Difference between revisions of "Scenario for developing a stormwater treatment train for an ultra-urban setting"
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{alert|This is a new page that is under construction. Anticipated completion date is June, 2015.|alert-under-construction}} | {{alert|This is a new page that is under construction. Anticipated completion date is June, 2015.|alert-under-construction}} | ||
| − | + | [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Using_the_treatment_train_approach_to_BMP_selection Stormwater treatment trains] combine multiple stormwater treatment processes and/or practices in a manner that ensures management of all pollutants that could affect a [[Glossary#R|receiving water]]. To provide guidance for stormwater managers, hypothetical treatment trains were developed for five common stormwater management scenarios. This page provides information on implementing a stormwater BMP treatment train for an [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Glossary#U ultra-urban setting]. To see other scenarios, see [[Scenario for developing a stormwater treatment train for an ultra-urban setting#Related articles|related articles]] at the bottom of this page. | |
| − | + | ==Step 1: Review project goals and site conditions== | |
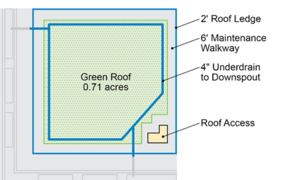
| + | [[File:Ultra-Urban Scenario Base.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Ultra-Urban Scenario Base |<font size=3>Site layout for a treatment train scenario for an ultra-urban setting (source: CDM Smith).</font size>]] | ||
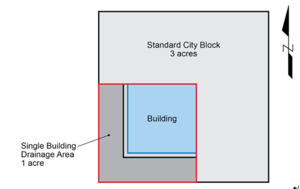
| − | + | The ultra-urban site is characterized by high impervious cover in the form of residences, parking, or commercial development. For the purposes of this scenario, the drainage conditions for a single building on a city block in downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota were considered. A single city block covers an average area of 3 acres and generally contains 2 to 4 buildings. For this scenario, it is assumed that a single building, including its frontage, sidewalk and half of the road covers a drainage area of 1 acre, as shown in the schematic to the right. | |
| − | The basic site conditions for the | + | The basic site conditions for the ultra-urban setting are summarized in the table below. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
High imperviousness results in high velocity and erosive stormwater flows that can damage building integrity and overwhelm stormwater infrastructure. The soil type, although fairly well draining, is assumed to be compacted due to high urbanization. Lack of vegetation and infiltration opportunities also prevent pollutant removal which leads to reduced water quality. The goal of this project is to install a BMP treatment train to reduce runoff volume and pollutant loads for the Water Quality Event. | High imperviousness results in high velocity and erosive stormwater flows that can damage building integrity and overwhelm stormwater infrastructure. The soil type, although fairly well draining, is assumed to be compacted due to high urbanization. Lack of vegetation and infiltration opportunities also prevent pollutant removal which leads to reduced water quality. The goal of this project is to install a BMP treatment train to reduce runoff volume and pollutant loads for the Water Quality Event. | ||
| − | + | ==Step 2: Review Pollutant Removal Processes & Identify Potential Practices== | |
| − | |||
The BMPs selected for the Ultra-Urban site, must achieve the goals of decreased runoff volume and pollutant removal, as well as fit within the site constraints. the Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Practice Selection table summarizes the BMP categories and their applicability to this site. | The BMPs selected for the Ultra-Urban site, must achieve the goals of decreased runoff volume and pollutant removal, as well as fit within the site constraints. the Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Practice Selection table summarizes the BMP categories and their applicability to this site. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
Infiltrator and Filter BMPs are determined to best address the goals of this project for the Ultra-Urban scenario. The process of selecting and placing BMPs on a site is typically iterative, working between the site constraints, project goals, and available budget. The approach and considerations for this scenario are discussed in the following sections. | Infiltrator and Filter BMPs are determined to best address the goals of this project for the Ultra-Urban scenario. The process of selecting and placing BMPs on a site is typically iterative, working between the site constraints, project goals, and available budget. The approach and considerations for this scenario are discussed in the following sections. | ||
| − | + | ==Step 3: Determine Site Constraints & BMP Placement== | |
| − | + | [[File:Ultra-Urban Scenario Street Level BMP Placement Schematic.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Ultra-Urban Scenario Street Level BMP Placement |Ultra-Urban Scenario Street Level BMP Placement Schematic<font size=3></font size>]] | |
The Ultra-Urban Setting can pose a unique set of site constraints due to limited space for development and high pedestrian traffic. Specific site constraints for a typical city block in Minneapolis include: | The Ultra-Urban Setting can pose a unique set of site constraints due to limited space for development and high pedestrian traffic. Specific site constraints for a typical city block in Minneapolis include: | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
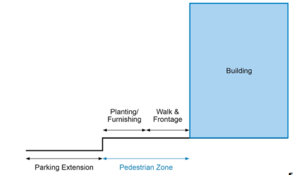
