Example phosphorus calculations for street sweeping using different methods Revision as of 11:58, 11 April 2023 by Mtrojan (talk | contribs) (→Volume measurement using an estimated default bulk density)
This memo presents various street sweeping crediting methods that rely on mass and volume conversions of wet or dry material to calculate an estimated reduction of total phosphorus (TP). The crediting methods include a dry mass-based measurement, wet mass-based measurement, and volume measurements using both determined and default bulk densities. Summaries and examples of each of the crediting methods are provided below.
Contents
Determining weight and volume
All crediting methods require the initial measurement of the weight or volume of street sweeping waste collected during sweeping efforts. Over time, the weight and volume of solids collected may be estimated, but it is recommended that weight and volume street sweeping data are collected for a minimum of one year before making estimates (FSA 2019). Enough data need to be collected to be able to reliably estimate how much material certain equipment and types of vehicles are carrying. The options for determining mass and volume include:
- Mass – The mass of street sweeping material can be determined through direct measurement using a scale (typically used at a landfill) – the known weight of an empty sweeper truck (including fuel) can be subtracted from a full sweeper truck (minus the fuel used during sweeping) to determine the weight of the materials collected.
- Volume – The volume of solids collected by a street sweeper can be estimated because the volume of the hopper on a street sweeper is a known value, so when a street sweeper is full, the volume of solids is known. Volume collected in partially full hoppers can be estimated based on the proportion of the hopper that has been filled. Volume of waste can also be determined once the street sweeper waste is dumped by measuring material piles (e.g., in cubic yards [yd3] or cubic meters [m3]).
Wet mass measurement
Wet mass can be used to determine TP reduction credits with known TP concentrations in wet street sweeper waste. The credit is determined by applying conversion factors to the weight of freshly collected material (wet). The product of the weight of material collected and the conversion factor is the mass of phosphorus removed. The credit formula is: TP = wet mass x default dry mass conversion factor x phosphorus concentration To determine the wet mass, the following information should be calculated:
- Weigh the sweeper vehicle with an empty hopper, including the fuel that will be used during sweeping (vehicle mass)
- Weigh the sweeper vehicle after returning from sweeping (vehicle gross mass)
- Calculate the fuel used during sweeping (fuel consumed mass)
- Mass of fuel consumed (pounds) = total vehicle operation time (hours) x 4.85 gallons/hour x 6.943 pounds/gallon
- Subtract the vehicle mass and fuel consumed mass from the vehicle gross mass to yield wet mass of sweepings.
- Following calculation of the wet mass, enter the required information into the MPCA Street Sweeping tool, Option 2.
Example
- Sweeper with an empty hopper and a full fuel tank is weighed before beginning sweeping operations = 20,000 pounds (vehicle mass)
- Sweeper conducts sweeping operations for 3 hours in October.
- Sweeper weight after sweeping = 25,000 pounds (vehicle gross mass)
- Fuel used during sweeping = 3 hours x 4.85 gallons/hour x 6.943 pounds/gallon = 101.0 pounds (fuel consumed mass)
- Wet mass of sweepings = 25,000 pounds – 20,000 pounds – 101.0 pounds = 4,899 pounds of wet mass sweeping
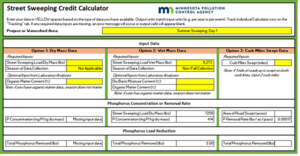
Using the MPCA Street Sweeping Credit Calculator tool, Option 2, enter 4,899 pounds of wet mass and select the appropriate season. In this example the season is fall leaf collection because sweeping occurred in October. The tool will calculate the dry mass of the street sweeping load and phosphorus concentration based on default values and return the TP removed. In this example TP removed = 2.20 pounds, as shown in Figure 1.
This method may be refined further by following the MPCA Standard Operating Procedures to calculate the dry basis moisture content and/or the organic matter content and entering these values in the Optional Inputs from Laboratory Analysis under Option 2.
Dry mass measurement
When using a dry mass-based measurement, one must determine the moisture content of the material to convert wet mass to dry mass. MPCA’s Methods for sampling street sweeping material - Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) (2022) presents methods for developing statistically valid values for moisture content through laboratory analyses. Moisture will likely differ for wet sediment versus wet organic matter. The following equation can be used to determine TP credits based on dry mass:
TP Reduction = Wet Mass x Dry/Wet Mass Ratio x Dry Weight Pollutant Concentration
Following the procedures in Section 2 (wet mass-based measurement) the wet mass should be calculated for a sweeping event. Once the wet mass has been established, a subsample of the swept materials should be collected for laboratory analysis (per the MPCA SOPs) to determine the ratio of dry mass to wet mass. This ratio is multiplied by the total sweeper load wet mass to calculate the sweeper load dry mass.
- Determine the sweeper load wet mass (pounds)
- Calculate the ratio of dry mass to wet mass of the subsample (MPCA SOPs) through laboratory analysis
- Sweeper load dry mass (pounds) = sweeper load wet mass (pounds) * (dry mass/wet mass ratio)
- Following calculation of the wet mass, enter the required information into the MPCA Street Sweeping tool, Option 2.
Example
- Wet mass of sweepings = 4,899 pounds (derived in example from Section 2)
- Sweeping staff collect a representative subsample from the sweeping materials.
