Difference between revisions of "Case studies for street sweeping"
| Line 261: | Line 261: | ||
|} | |} | ||
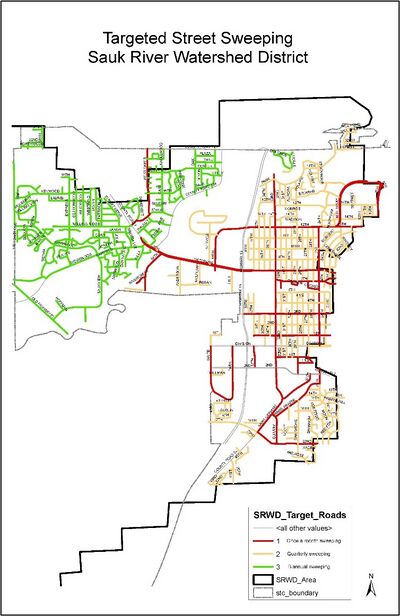
| − | [[File:St Cloud sweeping.jpg|400px|thumb|alt=map of targeted street sweeping Sauk River Watershed District|<font size=3>Mmap of targeted street sweeping for the Sauk River Watershed District</font size> | + | [[File:St Cloud sweeping.jpg|400px|thumb|alt=map of targeted street sweeping Sauk River Watershed District|<font size=3>Mmap of targeted street sweeping for the Sauk River Watershed District</font size>]] |
St. Cloud uses a variety of ways to gather street materials throughout the year. In the spring and after summer storms, the sweepers are run together in tandem. The broom sweeper is first and then the regenerative sweeper follows behind to gather smaller particulates and fines such as dust. | St. Cloud uses a variety of ways to gather street materials throughout the year. In the spring and after summer storms, the sweepers are run together in tandem. The broom sweeper is first and then the regenerative sweeper follows behind to gather smaller particulates and fines such as dust. | ||
Revision as of 02:09, 2 January 2022
Street sweeping is an effective non-structural water quality best management practice for controlling pollutant loading from municipal road surfaces. Debris from road surface degradation and associated pollutants, leaf litter, and trash can accumulate on road surfaces over time. If not controlled, built-up debris will eventually make its way to storm sewer inlets and into the municipal separate storm sewer system (MS4), degrading water quality in receiving waterbodies.
This page provides case studies for street sweeping.
Contents
- 1 City of Roseville
- 2 City of Lakeville – Using sweepers in tandem along with education and outreach to address their rapidly growing city
- 3 City of Mankato – Providing Multiple Leaf Disposal Options for Residents
- 4 City of Rochester – Leveraging Staff Flexibility and Expertise for Sweeping Success
- 5 City of St. Cloud – Capitalizing on Cost Share and Screening of Materials to Minimize Disposal Fees
City of Roseville
The City of Roseville implemented a City-wide street sweeping program in 1990 which completed three to four sweeps a year. Since 2015, the City has completed four to five city-wide street sweeping operations over the course of a given year, targeting periods of street debris buildup associated with spring thaw (March-April), twice during fall leaf litter (October-November), and targeting areas of the City discharging to sensitive water resources. Street sweeping operations are organized by the City’s Streets Maintenance Department. On average, the City removes of 400 tons of material annually during initial spring sweeping operations and about 600 tons annually with all sweepings. The average cost to the City of spring sweeping operations is $46,000 and 440 hours of labor, with subsequent sweeps being significantly less expensive and requiring fewer labor hours.
A barrier encountered by the City early in development of their street sweeping program was related to material testing (i.e., when should collected street sweeping material be tested, how often, and what to do with contaminated materials). After years of operations, the City found the spring sweepings were almost always contaminated, primarily with diesel range organics. Due to the low cost-benefit of screening collected material and limited storage capacity for screened material, the City now ships and landfills all material collected during spring operations. Sweepings collected outside the spring season have not been considered contaminated.