To meet space allotments and reduce degradation due to interaction with people and vehicles, the most viable locations for BMPs are the building rooftop, the pedestrian sidewalk and parking/bike lane. For reference, the street level areas are depicted in the Ultra-Urban Scenario Street Level BMP Placement Schematic below | To meet space allotments and reduce degradation due to interaction with people and vehicles, the most viable locations for BMPs are the building rooftop, the pedestrian sidewalk and parking/bike lane. For reference, the street level areas are depicted in the Ultra-Urban Scenario Street Level BMP Placement Schematic below | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Further considerations for placement of BMPs on the street level are the required minimum dimensions for high capacity roads, curbs, sidewalks and planting and furnishing zones as well as the 10 foot minimum setback from a building foundation. | Further considerations for placement of BMPs on the street level are the required minimum dimensions for high capacity roads, curbs, sidewalks and planting and furnishing zones as well as the 10 foot minimum setback from a building foundation. | ||
| − | + | ==Step 4: Select Individual BMPs & Evaluate Range of Performance== | |
| − | |||
Step 2 introduced the practices that would best address the goals and site constraints for the Ultra-Urban setting as infiltrators and Filters. Infiltration is a hydraulic process that serves to reduce volume runoff and pollutant loads by complete abstraction of runoff. Physical, chemical and biological processes remove pollutant loads as water moves through the media mix. In contrast, filtration is a physical process that uses the same physical, chemical and biological principles to reduce pollutant loads as water moves through the media. However, excess water is drained through an underdrain. | Step 2 introduced the practices that would best address the goals and site constraints for the Ultra-Urban setting as infiltrators and Filters. Infiltration is a hydraulic process that serves to reduce volume runoff and pollutant loads by complete abstraction of runoff. Physical, chemical and biological processes remove pollutant loads as water moves through the media mix. In contrast, filtration is a physical process that uses the same physical, chemical and biological principles to reduce pollutant loads as water moves through the media. However, excess water is drained through an underdrain. | ||
| − | '''Filter: Green Roof''' | + | :'''Filter: Green Roof''' |
*Green roofs are primary treatment BMPs which act as filters. Installing a green roof substantially reduces impervious cover and the volume and rate of water draining to the street level. Green roofs have a median TSS removal of 85%. Although green roofs do not have high rates of TP removal, in a northern temperate region such as Minnesota a green roof can reduce runoff volume by 50% to 70%. Volume and rate reduction will reduce loading on downstream BMPs allowing for more effective pollutant reduction. Studies show that green roofs actually become more effective over time. As vegetation becomes more established, water quality may improve due to mature plants ability absorb and filter more pollutants. A green roof with an underdrain will allow for reduction in runoff volume, peak discharge, delay peak runoff, and divert excess water to downstream BMPs for further pollutant reduction. | *Green roofs are primary treatment BMPs which act as filters. Installing a green roof substantially reduces impervious cover and the volume and rate of water draining to the street level. Green roofs have a median TSS removal of 85%. Although green roofs do not have high rates of TP removal, in a northern temperate region such as Minnesota a green roof can reduce runoff volume by 50% to 70%. Volume and rate reduction will reduce loading on downstream BMPs allowing for more effective pollutant reduction. Studies show that green roofs actually become more effective over time. As vegetation becomes more established, water quality may improve due to mature plants ability absorb and filter more pollutants. A green roof with an underdrain will allow for reduction in runoff volume, peak discharge, delay peak runoff, and divert excess water to downstream BMPs for further pollutant reduction. | ||
| − | '''Infiltrator: Tree Trench/Box System''' | + | :'''Infiltrator: Tree Trench/Box System''' |
*Tree trenches and boxes on the street level between the sidewalk and street can capture and reduce runoff from the road, sidewalk, and underdrain outlet from the green roof. Tree trenches/boxes act as infiltrators where the soil media, trees and microbes work in conjunction to absorb, filter or transform pollutants. The media in tree trenches/boxes also holds pollutants to be utilized by vegetation or microbes during periods of low rainfall. Soil Media Mix D is recommended for tree BMPs. Together they provide the most effective design for nutrient and pollutant removal because of the interplay of physical, chemical and biological processes. Infiltration basins could provide similar runoff volume and pollutant reductions, however because this was an area with high pedestrian interaction, tree trenches/boxes provide a higher aesthetic value. | *Tree trenches and boxes on the street level between the sidewalk and street can capture and reduce runoff from the road, sidewalk, and underdrain outlet from the green roof. Tree trenches/boxes act as infiltrators where the soil media, trees and microbes work in conjunction to absorb, filter or transform pollutants. The media in tree trenches/boxes also holds pollutants to be utilized by vegetation or microbes during periods of low rainfall. Soil Media Mix D is recommended for tree BMPs. Together they provide the most effective design for nutrient and pollutant removal because of the interplay of physical, chemical and biological processes. Infiltration basins could provide similar runoff volume and pollutant reductions, however because this was an area with high pedestrian interaction, tree trenches/boxes provide a higher aesthetic value. | ||
| − | + | [[File:Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Layout.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Layout|Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Layout<font size=3></font size>]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | :'''Infiltrator: Permeable Pavement''' | |
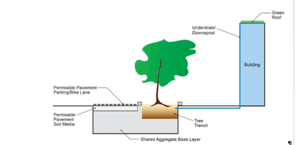
