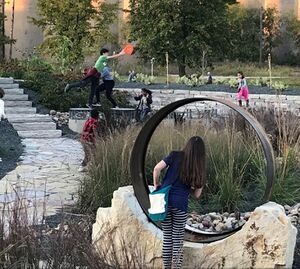Difference between revisions of "Green Infrastructure Case Study: Mississippi Watershed Management Organization Towerside District Stormwater System"
m |
m |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
*Project was a finalist for the [https://mnbrownfields.org/case-studies/towerside-stormwater-system/ ReScape Award]. | *Project was a finalist for the [https://mnbrownfields.org/case-studies/towerside-stormwater-system/ ReScape Award]. | ||
| − | [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Green_Stormwater_Infrastructure_(GSI)_and_sustainable_stormwater_management Link to more information on green infrastructure] | + | '''Additional links''' |
| + | *[https://www.mwmo.org/projects/towerside-district-stormwater-system/ MWMO Towerside web page] | ||
| + | *[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Green_Stormwater_Infrastructure_(GSI)_and_sustainable_stormwater_management Link to more information on green infrastructure] | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 10 February 2021
The 370-acre Towerside Innovation District is a rapidly developing area adjacent to the University of Minnesota and encompasses portions of Minneapolis and Saint Paul. Beginning in 2013, the Mississippi Watershed Management Organization (MWMO) (working with Barr Engineering Co. and Bruce Jacobson from the Minnesota Design Center) evaluated the feasibility of providing district stormwater management to create stormwater treatment and harvest and reuse opportunities.
As a result of the feasibility study, MWMO and Barr collaborated with four private developers to design and construct a system to manage stormwater runoff from an 8-acre area in the City of Minneapolis adjacent to the Prospect Park Green Line Light Rail Transit station. MWMO developed a district stormwater system that treats all the runoff from the four developments, exceeding the City of Minneapolis stormwater treatment requirements. The design includes stormwater conveyance systems from private developments to the district stormwater system, pretreatment in a sump manhole with a SAFL Baffle as well as an artful concrete sediment forebay, two large biofiltration basins (rain gardens) to filter out pollutants, an underground concrete tank under a biofiltration basin to store the treated stormwater, and a treatment and pumping system to enable the stormwater to be reused for irrigation by the private developers and the Minneapolis Park and Recreation Board (MPRB). Most of the district system was completed in 2016 with the treatment system completed in 2020. The initial construction cost of the district system totaled approximately $1,300,000, of which $430,000 represented the reuse treatment, pumping, and an enclosure for the treatment system that provided significant park recreation benefits.
Creating a district system allowed stormwater to be managed more efficiently in two centralized locations rather than encumbering developable land on each parcel, thus incentivizing and maximizing development opportunities in this growing community. All told, the stormwater system treats runoff from four multi-family housing developments and a grocery store representing approximately a quarter billion dollars in economic investment and providing more than 1,000 housing units. The housing includes affordable, senior, and market rate units.
The district system also facilitated the creation of an artful stormwater park that provides pollinator habitat and that is used for passive recreation in the stormwater basin itself in between storm events. The stormwater park, completed in 2016, is open to the public at all times, and has facilitated an expansion of the public realm through the construction of the adjacent MPRB park (the newest MPRB park, temporarily named Towerside Park) in 2019. The stormwater park and MPRB park are visually seamlessly integrated, and the stormwater from the district system is treated by a filtration and UV system located in a new building within the MPRB park that also serves as a covered picnic pavilion and provides storage for the community garden. The treated stormwater provides irrigation for a pollinator-friendly “bee lawn” in the MPRB park as well as the community garden itself.
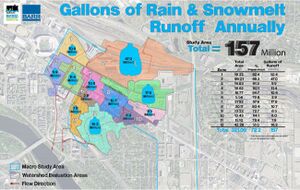
The district system treats more than 90 percent of all runoff from the 8 acres of developments, removing 90 percent of total suspended solids and 60 percent of total phosphorus. The reuse system is projected to reuse up to 4.5 million gallons of stormwater each year.
MWMO is operating and maintaining the district system for the first 5 years, after which the system will collaboratively owned and operated the benefitting landowners. Since 2016, MWMO has hired a landscaping company to perform annual maintenance of vegetation in the biofiltration basins, clean out pretreatment features, and winterize the stormwater reuse system.
For more information, please contact Dan Kalmon at the Mississippi Watershed Management Organization.
Project Highlights:
- District system treatment completed in 2016. Reuse system completed in 2020.
- System includes 1,600 linear feet of conveyance, 2 large biofiltration basins, a 207,000-gallon storage tank, and a UV treatment and filtration system for stormwater reuse.
- District stormwater system providing treatment for 8 acres of new multi-family housing.
- Incentivizing a quarter billion dollars in redevelopment along a major transit line.
- Creation of a publicly-accessible pocket park that also treats stormwater, and formed the nucleus of an adjacent, new Minneapolis park.
- Treated stormwater more efficiently, saving more than 15% in capital costs as opposed to stormwater management treated on site-by-site basis. The initial capital construction costs were $860,000.
- Removes estimated 90% TSS and 60% total phosphorus from runoff annually
- Provides approximately 4.5 million gallons of treated stormwater for annual reuse
- Stormwater reused by the contributing developments and Minneapolis park for irrigation of plantings and a community garden.
- Biofiltration basins provide pollinator-friendly corridor and connect with other habitat improvement projects along the adjacent street in a dense urban environment.
- Construction and operations and maintenance required an innovative legal agreement between the four developers, the Minneapolis Park and Recreation Board, and the MWMO.
- Project was a finalist for the ReScape Award.
Additional links