BMP options sheet for highway and road runoff management
BMP options for highway and road runoff management
Link to this table
| BMP Type | Objective | BMP Examples | Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuse flow energy from concentrated roadway surface before discharging over a slope; reinforce discharge point and slopes; promote sheet flow | Compost sock (see image), bio-slope, outlet reinforcement, spray mulch, compost rip rap matrix (between rocks) | May increase slipperiness of shoulder slope | |
| Filter litter and debris from flow as it enters catch basins; preferably with pollutant sorbents 2 | Catch basin insert (see image); hooded outlet pipe; oil and grease separator | Might become heavy for maintenance crews to lift; must be cleaned to prevent clogging | |
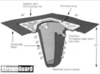
| Route runoff through a screen or filter material to remove litter and treat particulate, and the associated nutrients, toxics and hydrocarbons | Gross Solids Removal Device (GSRD) (see image), compost tube inside of rock weep, | Often contained in confined space; maintenance crew will need confined space training | |
| Diffuse heat from road and parking surfaces prior to discharge to sensitive waters | Geotextile wrapped rip rap thermal tube (see image), infiltration trench | None | |
| Provide vegetated swale drainage systems with low head grade breaks in rural sections | “Living ditch” (see image), check dams (rip rap, bio-weeper, bio-ditch filter) | Can hold water for a time after runoff occurs so need to keep design depths shallow; grade breaks can be obstruction hazard to recreational vehicles using swale | |
| Retrofit stored water BMPs with proper outlet and skimmer devices | Particulate skimmer (see image), baffle weir, Faircloth skimmer (proprietary device) | None | |
| Use pervious paving material in areas that will support it | Pervious asphalt and concrete (see image), paving blocks | None for pavement; blocks can pose walking problems if not designed properly; recommendation for minimal salt use could mean ice might be present for short periods | |
| Route water to bioretention, filtration or infiltration areas where conditions appropriate | Rain garden (see image) | Near-road locations could possibly impede vision at intersections if vegetation not kept low; water might collect adjacent to roadway | |
| Geomorphically stabilize channels | Cross vanes, fish steps, curvilinear channel restoration (see image), reinforced streambank, grade adjustments, revetments, root wads | None | |
| Use off-line storage in available floodplain, open space | Off-line pools (see image), enhanced floodplains, wetland restoration/preservation | None if kept away from areas where vehicles expected to travel or go off of the road | |
| Use sub-grade storage with or without perforations to allow for storage and infiltration where drainage determined not to impact road structure | Under street infiltration trenches (see image), vault storage to replace surface ponds, rest areas parking lots | Maintenance crew will need confined-space training |
1Use of proprietary devices or images merely for illustrative purposes and does not mean endorsement of a product
2Note that housekeeping practices like street sweeping and chemical use are discussed in the Pollution Prevention section
This page was last edited on 4 August 2022, at 20:03.