| + | *Permeable pavement acts as a final filter to remove phosphorous and other pollutants and to reduce road and storm sewer flooding. Although permeable pavements can be prone to clogging in areas of high TSS loading, the preceding BMPs will reduce pollutant loading from the sidewalk and buildings, and allow for more effective pollutant removal from the adjacent impervious street. Permeable pavement offers structural stability to allow for traffic loading from cars and bikes, while allowing water to infiltrate through voids in the surface. The aggregate storage media under the permeable pavement and tree boxes will be a single unit as shown in the figure to the right, allowing for captured stormwater and pollutants to be available for vegetation in the tree trenches/boxes. | ||
A multitude infiltrator or filter BMPs may be considered for an Ultra-Urban setting where the goals of stormwater management are the reduction of runoff volumes and pollutant loads. A green roof, tree trenches, and permeable pavement were selected as plausible treatment train BMPs for the Ultra-Urban setting in downtown Minneapolis. | A multitude infiltrator or filter BMPs may be considered for an Ultra-Urban setting where the goals of stormwater management are the reduction of runoff volumes and pollutant loads. A green roof, tree trenches, and permeable pavement were selected as plausible treatment train BMPs for the Ultra-Urban setting in downtown Minneapolis. | ||
| − | + | ==Step 5: Size BMPs & Assess Performance== | |
| − | + | For the ultra-urban setting, space is a significant site constraint and therefore BMP sizing must be very strategic to allow for maximum BMP efficiency while meeting performance goals. Assumptions included an annual Phosphorus EMC of 0.3 milligrams per liter, and an annual TSS EMC of 54.5 milligrams per liter. The following table summarizes the existing site runoff, volume and pollutant retention goals. The MIDS calculator provides a performance goal requirement based on the site conditions for the treatment train which is shown in the Ultra-Urban Scenario Performance Goal table .below. | |
| − | For the | ||
{{:Ultra-Urban Scenario Performance Goal}} | {{:Ultra-Urban Scenario Performance Goal}} | ||
| Line 75: | Line 71: | ||
BMP Sizing for each component of a treatment train is an iterative process where available space, performance goals and regulatory requirements must be considered. | BMP Sizing for each component of a treatment train is an iterative process where available space, performance goals and regulatory requirements must be considered. | ||
| − | + | ===Green Roof=== | |
| − | |||
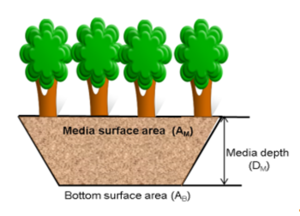
The design of a green roof is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for green roofs. The MIDS calculator is able to determine the performance of the Green Roof BMP based on the parameters shown in the MIDS Green Roof Configuration schematic. | The design of a green roof is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for green roofs. The MIDS calculator is able to determine the performance of the Green Roof BMP based on the parameters shown in the MIDS Green Roof Configuration schematic. | ||
| − | + | [[File:MIDS Green Roof Configuration.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating MIDS Green Roof Configuration|<font size=3>Green roof configuration (Source: CDM Smith).</font size>]] | |
| − | [[File:MIDS Green Roof Configuration.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating MIDS Green Roof Configuration| | ||
The surface area of a green roof is controlled by the available area on the building rooftop. The rooftop size is dictated by the space available on the existing building. The sizing input parameters for the green roof are shown in the Ultra-Urban Green Roof Sizing Input Parameters table below. | The surface area of a green roof is controlled by the available area on the building rooftop. The rooftop size is dictated by the space available on the existing building. The sizing input parameters for the green roof are shown in the Ultra-Urban Green Roof Sizing Input Parameters table below. | ||
| Line 86: | Line 80: | ||
{{:Ultra-Urban Green Roof Sizing Input Parameters}} | {{:Ultra-Urban Green Roof Sizing Input Parameters}} | ||
| − | For this setting, space was allotted for a 6 foot walkway around the perimeter of the green roof to provide maintenance access to the BMP without hindering its functionality and the performance. To route excess water to the downstream BMPs on the south and west side of the building, two- | + | For this setting, space was allotted for a 6 foot walkway around the perimeter of the green roof to provide maintenance access to the BMP without hindering its functionality and the performance. To route excess water to the downstream BMPs on the south and west side of the building, two 4-inch downspouts were included. Two downspouts reduce the risk of clogging and provides an extra outlet for water if one downspout is undergoing maintenance. A schematic of the green roof design is shown to the right. |
| − | [[File:Ultra-Urban Green Roof Design.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Ultra-Urban Green Roof Design.PNG|Ultra-Urban Green Roof Design.PNG | + | [[File:Ultra-Urban Green Roof Design.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Ultra-Urban Green Roof Design.PNG|<font size=3>Ultra-Urban Green Roof Design.PNG</font size>]] |
These parameters were entered into the MIDS calculator to evaluate performance of the green roof BMP for a runoff volume and pollutant load reductions. These results are summarizes in the Green Roof Performance Summary table below. | These parameters were entered into the MIDS calculator to evaluate performance of the green roof BMP for a runoff volume and pollutant load reductions. These results are summarizes in the Green Roof Performance Summary table below. | ||
| Line 95: | Line 89: | ||
===Tree Trench/Box System=== | ===Tree Trench/Box System=== | ||
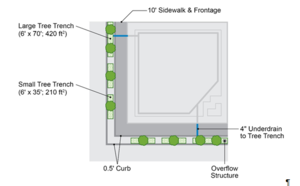
