Difference between revisions of "Overview of stormwater infiltration"
m |
m |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
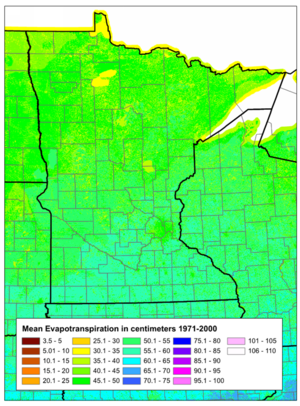
[[file:Minnesota ET.png|300px|thumb|alt=map of ET in Minnesota|<font size=3>Average Evapotranspiration Rates for Minnesota (Source: US Geological Survey, with permission).</font size>]] | [[file:Minnesota ET.png|300px|thumb|alt=map of ET in Minnesota|<font size=3>Average Evapotranspiration Rates for Minnesota (Source: US Geological Survey, with permission).</font size>]] | ||
*'''Evapotranspiration rate''': The evapotranspiration (ET) rate is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration. It is an important function when the infiltration BMP relies at least in part on vegetation for its stormwater management. The average ET rate in Minneapolis and St. Paul from 2001 to 2010 was 0.16 inches per day during the growing season. This is a general value and is subject to variation due to several coarse and fine-scale conditions. Detailed records for certain areas of Minnesota are available on the [http://www.dnr.state.mn.us/climate/summaries_and_publications/index.html Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Climate Summaries and Publications web site]. It should be noted that in calculating [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Overview_of_stormwater_credits credits] for stormwater volume, differentiating between ET and infiltration may be unimportant. But actively transpiring vegetation in an infiltration system can significantly reduce the actual volume that infiltrates. | *'''Evapotranspiration rate''': The evapotranspiration (ET) rate is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration. It is an important function when the infiltration BMP relies at least in part on vegetation for its stormwater management. The average ET rate in Minneapolis and St. Paul from 2001 to 2010 was 0.16 inches per day during the growing season. This is a general value and is subject to variation due to several coarse and fine-scale conditions. Detailed records for certain areas of Minnesota are available on the [http://www.dnr.state.mn.us/climate/summaries_and_publications/index.html Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Climate Summaries and Publications web site]. It should be noted that in calculating [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Overview_of_stormwater_credits credits] for stormwater volume, differentiating between ET and infiltration may be unimportant. But actively transpiring vegetation in an infiltration system can significantly reduce the actual volume that infiltrates. | ||
| − | *'''Storm intensity''': When the intensity of the storm is greater than the IR of the soil, runoff may occur (WEF, 2012). This is due to the fact that as storm intensity increases, the storage on the surface and in the subsurface macropores is more quickly exhausted and the soils rapidly reach saturation. | + | *'''Storm intensity''': When the intensity of the storm is greater than the IR of the soil, runoff may occur ([http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/References_for_stormwater_infiltration WEF, 2012]). This is due to the fact that as storm intensity increases, the storage on the surface and in the subsurface macropores is more quickly exhausted and the soils rapidly reach saturation. |
*'''Antecedent soil moisture condition''': The antecedent moisture condition, or the moisture condition of the soil prior to the storm event, will affect the space available in the subsurface for infiltration. High antecedent moisture conditions reduce the amount of pore space available for infiltration, which in turn decreases the amount of runoff water entering the soil. | *'''Antecedent soil moisture condition''': The antecedent moisture condition, or the moisture condition of the soil prior to the storm event, will affect the space available in the subsurface for infiltration. High antecedent moisture conditions reduce the amount of pore space available for infiltration, which in turn decreases the amount of runoff water entering the soil. | ||
*'''Soil characteristics''': While infiltration is more rapid in coarser soils (e.g., medium to coarse sands or gravels) than in fine grained soils (e.g. silts and clays), other soil properties also affect infiltration. Examples include the following. | *'''Soil characteristics''': While infiltration is more rapid in coarser soils (e.g., medium to coarse sands or gravels) than in fine grained soils (e.g. silts and clays), other soil properties also affect infiltration. Examples include the following. | ||
**Bulk density of the soil: As the bulk density of the soil increases, the IR generally decreases. The average bulk density of different soils can be found [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Comparison_of_bulk_densities_for_undisturbed_soils_and_common_urban_conditions here]. | **Bulk density of the soil: As the bulk density of the soil increases, the IR generally decreases. The average bulk density of different soils can be found [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Comparison_of_bulk_densities_for_undisturbed_soils_and_common_urban_conditions here]. | ||
**Soil layering: Infiltration rates into a soil are typically controlled by the lowest infiltration layer in the soil, particularly when low infiltration layers are thick and located near the surface. | **Soil layering: Infiltration rates into a soil are typically controlled by the lowest infiltration layer in the soil, particularly when low infiltration layers are thick and located near the surface. | ||
| − | *'''Temperature''': Infiltration rates tend to decrease as temperature decreases. This is due to the increase in viscosity of the stormwater at lower temperatures (Lin et al., 2003; Braga et al., 2007; Emerson and Traver, 2008). | + | *'''Temperature''': Infiltration rates tend to decrease as temperature decreases. This is due to the increase in viscosity of the stormwater at lower temperatures ([http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/References_for_stormwater_infiltration Lin et al.], 2003; [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/References_for_stormwater_infiltration Braga et al.], 2007; [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/References_for_stormwater_infiltration Emerson and Traver], 2008). |
===Limitations and disadvantages of stormwater infiltration=== | ===Limitations and disadvantages of stormwater infiltration=== | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 4 June 2015
This site is being updated. Anticipated completion date is June, 2015.