- The subsample is sent to the lab where it is weighed: wet mass subsample = 250 grams
- The subsample is dried and weighed: dry mass subsample = 185 grams
- The ratio of dry to wet mass is calculated = 185 grams/250 grams = 0.74
- Dry mass = 4,899 pounds x 0.74 = 3,625.3 pounds
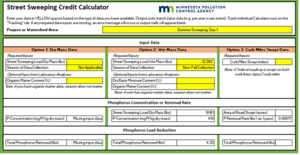
Using the MPCA Street Sweeping tool, Option 1, enter 3,625 pounds of dry mass and select the appropriate season. In this example the season is fall leaf collection because sweeping occurred in October. The tool will calculate the TP removed based on the default TP concentration and return the TP removed. In this example TP removed = 3.11 pounds, as shown in Figure 2. This method may be refined further by following the MPCA Standard Operating Procedures to calculate the organic matter content and entering that value in the Optional Inputs from Laboratory Analysis under Option 1.
Note: If the lab provides a dry basis moisture content, this can be used to calculate the dry mass using the following formula: Dry mass (pounds) = (wet mass * 100) / (dry basis moisture content %+100) In the above example, the dry basis moisture content provided by the lab is 35.135% Dry mass = (4899 pounds *100) / (35.135+100) = 3625.3 pounds
Volume measurement using an estimated default bulk density
Measured solids volume needs to be converted to mass to calculate a TP reduction credit. This is done using a bulk density value. MPCA recommends the default values of 0.5 grams (g)/cubic centimeter (cm3) for fall leaf collection and 1.0 g/cm3 for non-leaf collection. After determining the volume of sweeping materials, the conversion uses the following formulas: Wet mass (g) = wet volume (in cubic yards (yd3) x 0.7646 (yd3/m3) x 1000000 (cm3/m3) x bulk density (g/cm3) Wet mass (pounds) = wet mass (g) x 0.002205 (g/pound) After converting to wet mass, the resulting mass can be entered into Option 2 in the MPCA Street Sweeping Credit Calculator Tool.
Example 1 A small town collected 5.5 yd3 of street sweeping material during street sweeping efforts in June. The town applied a standard bulk density of 1.0 g/cm3 for the non-leaf litter street sweeping material. The conversion to wet mass is: Wet mass (g) = 5.5 yd3 x 0.7646 (yd3/m3) x 1000000 (cm3/m3) x 1.0 g/cm3 = 4,205,300 g Wet mass (pounds) = 4,205,300 x 0.002205 (g/pound) = 9,272.7 pounds. The wet mass can now be entered into Option 2 in the Tool, and the resulting TP reduction is 3.00 pounds, as shown in Figure 3. Note: If the initial volume is measured in m3, the yd3/m3 conversion factor should be omitted from the above calculations.
Example 2 The same small town conducted street sweeping for 5 days in October after leaf fall. They collected 15 m3 of debris and assumed a standard bulk density of 0.5 g/cm3 for all street sweeping debris collected in the fall when leaf litter is present. Wet mass (g) = 15 m3 x 1000000 (cm3/m3) x 0.5 g/cm3 = 7,500,000 g Wet mass (pounds) = 7,500,000 x 0.002205 (g/pound) = 16,537.5 pounds. The wet mass can now be entered into Option 2 in the Tool, and the resulting TP reduction is 7.44 pounds, as shown in Figure 3. In this example, the initial volume is measured in m3, so the yd3/m3 conversion factor is omitted from the above calculations.
Volume measurement using a determined bulk density
As mentioned in Section 4.0, measured solids volume is converted to wet mass using a bulk density value. A community may choose to conduct their own bulk density analysis instead of using the default bulk densities provided by MPCA. After determining the volume of swept material, a representative subsample of sweeping material should be collected and sent to a laboratory for bulk density analysis. This lab-based bulk density will replace the default values in the formulas in Section 4, shown again below. Wet mass (g) = wet volume (in cubic yards (yd3) x 0.7646 (yd3/m3) x 1000000 (cm3/m3) x bulk density (g/cm3) Wet mass (pounds) = wet mass (g) x 0.002205 (g/pound)
Example A small town collected 5.5 yd3 of street sweeping debris during street sweeping efforts in June. The town wants to replace the default bulk density values with bulk density specific to their sweeping efforts. A subsample is collected from the sweeping material and sent to the lab for analysis. The result is a lab-calculated bulk density of 1.4 g/cm3. The conversion to wet mass is: Wet mass (g) = 5.5 yd3 x 0.7646 (yd3/m3) x 1000000 (cm3/m3) x 1.4 g/cm3 = 5,887,420 g Wet mass (pounds) = 4,205,300 x 0.002205 (g/pound) = 12,981.8 pounds. The wet mass can now be entered into Option 2 in the Tool, and the resulting TP reduction is 4.20 pounds, as shown in Figure 4. Note: If the initial volume is measured in m3, the yd3/m3 conversion factor should be omitted from the above calculations.
References
- FSA (Florida Stormwater Association). 2019. FSA MS4 Load Reduction Assessment Tool, updated 7-28-19.
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA). 2022. Methods for sampling street sweeping material – Standard Operating Procedures. https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Methods_for_sampling_street_sweeping_material_-_Standard_Operating_Procedures