More information regarding the City of Roseville’s street sweeping operations can be found on their municipal website, or by contacting Ryan Johnson, Environmental Specialist, City of Roseville Engineering Department (Ryan.Johnson@cityofroseville.com).
- Project Location: City of Roseville
- Completion Date: 1990 to Present (Ongoing)
- Organizations Involved: City of Roseville Streets Maintenance Department
- Project Budget Summary: Annual cost / hours for Spring street sweeping operations: $46,000, 440 labor hours
- Quantitative Outcomes: An average of 400 tons of debris is collected during spring sweeping operations each year. Using the MPCA street sweeping calculator and assuming an average moisture content of 27.8%, this equates to 238 pounds of phosphorus removed at a cost of $193/lb-P for the spring sweeping.
City of Lakeville – Using sweepers in tandem along with education and outreach to address their rapidly growing city
| Summary information | |
| City size (square miles) | 37.8 |
| City population (2020) | 69,490 |
| Number and Type of Sweepers Owned by the City | 2 mechanical and 1 vacuum (replaced every 10 years) |
| Does the City Use Contractors for Sweeping? | No |
| Curb Miles (either owned or managed by the City) | 600 lane miles |
| Miles Swept Annually | 1,200 lane miles |
| Frequency of Sweeping | Spring and Fall |
| Disposal | After materials are gathered, they are stockpiled, tested, and then hauled to the landfill. The fall leaves are composted. The amount of fall compost is more than what the city needs. The city is exploring uses for extra material. |
| Annual Sweeping Costs | $246,000 |
| Funding Source | General fund and the stormwater utility fee |
Lakeville is a rapidly developing community in the Minneapolis-St Paul Metro Area and is adapting to changing needs related to street sweeping. Lakeville currently sweeps in the spring and the fall, focusing on the older parts of the community with more mature trees and in areas close to streams and lakes. The city also deploys sweepers following large storm events.
Lakeville begins spring sweeping activities as soon as the gutters are free of snow and ice. Each of the sweepers are equipped with GPS technology, which the city uses to track areas of high-frequency sweeping. In the fall, the city prioritizes leaf pickup based on the species of the old growth trees and when they drop their leaves. Staff move to other locations as priority areas are completed, visiting all city streets two to three times in the fall months. Staff spend approximately 600 hours sweeping during the fall season. In the spring, all three sweepers are used throughout the city multiple times for a total of 900 staff hours. The mechanical and vacuum sweepers are run in tandem in heavy debris areas, with the mechanical sweeper collecting larger debris and vegetation while the vacuum sweeper removes salt and dirt.
Education and Outreach for Residents and City Staff
Lakeville communicates the importance of street sweeping to city residents through educational segments (written and filmed) in social media postings on Facebook, NextDoor, Twitter and the city’s YouTube channel. The Adopt-a-Drain and storm drain stenciling programs are also promoted on these platforms and at local community outreach events. The Adopt-a-Drain program and associated door hangers educate residents to avoid discarding their leaves and grass clippings into the street and encourages residents to do their part cleaning neighborhood storm drains. Lakeville directs city residents to use local waste haulers or the Mulch Store in Burnsville for yard debris disposal.
The Streets, Parks and Utilities departments have an annual meeting in the spring where they provide ongoing training and education to staff about the importance of sweeping, illicit discharges, erosion control, and good housekeeping concepts.
Lessons Learned and Advice
- Tree Inventory: Lakeville recommends conducting a tree inventory to more easily predict leaf drop and spring budding and determine where sweepers will be needed.
- Costs: Don’t neglect to include disposal costs in overall programmatic costs.
- Plan Accordingly: What you put down in the winter (i.e., sand) you’ll need to pick-up in the spring. Lakeville has eliminated use of sand for winter road maintenance and credits this with reduced phosphorus loading, less material on the roads in the spring, and less required maintenance.