| + | [[File:MIDS Tree Trench - Box System Configuration.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating MIDS Tree Trench - Box System Configuration|MIDS Tree Trench - Box System Configuration<font size=3></font size>]] | ||
| − | The design of a Tree Trench System BMP is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for tree trenches without underdrains. The MIDS calculator is able to determine the performance of the tree trench BMP based on the parameters shown in | + | The design of a Tree Trench System BMP is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for tree trenches without underdrains. The MIDS calculator is able to determine the performance of the tree trench BMP based on the parameters shown in the figure to the right. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Two types of tree trenches were designed for the Ultra-Urban setting. Two large tree trenches were placed at the outlets of each downspout to account for flow from the upstream Green Roof BMP as well as runoff from the adjacent sidewalk. Four small tree trenches were added to intercept runoff from the sidewalk, preventing flow into the street. Sizing of the tree trenches is limited by pedestrian zone spacing requirements. Installations in the pedestrian zone should conform to all local rules and regulations. This Ultra-Urban scenario was set in downtown Minneapolis, MN and as such, sizing for the frontage, sidewalk and planting zones are determined based on the [http://www.minneapolismn.gov/www/groups/public/@publicworks/documents/webcontent/convert_256028.pdf Minneapolis Public Works Pedestrian Facility Design Guidelines]. The required [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Minimum_setback_requirements 10 foot minimum setback] for infiltration practices from a building foundation and [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Design_guidelines_for_soil_characteristics_-_tree_trenches_and_tree_boxes soil volume requirements] for the chosen tree type also factored into tree trench sizing. The tree trench sizing input parameters are summarized in the Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Sizing Input Parameters table below. | Two types of tree trenches were designed for the Ultra-Urban setting. Two large tree trenches were placed at the outlets of each downspout to account for flow from the upstream Green Roof BMP as well as runoff from the adjacent sidewalk. Four small tree trenches were added to intercept runoff from the sidewalk, preventing flow into the street. Sizing of the tree trenches is limited by pedestrian zone spacing requirements. Installations in the pedestrian zone should conform to all local rules and regulations. This Ultra-Urban scenario was set in downtown Minneapolis, MN and as such, sizing for the frontage, sidewalk and planting zones are determined based on the [http://www.minneapolismn.gov/www/groups/public/@publicworks/documents/webcontent/convert_256028.pdf Minneapolis Public Works Pedestrian Facility Design Guidelines]. The required [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Minimum_setback_requirements 10 foot minimum setback] for infiltration practices from a building foundation and [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Design_guidelines_for_soil_characteristics_-_tree_trenches_and_tree_boxes soil volume requirements] for the chosen tree type also factored into tree trench sizing. The tree trench sizing input parameters are summarized in the Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Sizing Input Parameters table below. | ||
| Line 112: | Line 101: | ||
{{:Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Tree Selection Parameters}} | {{:Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Tree Selection Parameters}} | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Tree Trench System Design.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Tree Trench System Design|Tree Trench System Design<font size=3></font size>]] | ||
| − | + | The MIDS calculator also accounts for soil media within the tree trench system, underlying soils, and tree types. As previously stated, Media Mix D is highly recommended for best results with a Tree BMP. The selected media mix dictates the MIDS inputs for soil-water storage properties, including a media field capacity of 0.09 ft3/ft3 and a media porosity of 0.31 ft3/ft3. Although the area’s underlying Hydrologic Soil Group B is relatively well-draining with an infiltration rate of 0.45 in/hr, high soil compaction was assumed because of the intense urbanization. Therefore an overflow structure was included in the tree trench for larger storm bypass and reduced infiltration capacity over time. The figure to the right displays the overall layout for the tree trench system. | |
These parameters were entered into the MIDS calculator to evaluate performance of the tree trench BMPs for a runoff volume and pollutant load reductions. These results are summarizes in the Tree Trench Performance Summary table below. | These parameters were entered into the MIDS calculator to evaluate performance of the tree trench BMPs for a runoff volume and pollutant load reductions. These results are summarizes in the Tree Trench Performance Summary table below. | ||
| Line 121: | Line 110: | ||
{{:Tree Trench Performance Summary}} | {{:Tree Trench Performance Summary}} | ||
| − | ===Permeable | + | ===Permeable pavement=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
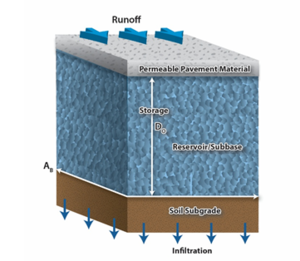
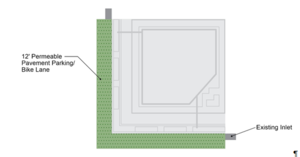
[[File:Typical Permeable Pavement Configuration.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Typical Permeable Pavement Configuration|Typical Permeable Pavement Configuration<font size=3></font size>]] | [[File:Typical Permeable Pavement Configuration.PNG|thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Typical Permeable Pavement Configuration|Typical Permeable Pavement Configuration<font size=3></font size>]] | ||
| − | + | [[File:Permeable Pavement Layout.PNG |thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Permeable Pavement Layout|Permeable Pavement Layout<font size=3></font size>]] | |
