspended solids and turbidity
- USEPA. Stormwater Menu of BMPs. Permeable Pavements. 2009.
- See Table 2 for list of monitored pollutant removal for permeable pavement
- Provides values for TSS, Metals, and Nutrients
Credits based on field monitoring
Field monitoring may be used to calculate stormwater credits in lieu of desktop calculations or models/calculators as described. Careful planning is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED before commencing a program to monitor the performance of a BMP. The general steps involved in planning and implementing BMP monitoring include the following.
- Establish the objectives and goals of the monitoring.
- Which pollutants will be measured?
- Will the monitoring study the performance of a single BMP or multiple BMPs?
- Are there any variables that will affect the BMP performance? Variables could include design approaches, maintenance activities, rainfall events, rainfall intensity, etc.
- Will the results be compared to other BMP performance studies?
- What should be the duration of the monitoring period? Is there a need to look at the annual performance vs the performance during a single rain event? Is there a need to assess the seasonal variation of BMP performance?
- Plan the field activities. Field considerations include:
- Equipment selection and placement
- Sampling protocols including selection, storage, delivery to the laboratory
- Laboratory services
- Health and Safety plans for field personnel
- Record keeping protocols and forms
- Quality control and quality assurance protocols
- Execute the field monitoring
- Analyze the results
The following guidance manuals have been developed to assist BMP owners and operators on how to plan and implement BMP performance monitoring.
Geosyntec Consultants and Wright Water Engineers prepared this guide in 2009 with support from the USEPA, Water Environment Research Foundation, Federal Highway Administration, and the Environment and Water Resource Institute of the American Society of Civil Engineers. This guide was developed to improve and standardize the protocols for all BMP monitoring and to provide additional guidance for Low Impact Development (LID) BMP monitoring. Highlighted chapters in this manual include:
- Chapter 2: Designing the Program
- Chapters 3 & 4: Methods and Equipment
- Chapters 5 & 6: Implementation, Data Management, Evaluation and Reporting
- Chapter 7: BMP Performance Analysis
- Chapters 8, 9, & 10: LID Monitoring
AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials) and the FHWA (Federal Highway Administration) sponsored this 2006 research report, which was authored by Oregon State University, Geosyntec Consultants, the University of Florida, and the Low Impact Development Center. The primary purpose of this report is to advise on the selection and design of BMPs that are best suited for highway runoff. The document includes the following chapters on performance monitoring that may be a useful reference for BMP performance monitoring, especially for the performance assessment of a highway BMP:
- Chapter 4: Stormwater Characterization
- 4.2: General Characteristics and Pollutant Sources
- 4.3: Sources of Stormwater Quality data
- Chapter 8: Performance Evaluation
- 8.1: Methodology Options
- 8.5: Evaluation of Quality Performance for Individual BMPs
- 8.6: Overall Hydrologic and Water Quality Performance Evaluation
- Chapter 10: Hydrologic Evaluation
- 10.5: Performance Verification and Design Optimization
In 2014 the Water Environment Federation released this White Paper that investigates the feasibility of a national program for the testing of stormwater products and practices. The information contained in this White Paper would be of use to those considering the monitoring of a manufactured BMP. The report does not include any specific guidance on the monitoring of a BMP, but it does include a summary of the existing technical evaluation programs that could be consulted for testing results for specific products (see Table 1 on page 8).
The most current version of this manual was released by the State of California, Department of Transportation in November 2013. As with the other monitoring manuals described, this manual does include guidance on planning a stormwater monitoring program. However, this manual is among the most thorough for field activities. Relevant chapters include:
- Chapter 4: Monitoring Methods and Equipment
- Chapter 5: Analytical Methods and Laboratory Selection
- Chapter 6: Monitoring Site Selection
- Chapter 8: Equipment Installation and Maintenance
- Chapter 10: Pre-Storm Preparation
- Chapter 11: Sample Collection and Handling
- Chapter 12: Quality Assurance / Quality Control
- Chapter 13: Laboratory Reports and Data Review
- Chapter 15: Gross Solids Monitoring
This online manual was developed in 2010 by Andrew Erickson, Peter Weiss, and John Gulliver from the University of Minnesota and St. Anthony Falls Hydraulic Laboratory with funding provided by the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. The manual advises on a four-level process to assess the performance of a Best Management Practice, involving:
- Level 1: Visual Inspection
- Level 2: Capacity Testing
- Level 3: Synthetic Runoff Testing
- Level 4: Monitoring
- Level 1 activities do not produce numerical performance data that could be used to obtain a stormwater management credit. BMP owners and operators who are interested in using data obtained from Levels 2 and 3 should consult with the MPCA or other regulatory agency to determine if the results are appropriate for credit calculations. Level 4, Monitoring, is the method most frequently used for assessment of the performance of a BMP.