Contact Information
- Kelly Perrine, Environmental Resources Specialist, Kelly Perrine
- McKenzie (Mac) Cafferty, Environmental Resources Manager, McKenzie Mac Cafferty
- City of Lakeville Street Sweeping Program
City of Mankato – Providing Multiple Leaf Disposal Options for Residents
| Summary information | |
| City Size (square miles) | 20.14 |
| City Population (2020) | 44,488 |
| Number and Type of Sweepers Owned by the City | 3 sweepers and 3 leaf vacuums: 2 Elgin Pelicans (mechanical), 1 Elgin Road Wizard (mechanical), 3 ODB leaf vacuums. Replacement schedule is 10-12 years. |
| Does the City Use Contractors for Sweeping? | No |
| Lane Miles (either owned or managed by the City) | 583.76 lane miles, including alleys |
| Miles Swept Annually | 11,814 miles (2021) |
| Frequency of Sweeping The entire city (all paved roads and alleys) is swept every 30 days during the sweeping season. Mankato sweeps major areas such as the downtown area once a week primarily for trash. | |
| Disposal | Materials are screened and the majority are composted. The city makes and uses their own compost from the leaves. Items that can’t be composted are used as top cover at the landfill (note – the landfill does not charge the city for this material). They also send material to a local composting site. |
| Annual Sweeping Costs | Street sweeping budget: $250-300K/year |
| Leaf pickup budget | $150-200K/year |
| Total costs (average approximately) | $400K/year |
| Funding Source | General fund for the purchase and maintenance of the sweepers. The existing residential and commercial utility rates support the current leaf vacuum collection throughout the city of Mankato. |
Mankato’s water quality goals are to keep phosphorus, nitrogen, suspended solids, refuse and floatable debris out of the storm system to the extent possible. Mankato’s high priority areas are downtown, college campus areas, and due to their high pollutant loading, the older residential areas with a large tree canopy. Because Mankato is bordered by two major rivers (Minnesota River and Blue Earth River), both of which are subject to TMDLs, water quality and aesthetics have long been a priority. Sweeping activities are considered just as essential as snow plowing or mowing in the city. It keeps the city looking clean, the storm drains open and the ponds and rivers clean. Those benefits are clear and outweigh the cost.
Mankato sweeps their streets throughout the non-frozen months, averaging one full city sweep every 30 days. Sweeping activities are tracked using GPS. Mankato currently weighs their sweeper loads and is utilizing the MPCA’s Street Sweeping Phosphorus Credit Calculator. In 2021, the city collected 1,185.79 tons of sweepings and 7,575 cubic yards of leaves (approximately 1,515 tons). In addition to city streets and alleys, Mankato partners with MnDOT and the county to also sweep those roads in the city limits.
The city of Mankato provides three options to residents each year to dispose of yard waste, including fall leaves:
- City-owned leaf vacuum collection conducted in the fall along all Mankato residential streets at no additional cost.
- Private composting site, at no additional cost for Mankato residents to drop off compostable material.
- Curbside pick-up for an extra cost through a private contractor.
Mankato encourages residents to rake their leaves into the street during a specified window in the fall. The three leaf vacuums run 12+ hours a day in the fall to conduct complete leaf clean-up. The city has found that raking the leaves into the street is more efficient because the citizens are more likely to do it if they don’t have to bag and haul them. Also, the high-powered vacuums will be going by to clean the streets anyway and they cause less damage and are more effective vacuuming leaves off the pavement.
Fall leaf pick-up with the leaf vacuums generally begins when the majority of leaves are on the ground and runs for approximately four weeks. The city forester helps determine when the city should begin leaf collection based on the tree canopy species. The leaf vacuum removes leaves and then chops and compacts them in a self‐contained unit. The chopped, compacted leaves are then composted.
Mankato has 25 people trained to operate the equipment. With so many staff trained, the crews are always out on the road giving them the opportunity to identify illicit discharges such as spills, leaks, garbage, and illegal dumping. In addition, the street crews have spill and drop kits to begin the clean-up process immediately. The kits give the staff time to call for assistance.