| + | The design of a permeable pavement parking/bike lane is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for permeable pavement. A typical permeable pavement configuration is shown in the figure to the right. | ||
| − | [[ | + | The sizing of the permeable pavement parking/bike lane varies depending on scenario, available space and should conform to all local rules and regulations for transportation zones. This Ultra-Urban scenario was set in downtown Minneapolis, MN and as such local sizing guidelines for traffic ways, parking lanes and bike lines were considered. The [http://www.minneapolismn.gov/www/groups/public/@publicworks/documents/webcontent/convert_283657.pdf Minneapolis Public Works Street and Sidewalk Design Guidelines] offers desired minimum lane widths for urban roads, parking and bike lanes. These recommendations conform to the minimum design standards set forth by the [https://www.revisor.mn.gov/rules/?id=8820.9936 Minnesota Administrative Rules]. The dimensions for the permeable pavement lane, including space for parking and bike passage, were designed to be 12 feet wide, and extend the length of the block. This meets the [http://www.minneapolismn.gov/www/groups/public/@publicworks/documents/webcontent/convert_283657.pdf Minneapolis Public Works Design Guidelines for Streets and Sidewalks] requirements for the minimum functional lane widths. |
| − | The additional considerations for permeable pavement infiltration BMP sizing are depth of the aggregate reservoir and the required drawdown time. The sizing input parameters for the permeable pavement BMP are summarized | + | The additional considerations for permeable pavement infiltration BMP sizing are depth of the aggregate reservoir and the required drawdown time. The sizing input parameters for the permeable pavement BMP are summarized below. |
{{:Ultra urban Permeable Pavement Sizing Input Parameters}} | {{:Ultra urban Permeable Pavement Sizing Input Parameters}} | ||
| − | Although the underlying Hydrologic Soil Group B is considered to be well draining with an infiltration rate of 0.45 in/hr., high soil compaction was assumed because this is a highly urbanized area. In addition, the Permeable Pavement BMP will need to support vehicular loads and therefore further compaction of underlying soils may be required. For this reason, an existing inlet will be maintained directly downstream of the permeable pavement for bypass and overflow from larger storm events. The porosity of the aggregate media was assumed to be 0.4 ft3/ft3. These parameters were input into the MIDS calculator to evaluate the pollutant removal and volume reduction performance of the BMP. The results of the MIDS credit calculations for volume reduction and pollutant loading are | + | Although the underlying Hydrologic Soil Group B is considered to be well draining with an infiltration rate of 0.45 in/hr., high soil compaction was assumed because this is a highly urbanized area. In addition, the Permeable Pavement BMP will need to support vehicular loads and therefore further compaction of underlying soils may be required. For this reason, an existing inlet will be maintained directly downstream of the permeable pavement for bypass and overflow from larger storm events. The porosity of the aggregate media was assumed to be 0.4 ft3/ft3. These parameters were input into the MIDS calculator to evaluate the pollutant removal and volume reduction performance of the BMP. The results of the MIDS credit calculations for volume reduction and pollutant loading are shown below. |
{{:Permeable Pavement Performance Summary}} | {{:Permeable Pavement Performance Summary}} | ||
| − | ===Overall Ultra-Urban BMP Treatment Train | + | ===Overall ultra-urban BMP treatment train performance=== |
| + | [[File:Ultra-Urban BMP Treatment Train MIDS Calculator Schematic.PNG |thumb|300 px|alt=schematic illustrating Ultra-Urban BMP Treatment Train MIDS Calculator|<font size=3>Ultra-Urban BMP Treatment Train MIDS Calculator Schematic</font size>]] | ||
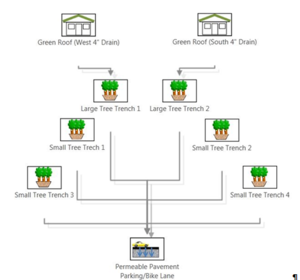
| − | The overall performance of the BMP Treatment Train was evaluated by the MIDS Calculator. The treatment train configuration consisting of a green roof, 2 large tree trenches, 4 small tree trenches and a permeable pavement parking/bike lane is shown | + | The overall performance of the BMP Treatment Train was evaluated by the MIDS Calculator. The treatment train configuration consisting of a green roof, 2 large tree trenches, 4 small tree trenches and a permeable pavement parking/bike lane is shown on the right. |
| − | + | This treatment train was able to significantly reduce the volume and pollutant loadings in the Ultra-Urban setting. The treatment train achieved removal efficiencies of 97 percent for each of the components of interest: runoff volume, Total phosphorus and TSS. The results from the MIDS calculator run is summarized in the following table. | |
| − | |||
| − | This treatment train was able to significantly reduce the volume and pollutant loadings in the Ultra-Urban setting. The treatment train achieved removal efficiencies of 97 | ||
{{:Ultra urban Annual BMP Treatment Train Performance Summary}} | {{:Ultra urban Annual BMP Treatment Train Performance Summary}} | ||
| − | + | ==Step 6: Review Construction & Operations Criteria== | |
| − | + | Each of the BMPs included in the treatment train have unique criteria for construction and operations. Information regarding construction and operations should be reviewed in detail before design and construction of the BMPs take place. Available information for each of the BMPs is provided below. | |
| − | Each of the BMPs included in the treatment train have unique criteria for construction and operations. Information regarding construction and operations should be reviewed in detail before design and construction of the BMPs take place. Available information for each of the BMPs | ||
{{:Construction and Operations Guidance for Ultra-Urban BMPs}} | {{:Construction and Operations Guidance for Ultra-Urban BMPs}} | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 30 June 2015
This is a new page that is under construction. Anticipated completion date is June, 2015.
