Difference between revisions of "Types of iron enhanced sand filter"
(Created page with "==Iron-enhanced sand filter basin== An iron-enhanced sand filter basin is similar to a surface sand filter with iron mixed evenly throughout a portion of the filtration media...") |
m (→Related pages) |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:Pdf image.png|100px|left|thumb|alt=pdf image|<font size=3>[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=File:Types_of_iron_enhanced_sand_filter_-_Minnesota_Stormwater_Manual.pdf Download pdf]</font size>]] | ||
| + | [[File:General information page image.png|left|100px|alt=image]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This page describes two types of iron-enhanced practices - sand filters and pond benches. | ||
| + | |||
==Iron-enhanced sand filter basin== | ==Iron-enhanced sand filter basin== | ||
| + | [[File:Sand infiltration 2.JPG|thumb|left|300px|alt=photo of an iron ehanced sand filter basin|<font size=3>Iron enhanced sand filter basin, Maplewood, MN. Photo courtesy of Ramsey-Washington Watershed District.</font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | An <span title="Iron-enhanced sand filters are filtration Best Management Practices (BMPs) that incorporate filtration media mixed with iron. The iron removes several dissolved constituents, including phosphate, from stormwater. Iron-enhanced sand filters may be particularly useful for achieving low phosphorus levels needed to improve nutrient impaired waters. "> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Iron_enhanced_sand_filter_(Minnesota_Filter) '''iron-enhanced sand filter''']</span> basin is similar to a surface <span title="Filtration of stormwater through a sand filtering material whose purpose is to remove pollution from runoff"> '''[https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Filtration sand filter]'''</span> with iron mixed evenly throughout a portion of the filtration media. Surface sand filter design and operating parameters also applicable to iron-enhanced sand filter basins include | ||
| + | *the use of a flow splitter to control inflow volume; | ||
| + | *''required'' <span title="Pretreatment reduces maintenance and prolongs the lifespan of structural stormwater BMPs by removing trash, debris, organic materials, coarse sediments, and associated pollutants prior to entering structural stormwater BMPs. Implementing pretreatment devices also improves aesthetics by capturing debris in focused or hidden areas. Pretreatment practices include settling devices, screens, and pretreatment vegetated filter strips."> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Pretreatment '''pretreatment''']</span> per the MPCA’s [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Construction_stormwater_program General Construction Stormwater Permit]; | ||
| + | *filtration bed depth (approximately 18 inches); and | ||
| + | *use of perforated pipes (or other appropriate drain pipe design) in a gravel bed to drain the filter. | ||
| + | To prepare the <span title="One of many different structural or non–structural methods used to treat runoff"> '''best management practice'''</span> (bmp) for runoff from the next storm event and because the filter bed contains iron which can foul the filter, the bed should drain within 48 hours of storm completion. | ||
| − | + | If the iron-enhanced sand filter lies below the groundwater table, an [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Liners_for_stormwater_management#Liner_specifications Level 1 impermeable liner] may be necessary to prevent groundwater inflows. The [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Construction_stormwater_program Construction Stormwater Permit] requires a liner for a filtration system with less than 3 feet of separation to the seasonally saturated water table. A [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Liners_for_stormwater_management#Liner_specifications Level 1 liner] is recommended. | |
| − | |||
| − | If the iron-enhanced sand filter lies below the groundwater table, an impermeable liner may be necessary to prevent groundwater inflows. The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
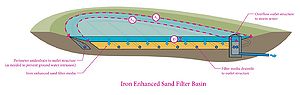
| − | + | [[File:iron enhanced sand filter basin schematic 1.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=schematic of an iron enhanced sand filter basin|<font size=3>Iron-enhanced sand filter basin schematic showing parameters used to calculate the treatment volume capacity.</font size>]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{alert|The draft MPCA Construction Stormwater Permit Requires a filtration system with less than 3 feet of separation to seasonally saturated soils to have an impermeable liner.|alert-danger}} | ||
| + | {{alert|The MPCA Construction Stormwater Permit Requires pretreatment for filtration systems.|alert-danger}} | ||
| + | ==Iron-enhanced sand bench in wet ponds== | ||
| + | [[File:iron enhanced sand bench Prior Lake 1.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=photo of an iron ehanced sand bench|<font size=3>Iron enhanced sand bench, Prior Lake, MN. Photo courtesy of Ross Bintner.</font size>]] | ||