Future Opportunities
- Mankato plans to continue to educate the citizens more about water quality and street sweeping.
- Mankato plans to continue to expand the street sweeping program to help reach their TMDL goals.
Lessons Learned and Advice
- Broken Window Theory: The constant presence of sweepers and the watchful eyes of the operators helps control vandalism of city infrastructure, illegal refuse disposal, and illicit discharges. City of Mankato sweeper operators catch a majority of reported illicit discharges.
- Median and Street Washing/ Sweeping: The MS4 permit requirements helped Mankato to reinvent the process of cleaning medians, sidewalks, and bridges. The city used to use water to wash debris from these areas onto the road that would then be swept. To save water and reduce sediment and debris from making its way to catch basins, the city bought a broom attachment for their bobcat to instead push the material onto the road and then sweep it up, allowing for better material recovery and no additional runoff. This process was improved by putting the challenge of meeting MS4 compliance to the operators who know the roads and issues the best. The result was a faster, better sweeping process that was compliant with the MS4 requirements.
- Communication is Key: Cities should also communicate with residents. More knowledge equals less complaints.
- Buy Wisely: Testing equipment prior to purchase is critical, especially in hilly areas and areas that are hard to reach (e.g., narrow alleys).
- Valuing Expertise: Cities should be flexible with the operators because they are the experts. Work with your operators because they can figure out a better way and are able to think outside the box.
Contact Information
- Rick Baird, Environmental Sustainability Coordinator, Rick Baird
- City of Mankato Street Sweeping and Leaf Pickup Program
City of Rochester – Leveraging Staff Flexibility and Expertise for Sweeping Success
| Summary information | |
| City Size (square miles) | 55 |
| City Population (2020) | 121,395 |
| Number and Type of Sweepers Owned by the City | 7 sweepers: Mechanical Broom:2010 Elgin Pelican sweeper, 2014 Elgin Pelican NP, 2010 Elgin Pelican NP sweeper, 2016 Elgin Pelican NP sweeper, 2017 Elgin Pelican sweeper, Regenerative Air – 2015 Tymco 500X Air sweeper, 2010 Elgin Cross Wind sweeper |
| Does the City Use Contractors for Sweeping? | No |
| Curb Miles (either owned or managed by the City) | About 900,458 centerline miles |
| Miles Swept Annually | Up to 11,000 |
| Frequency of Sweeping | Spring: 1 pass
Fall: 1-4 passes based on amount of leaves Central Business District: 4 passes/week with Tymco sweeper Year-round (non-freezing days) 60 non-Central Business District curb miles per week (2 sweepers out 2 nights a week) (see the map below) |
| Disposal | Leaves are composted, screened to remove trash and debris and then reused as dirt. Sand is screened and reused as sub-grade material. The remaining garbage is disposed at the landfill. Rochester has a materials processing facility to store the compost and sand. |
| Annual Sweeping Costs | $80,000 (not including monies spent on equipment replacement and maintenance) |
The city of Rochester began a formal street sweeping program in 2006. The city’s sweeping program has four main purposes: stormwater management, public safety, street maintenance and aesthetics. In addition, the city strives to foster sustainable behavior and environmental education. Some of the street sweepers are emblazoned with messages on preventing debris from getting into the street. The street sweepers also make appearances at community outreach events. To help keep leaves out of the street, the city sends an annual news release in the fall to remind residents about proper yard waste/leaf management. Complimenting these approaches, the city recently launched an Adopt-a-Drain program to promote clearing debris from catch basins. Street sweeping occurs city-wide in the spring and fall. Sweeping in early spring removes sand and residue remaining from winter deicing operations. To maximize the benefits of sweeping, areas at the base of Rochester’s steepest streets are prioritized for the first spring sweeps where sand and material accumulates disproportionately over the winter.