Stormwater treatment trains combine multiple stormwater treatment processes and/or practices in a manner that ensures management of all pollutants that could affect a receiving water. To provide guidance for stormwater managers, hypothetical treatment trains were developed for five common stormwater management scenarios. This page provides information on implementing a stormwater BMP treatment train for an ultra-urban setting. To see other scenarios, see related articles at the bottom of this page.
Contents
- 1 Step 1: Review project goals and site conditions
- 2 Step 2: Review Pollutant Removal Processes & Identify Potential Practices
- 3 Step 3: Determine Site Constraints & BMP Placement
- 4 Step 4: Select Individual BMPs & Evaluate Range of Performance
- 5 Step 5: Size BMPs & Assess Performance
- 6 Step 6: Review Construction & Operations Criteria
Step 1: Review project goals and site conditions
The ultra-urban site is characterized by high impervious cover in the form of residences, parking, or commercial development. For the purposes of this scenario, the drainage conditions for a single building on a city block in downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota were considered. A single city block covers an average area of 3 acres and generally contains 2 to 4 buildings. For this scenario, it is assumed that a single building, including its frontage, sidewalk and half of the road covers a drainage area of 1 acre, as shown in the schematic to the right.
The basic site conditions for the ultra-urban setting are summarized in the table below.
| Site | Ultra-Urban (Downtown Minneapolis) |
| Drainage Area | 1.0 acre |
| Impervious Area | 95% |
| Soil Conditions | Hydrologic Soil Group ‘B’, silty sands and silty gravelly sands. Permeability ranges between 0.30- 0.45 inches per hour at a depth of 3 feet. Bedrock was not observed in borings conducted on site. |
| Topography & Drainage | Rooftop runoff drains down to street level through downspouts. Street level runoff drains to the southwest corner of the city block. |
| Project Goals | Reduce stormwater runoff volume and pollutant loads by decreasing impervious cover to promote infiltration and nutrient uptake. |
High imperviousness results in high velocity and erosive stormwater flows that can damage building integrity and overwhelm stormwater infrastructure. The soil type, although fairly well draining, is assumed to be compacted due to high urbanization. Lack of vegetation and infiltration opportunities also prevent pollutant removal which leads to reduced water quality. The goal of this project is to install a BMP treatment train to reduce runoff volume and pollutant loads for the Water Quality Event.
Step 2: Review Pollutant Removal Processes & Identify Potential Practices
The BMPs selected for the Ultra-Urban site, must achieve the goals of decreased runoff volume and pollutant removal, as well as fit within the site constraints. the Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Practice Selection table summarizes the BMP categories and their applicability to this site.
Ultra-Urban Scenario BMP Practice Selection
Infiltrator and Filter BMPs are determined to best address the goals of this project for the Ultra-Urban scenario. The process of selecting and placing BMPs on a site is typically iterative, working between the site constraints, project goals, and available budget. The approach and considerations for this scenario are discussed in the following sections.
Step 3: Determine Site Constraints & BMP Placement
The Ultra-Urban Setting can pose a unique set of site constraints due to limited space for development and high pedestrian traffic. Specific site constraints for a typical city block in Minneapolis include:
- Available Space – In the Ultra-Urban setting the location of BMPs is restricted to rooftops and the narrow corridor between buildings and city streets. Impervious surfaces in the drainage area are necessary for supporting high foot and vehicle traffic, as well as structural support of buildings. Selected BMPs must be able to effectively reduce the adverse effects of stormwater while maintaining the function of the existing impervious surfaces.
- Public Integration – Ultra-Urban settings are usually characterized by high volumes of pedestrian and vehicular traffic. Selected BMPs must be resistant to degradation due to constant use. BMP aesthetics should also be a consideration.
- Utilities – when working in a downtown or Ultra-Urban setting, there is often little flexibility in the location and movement of utilities. BMP sizing and location should try to avoid major impact utilities.
- Regulatory Requirements - All local, state, and federal regulatory requirements must be met. The design criteria and recommendations from the Minnesota Stormwater Manual will be followed.