| − | An iron-enhanced sand | + | An iron-enhanced sand bench in wet ponds consists of a <span title="A stormwater retention basin that includes a combination of permanent pool storage and extended detention storage above the permanent pool to provide additional water quality or rate control"> [https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=Stormwater_ponds '''wet pond''']</span> with an iron-sand trench along the perimeter of the pond. The elevation at the top of the trench is at the normal water elevation of the pond. During a storm event, water rises above the trench elevation and fills the live storage area of the pond. Stormwater will filter through the bench with excess stormwater <span title="Stormwater runoff in excess of the design flow, which is diverted around a stormwater structure"> '''bypassing'''</span> the bench. Along with watershed, storm event, and pond geometry variables, the volume of stormwater passing through the bench will depend upon the outlet structure design. |
| − | + | Many of the design and operating considerations of an [[Types of iron enhanced sand filter#Iron enhanced sand filter basin|iron-enhanced sand filter basin]] also apply to the iron-enhanced sand bench. In addition to the 48-hour drain dry time, to prevent pond drawdown below the normal water level and allow the trench to dry and aerate, a geomembrane liner needs to be placed or the soils between the pond and the sand bench needs to be prepared to inhibit infiltration from the pond into the trench. A [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Liners_for_stormwater_management#Liner_specifications Level 1 liner] is recommended. | |
| − | |||
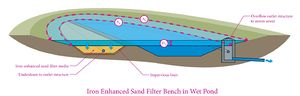
| − | + | [[File:iron enhanced sand filter bench schematic 1.jpg|thumb|300px|alt=schematic of an iron enhanced sand filter bench|<font size=3>Iron-enhanced sand filter bench schematic showing parameters used to calculate the treatment volume capacity.</font size>]] | |
| − | ==Iron-enhanced sand bench | ||
| + | <noinclude> | ||
| − | + | ==Related pages== | |
| + | *[[Overview for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Types of iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Design criteria for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | <!--*[[Construction specifications for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Construction observations for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Assessing the performance of iron enhanced sand filter]]--> | ||
| + | *[[Operation and maintenance of iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Calculating credits for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | <!--[[Cost-benefit considerations for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Additional considerations for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Links for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[External resources for iron enhanced sand filter]]--> | ||
| + | *[[References for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| + | *[[Supporting material for iron enhanced sand filter]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Structural practices/Iron enhanced sand filter]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Level 3 - Best management practices/Guidance and information/BMP types and terminology]] | |
| + | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:42, 23 November 2022
This page describes two types of iron-enhanced practices - sand filters and pond benches.
Iron-enhanced sand filter basin
An iron-enhanced sand filter basin is similar to a surface sand filter with iron mixed evenly throughout a portion of the filtration media. Surface sand filter design and operating parameters also applicable to iron-enhanced sand filter basins include
- the use of a flow splitter to control inflow volume;
- required pretreatment per the MPCA’s General Construction Stormwater Permit;
- filtration bed depth (approximately 18 inches); and
- use of perforated pipes (or other appropriate drain pipe design) in a gravel bed to drain the filter.
To prepare the best management practice (bmp) for runoff from the next storm event and because the filter bed contains iron which can foul the filter, the bed should drain within 48 hours of storm completion.
If the iron-enhanced sand filter lies below the groundwater table, an Level 1 impermeable liner may be necessary to prevent groundwater inflows. The Construction Stormwater Permit requires a liner for a filtration system with less than 3 feet of separation to the seasonally saturated water table. A Level 1 liner is recommended.
Iron-enhanced sand bench in wet ponds
An iron-enhanced sand bench in wet ponds consists of a wet pond with an iron-sand trench along the perimeter of the pond. The elevation at the top of the trench is at the normal water elevation of the pond. During a storm event, water rises above the trench elevation and fills the live storage area of the pond. Stormwater will filter through the bench with excess stormwater bypassing the bench. Along with watershed, storm event, and pond geometry variables, the volume of stormwater passing through the bench will depend upon the outlet structure design.
Many of the design and operating considerations of an iron-enhanced sand filter basin also apply to the iron-enhanced sand bench. In addition to the 48-hour drain dry time, to prevent pond drawdown below the normal water level and allow the trench to dry and aerate, a geomembrane liner needs to be placed or the soils between the pond and the sand bench needs to be prepared to inhibit infiltration from the pond into the trench. A Level 1 liner is recommended.
Related pages
- Overview for iron enhanced sand filter
- Types of iron enhanced sand filter
- Design criteria for iron enhanced sand filter
- Operation and maintenance of iron enhanced sand filter
- Calculating credits for iron enhanced sand filter
- References for iron enhanced sand filter
- Supporting material for iron enhanced sand filter
This page was last edited on 23 November 2022, at 22:42.