The city is focused on effectively timing sweeping to maximize capturing leaves just after leaf drop. To achieve this, fall sweeping operations typically take three weeks, but can last up to two months since different trees drop their leaves at different times. The sweeping crew leader has the responsibility of evaluating neighborhoods in real-time to identify areas of heavy leaves and prioritizes the sweeping routes. Complementing this real-time evaluation, the city prioritizes fall leaf sweeping in older areas with more mature trees and saves newer development with fewer and smaller trees until later.
Aside from the core spring and fall sweeping, the city operates two sweepers an average of two days per week throughout the remainder of the year to conduct routine sweeping throughout the city (when the temperature is above freezing).The city also sweeps the Central Business District approximately four times a week using a vacuum sweeper to collect fine particles and litter. Sweeping is done overnight to minimize disruption and to maximize access to the curb line where fewer cars are typically parked overnight.
Rochester manages and conducts all their street sweeping activities in-house using city staff. They use up to 15 staff members during fall sweeping. Since the program’s inception, the city has kept all street sweeping activities in-house to maintain flexibility.
Future Opportunities
Rochester has identified several opportunities to improve their program:
- Technology: They’ve installed GPS tracking on one sweeper and would like to expand that capability to the entire sweeper fleet to more efficiently track where sweeping has occurred.
- Collaboration: They are considering partnering with the Parks and Recreation Department, which has developed an Urban Forest Master Plan that contains data on tree canopy throughout the city. The city identified an opportunity to leverage this information to better target priority areas for fall leaf sweeping.
- Data: The city recognizes there is a significant amount of institutional knowledge and experience within the street sweeping crews that is already being used to increase sweeping for water quality benefits but incorporating more data into the process can be important moving forward to help meet water quality goals and MS4 permit requirements. Additional data and evaluation can help establish priority sweeping routes and focus on areas with the most potential to pollute.
Lessons Learned and Advice
- Contractors: Hiring contractors can cause potential scheduling conflicts, limiting the city’s ability to sweep leaves timed with leaf drop. Rochester considered renting equipment to minimize the capital costs associated with owning sweepers but found that owning the equipment and using city staff allows Rochester to both be visible to their residents and gives them the control over targeting sweeping when and where it is needed.
- Drivers and Benefits: Cities should understand the drivers behind their sweeping program and the benefits of the program. Knowing the benefits of the program can provide good justification for a council or board to fund sweeping efforts.
- Technology: Focus on incorporating technology to understand hotspots and maximizing the benefits of sweeping with the least amount of effort.
- Parking Restrictions: New sweeping programs should consider parking restrictions to help maximize sweeper contact with the curb line where most material accumulates.
- Perception: Street sweeping is one of the services that residents see the most. A good street sweeping program can create a positive perception of how residents’ tax dollars are being spent.
Contact Information
- Stephanie Hatzenbihler, Environmental Education Specialist Stephanie Hatzenbihler
- Stormwater Management
- Street Maintenance
| Summary information | |
| City Size (square miles) | 41 |
| City Population (2020) | 68,881 |
| Number and Type of Sweepers Owned by the City | Mechanical Broom: 3 Elgin Pelican Regenerative Air: 2 Tymco 500X |
| Does the City Use Contractors for Sweeping? | No |
| Curb Miles (either owned or managed by the City) | 770 lane miles |
| Miles Swept Annually
1,825 miles, including alleys | |
| Frequency of Sweeping | 1 Spring sweep 1 Fall sweep |
| Priority/storm event summer sweeps: | Benton County, by priority areas: 2 times/year (low areas); 3 times/year (medium areas); 4 times/year (high areas) Sauk River Watershed District, by priority areas: 2 times/year (low areas); quarterly (medium areas); monthly (high areas) |
| Disposal | Primarily beneficial reuse and composting, minimal landfill waste |
| Annual Sweeping Costs | $70,000 (excludes sweeper replacement) |
| Funding Source | Stormwater Utility Fund |
St. Cloud uses a variety of ways to gather street materials throughout the year. In the spring and after summer storms, the sweepers are run together in tandem. The broom sweeper is first and then the regenerative sweeper follows behind to gather smaller particulates and fines such as dust. During the spring sweep, St. Cloud begins with the major roads then goes into nearby neighborhoods, sweeping every city road at least once. Arterials are often swept twice. Mid-year sweeping efforts in the summer are more focused on watershed areas that drain to the Sauk and Mississippi Rivers and routes with bike lanes. During fall leaf pickup, the entire city is covered one time, twice if weather permits.