To meet space allotments and reduce degradation due to interaction with people and vehicles, the most viable locations for BMPs are the building rooftop, the pedestrian sidewalk and parking/bike lane. For reference, the street level areas are depicted in the Ultra-Urban Scenario Street Level BMP Placement Schematic below
Further considerations for placement of BMPs on the street level are the required minimum dimensions for high capacity roads, curbs, sidewalks and planting and furnishing zones as well as the 10 foot minimum setback from a building foundation.
Step 4: Select Individual BMPs & Evaluate Range of Performance
Step 2 introduced the practices that would best address the goals and site constraints for the Ultra-Urban setting as infiltrators and Filters. Infiltration is a hydraulic process that serves to reduce volume runoff and pollutant loads by complete abstraction of runoff. Physical, chemical and biological processes remove pollutant loads as water moves through the media mix. In contrast, filtration is a physical process that uses the same physical, chemical and biological principles to reduce pollutant loads as water moves through the media. However, excess water is drained through an underdrain.
- Filter: Green Roof
- Green roofs are primary treatment BMPs which act as filters. Installing a green roof substantially reduces impervious cover and the volume and rate of water draining to the street level. Green roofs have a median TSS removal of 85%. Although green roofs do not have high rates of TP removal, in a northern temperate region such as Minnesota a green roof can reduce runoff volume by 50% to 70%. Volume and rate reduction will reduce loading on downstream BMPs allowing for more effective pollutant reduction. Studies show that green roofs actually become more effective over time. As vegetation becomes more established, water quality may improve due to mature plants ability absorb and filter more pollutants. A green roof with an underdrain will allow for reduction in runoff volume, peak discharge, delay peak runoff, and divert excess water to downstream BMPs for further pollutant reduction.
- Infiltrator: Tree Trench/Box System
- Tree trenches and boxes on the street level between the sidewalk and street can capture and reduce runoff from the road, sidewalk, and underdrain outlet from the green roof. Tree trenches/boxes act as infiltrators where the soil media, trees and microbes work in conjunction to absorb, filter or transform pollutants. The media in tree trenches/boxes also holds pollutants to be utilized by vegetation or microbes during periods of low rainfall. Soil Media Mix D is recommended for tree BMPs. Together they provide the most effective design for nutrient and pollutant removal because of the interplay of physical, chemical and biological processes. Infiltration basins could provide similar runoff volume and pollutant reductions, however because this was an area with high pedestrian interaction, tree trenches/boxes provide a higher aesthetic value.
- Infiltrator: Permeable Pavement
- Permeable pavement acts as a final filter to remove phosphorous and other pollutants and to reduce road and storm sewer flooding. Although permeable pavements can be prone to clogging in areas of high TSS loading, the preceding BMPs will reduce pollutant loading from the sidewalk and buildings, and allow for more effective pollutant removal from the adjacent impervious street. Permeable pavement offers structural stability to allow for traffic loading from cars and bikes, while allowing water to infiltrate through voids in the surface. The aggregate storage media under the permeable pavement and tree boxes will be a single unit as shown in the figure to the right, allowing for captured stormwater and pollutants to be available for vegetation in the tree trenches/boxes.
A multitude infiltrator or filter BMPs may be considered for an Ultra-Urban setting where the goals of stormwater management are the reduction of runoff volumes and pollutant loads. A green roof, tree trenches, and permeable pavement were selected as plausible treatment train BMPs for the Ultra-Urban setting in downtown Minneapolis.
Step 5: Size BMPs & Assess Performance
For the ultra-urban setting, space is a significant site constraint and therefore BMP sizing must be very strategic to allow for maximum BMP efficiency while meeting performance goals. Assumptions included an annual Phosphorus EMC of 0.3 milligrams per liter, and an annual TSS EMC of 54.5 milligrams per liter. The following table summarizes the existing site runoff, volume and pollutant retention goals. The MIDS calculator provides a performance goal requirement based on the site conditions for the treatment train which is shown in the Ultra-Urban Scenario Performance Goal table .below.
Ultra-Urban Scenario Performance Goal
BMP Sizing for each component of a treatment train is an iterative process where available space, performance goals and regulatory requirements must be considered.
Green Roof
The design of a green roof is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for green roofs. The MIDS calculator is able to determine the performance of the Green Roof BMP based on the parameters shown in the MIDS Green Roof Configuration schematic.
The surface area of a green roof is controlled by the available area on the building rooftop. The rooftop size is dictated by the space available on the existing building. The sizing input parameters for the green roof are shown in the Ultra-Urban Green Roof Sizing Input Parameters table below.
Ultra-Urban Green Roof Sizing Input Parameters
For this setting, space was allotted for a 6 foot walkway around the perimeter of the green roof to provide maintenance access to the BMP without hindering its functionality and the performance. To route excess water to the downstream BMPs on the south and west side of the building, two 4-inch downspouts were included. Two downspouts reduce the risk of clogging and provides an extra outlet for water if one downspout is undergoing maintenance. A schematic of the green roof design is shown to the right.
These parameters were entered into the MIDS calculator to evaluate performance of the green roof BMP for a runoff volume and pollutant load reductions. These results are summarizes in the Green Roof Performance Summary table below.