Use these links to obtain detailed information on the following topics related to BMP performance monitoring:
- Water Budget Measurement
- [Sampling Methods http://stormwaterbook.safl.umn.edu/content/sampling-methods]
- [Analysis of Water and Soils http://stormwaterbook.safl.umn.edu/content/analysis-water-and-soils]
- [Data Analysis for Monitoring http://stormwaterbook.safl.umn.edu/content/monitoring-data-analysis]
Other pollutants
Permeable pavements provide removal of sediment (TSS), nutrients (phosphorus and nitrogen), and metals through filtration, infiltration, and soil adsorption. Temperature control occurs in the stone reservoir/subbase and soil subgrade. Phosphorus, metals, and hydrocarbons are adsorbed onto soils within the subgrade. In addition, nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen may be biologically degraded.
According to the International BMP Database, studies have shown bioretention is effective at reducing concentration of pollutants including solids, bacteria, metals, and nutrients. A compilation of the pollutant removal capabilities from a review of literature of permeable pavement studies are summarized in the table below.
Relative pollutant reduction from permeable pavement systems for metals, nitrogen, bacteria, and organics.
Link to this table
| Pollutant | Constituent | Treatment capabilities1 |
|---|---|---|
| Metals2 | Cadmium, Chromium, Copper, Zinc, Lead, Nickel | Medium/High |
| Nitrogen | Total nitrogen, Total Kjeldahl nitrogen | Medium/High |
| Bacteria | Fecal coliform, e. coli | Insufficient data |
| Organics | Medium |
1 Low: < 30%; Medium: 30 to 65%; High: >65%
2 Results are for total metals only
References
- Brown, Chris; Angus Chu; Bert van Duin; Caterina Valeo. 2009. Characteristics of Sediment Removal in Two Types of Permeable Pavement. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. Volume 44, No. 1, 59-70.
- Geosyntec and Wright Water Engineers. 2012. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary Statistical Addendum: TSS, Bacteria, Nutrients, and Metals. Prepared under Support from WERF, FHWA, EWRI/ASCE and EPA. July 2012.
- New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services. 2008. New Hampshire Stormwater Manual. Volume 2 Appendix B.
- New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. 2004. New Jersey Stormwater BMP Manual. Standards for Pervious Paving Systems. Chapter 9.7.
- North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources. Water Quality Division. 2012. Stormwater BMP Manual & BMP Forms. Chapter 18. Permeable Pavement.
- Tennis, Paul D.; Michael L. Leming; David J. Akers. 2004. Pervious Concrete Pavements. EB302.02, Portland Cement Association and National Ready Mixed Concrete Association.
- Tota-Maharaj, K. and Scholz, M. 2010. Efficiency of permeable pavement systems for the removal of urban runoff pollutants under varying environmental conditions. Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy, 29: 358–369. doi: 10.1002/ep.10418
- USEPA. Stormwater Menu of BMPs. Permeable Pavements. 2009.
Related articles
- Permeable pavement
- Overview for permeable pavement
- Types of permeable pavement
- Design criteria for permeable pavement
- Construction specifications for permeable pavement
- Assessing the performance of permeable pavement
- Operation and maintenance of permeable pavement
- Calculating credits for permeable pavement
- Additional considerations for permeable pavement
- References for permeable pavement
- Fact sheets for permeable pavement
- Calculating credits
- Calculating credits for bioretention
- Calculating credits for infiltration basin
- Calculating credits for permeable pavement
- Calculating credits for green roofs
- Calculating credits for sand filter
- Calculating credits for stormwater ponds
- Calculating credits for stormwater wetlands
- Calculating credits for iron enhanced sand filter
- Calculating credits for swale
- Calculating credits for tree trenches and tree boxes