Portions of St. Cloud are in the Sauk River watershed, and the city works closely with the Sauk River Watershed District (SRWD) to improve water quality. The city received a cost-share grant from SWRD to purchase one of their regenerative air sweepers. As part of the agreement, the city sweeps the areas within the district more frequently. A similar grant was also provided through Benton County Soil and Water Conservation District for the purchase of the other regenerative air sweeper in exchange for more frequent sweeping.
Based on the prevalence of sediment accumulation, the city identified three priority sweeping regimes for the SRWD sweeping area. Main roads are swept once a month, quarterly sweeping occurs east of the Sauk River (gravel driveways are common and contribute to sediment loads), and biannual sweeping occurs west of the river (fewer trees, larger yards).
The city conducted a cost-benefit analysis to determine the most cost-effective way to dispose of sweeper materials. Results showed that conversion to clean fill for reuse and compost was more cost effective, despite the staff time, effort and space needed to manage and store sweepings. The cost-benefit analysis indicated the city would save about $75,000 in costs annually using this reuse strategy versus disposing of all non-leaf sweepings at the landfill.
The swept materials are stockpiled, then screened creating a clean fill and spoils (e.g. trash, rocks, debris) pile. The spoils are set aside to break down and screened again the following year, creating cleaner fill. The city follows MPCA reuse guidance and offers the clean fill for city construction projects and 3rd party contractors. Leaf sweepings go into a separate pile for composting along with yard waste collections. The spoils pile is disposed of at a solid waste landfill. On average, the city removes about 4,800 yards of material annually with its street sweeping program. Approximately 2,450 yards can be reused per MPCA guidance, 2,275 yards are leaf sweepings and 75 yards is spoils. By screening and composting the sweeper materials, the city diverts over 98% of swept materials to alternative uses. Less than 2% of the material is sent to the landfill.
Future Opportunities
There is a forthcoming Sauk River impairment. The city anticipates evaluating the use of MPCA’s Street Sweeping Calculator to quantify the benefits of sweeping to proactively help address the impairment.
Lessons Learned and Advice
- Training: St. Cloud recommends cross training staff and developing well-trained staff that can provide consistency across job functions.
- Education and Outreach: Conduct as much public education and outreach as possible—to residents and city staff. City MS4 staff talk to the operations staff every spring to help explain the importance of water quality and make the connection with their street sweeping operations. This leads to operator buy-in and interest. In-turn operators participate in public outreach efforts, including educational videos. St. Cloud has had success when staff see how their efforts are worthwhile and valuable.
- Fine Particles: Running the mechanical and regenerative air sweepers in tandem makes a noticeable difference in the collection of fine particles.
- Funding: Having a watershed/implementation plan that identifies street sweeping for water quality as a high priority is key to receiving funding for equipment.
- Tracking: Track hours and costs of operating a sweeping program. This can help document the true cost of the program as well as the return on investment. The city allocates over 2 FTEs to its street sweeping annually (4,500 hours). Tracking staff hours helps allocate and plan staff time and shows the need for additional staff time needed for routine stormwater inspection and maintenance activities.
- Data Collection: Find a simple method of data collection that works for your city so that staff will participate. If it’s too complicated, there can be resistance. Show staff the results of how their data are used so they understand what they are doing makes a difference. Data collection demonstrates the impacts of sweeping for water quality and when it comes time to seek funding to replace equipment.
Contact Information
- Noah Czech, Stormwater Compliance Specialist Noah Czech
- Tom Zabinski, Operations Manager – Street and Alley Tom Zabinski