Green Roof Performance Summary
Tree Trench/Box System
The design of a Tree Trench System BMP is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for tree trenches without underdrains. The MIDS calculator is able to determine the performance of the tree trench BMP based on the parameters shown in the figure to the right.
Two types of tree trenches were designed for the Ultra-Urban setting. Two large tree trenches were placed at the outlets of each downspout to account for flow from the upstream Green Roof BMP as well as runoff from the adjacent sidewalk. Four small tree trenches were added to intercept runoff from the sidewalk, preventing flow into the street. Sizing of the tree trenches is limited by pedestrian zone spacing requirements. Installations in the pedestrian zone should conform to all local rules and regulations. This Ultra-Urban scenario was set in downtown Minneapolis, MN and as such, sizing for the frontage, sidewalk and planting zones are determined based on the Minneapolis Public Works Pedestrian Facility Design Guidelines. The required 10 foot minimum setback for infiltration practices from a building foundation and soil volume requirements for the chosen tree type also factored into tree trench sizing. The tree trench sizing input parameters are summarized in the Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Sizing Input Parameters table below.
Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Sizing Input Parameters
The tree types and sizes for the tree trench system BMPs are restricted by the available soil volume. Deciduous trees are most suitable for the Ultra-Urban Design as they provide more clearance for pedestrian passage around the trees. The Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Tree Selection Parameters table below shows the tree inputs for the MIDS calculator.
Ultra-Urban Tree Trench Tree Selection Parameters
The MIDS calculator also accounts for soil media within the tree trench system, underlying soils, and tree types. As previously stated, Media Mix D is highly recommended for best results with a Tree BMP. The selected media mix dictates the MIDS inputs for soil-water storage properties, including a media field capacity of 0.09 ft3/ft3 and a media porosity of 0.31 ft3/ft3. Although the area’s underlying Hydrologic Soil Group B is relatively well-draining with an infiltration rate of 0.45 in/hr, high soil compaction was assumed because of the intense urbanization. Therefore an overflow structure was included in the tree trench for larger storm bypass and reduced infiltration capacity over time. The figure to the right displays the overall layout for the tree trench system.
These parameters were entered into the MIDS calculator to evaluate performance of the tree trench BMPs for a runoff volume and pollutant load reductions. These results are summarizes in the Tree Trench Performance Summary table below.
Tree Trench Performance Summary
Permeable pavement
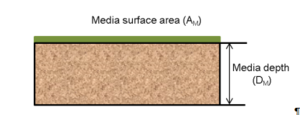
The design of a permeable pavement parking/bike lane is based around the input parameters needed for the MIDS program and the MIDS calculator requirements for permeable pavement. A typical permeable pavement configuration is shown in the figure to the right.
The sizing of the permeable pavement parking/bike lane varies depending on scenario, available space and should conform to all local rules and regulations for transportation zones. This Ultra-Urban scenario was set in downtown Minneapolis, MN and as such local sizing guidelines for traffic ways, parking lanes and bike lines were considered. The Minneapolis Public Works Street and Sidewalk Design Guidelines offers desired minimum lane widths for urban roads, parking and bike lanes. These recommendations conform to the minimum design standards set forth by the Minnesota Administrative Rules. The dimensions for the permeable pavement lane, including space for parking and bike passage, were designed to be 12 feet wide, and extend the length of the block. This meets the Minneapolis Public Works Design Guidelines for Streets and Sidewalks requirements for the minimum functional lane widths.
The additional considerations for permeable pavement infiltration BMP sizing are depth of the aggregate reservoir and the required drawdown time. The sizing input parameters for the permeable pavement BMP are summarized below.
Ultra urban Permeable Pavement Sizing Input Parameters
Although the underlying Hydrologic Soil Group B is considered to be well draining with an infiltration rate of 0.45 in/hr., high soil compaction was assumed because this is a highly urbanized area. In addition, the Permeable Pavement BMP will need to support vehicular loads and therefore further compaction of underlying soils may be required. For this reason, an existing inlet will be maintained directly downstream of the permeable pavement for bypass and overflow from larger storm events. The porosity of the aggregate media was assumed to be 0.4 ft3/ft3. These parameters were input into the MIDS calculator to evaluate the pollutant removal and volume reduction performance of the BMP. The results of the MIDS credit calculations for volume reduction and pollutant loading are shown below.
Permeable Pavement Performance Summary
Overall ultra-urban BMP treatment train performance
The overall performance of the BMP Treatment Train was evaluated by the MIDS Calculator. The treatment train configuration consisting of a green roof, 2 large tree trenches, 4 small tree trenches and a permeable pavement parking/bike lane is shown on the right.
This treatment train was able to significantly reduce the volume and pollutant loadings in the Ultra-Urban setting. The treatment train achieved removal efficiencies of 97 percent for each of the components of interest: runoff volume, Total phosphorus and TSS. The results from the MIDS calculator run is summarized in the following table.
Ultra urban Annual BMP Treatment Train Performance Summary
Step 6: Review Construction & Operations Criteria
Each of the BMPs included in the treatment train have unique criteria for construction and operations. Information regarding construction and operations should be reviewed in detail before design and construction of the BMPs take place. Available information for each of the BMPs is provided below.