Stormwater infiltration is the process by which rainfall and stormwater runoff flows into and through the subsurface soil. Stormwater infiltration occurs when rainfall lands on pervious surfaces, when runoff flows across pervious surfaces, and when runoff is collected and directed to a stormwater infiltration Best Management Practice (BMP).
Current stormwater management policies encourage, when appropriate, maximizing the infiltration of stormwater to reduce the volume of runoff discharging to surface waters. In addition to reducing runoff volume, stormwater infiltration helps reduce stormwater pollutant loading to surface waters. Many factors influence the rate and volume of stormwater infiltration including soil characteristics, storage capacity, and vegetation. These and other factors are discussed in further detail in subsequent sections. Once stormwater infiltrates into the soil, it has the potential to enter the groundwater and become part of the subsurface flow.
For the purposes of this section, infiltration BMPs are considered those without underdrains.
Contents
Basic concepts of stormwater infiltration
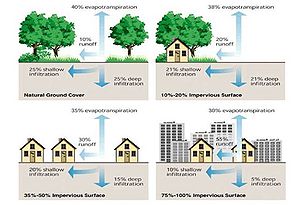
Stormwater runoff is considered to be any water that runs off pervious and impervious surfaces after a rainfall or snowmelt event, with a greater percentage running off from impervious surfaces. In urban areas, runoff can constitute approximately 30 to 55 percent of the water budget. In comparison, runoff may constitute as little as 10 percent in forested or rural areas (FISRWG, 1998).
Role of stormwater infiltration in the natural water cycle
The increase in impervious surfaces can disrupt the natural water cycle and alter the surrounding environment via the decrease of groundwater recharge and the increase of water directly flowing to surface waters. As a likely consequence, this can lead to a reduction in the baseflow of streams, a decrease in the elevation of the groundwater table, and transport of sediment and pollutant loads into surface waters. A more detailed explanation of stormwater runoff and its effects on the environment can be found here.
Stormwater infiltration in urban areas can be enhanced by the disconnection of impervious surfaces and by the improvement of pervious surfaces such as turf. Impervious surface disconnection is the direction or redirection of stormwater runoff from impervious surfaces (e.g., sidewalks, parking lots, rooftops, etc.) onto pervious surfaces, such as a roof drain discharging onto a lawn. Redirection of impervious surface runoff to pervious areas promotes infiltration and reduces overall site runoff. The reduction in site runoff from impervious surface disconnection can vary considerably depending on many factors including the size of the contributing drainage area, size and infiltration capacity of the soils, vegetation in the area receiving the additional stormwater, slope and site grading and other site conditions. Stormwater infiltration can also be enhanced by improvement of pervious surfaces, such as amending soil with compost to increase the water holding capacity of the soil.
In new developments, stormwater infiltration is often intended to mimic the natural hydrologic cycle. Stormwater infiltration in redevelopment aims to mitigate changes in the urban water cycle brought about by increases in impervious surfaces caused by the urbanization. Infiltration can achieve the following objectives.
- Decrease peak runoff flow rates
- Decrease the volume of stormwater runoff
- Reduce stormwater pollutant loading to surface waters
- Promote retention and breakdown of contaminants in the soil and act as a pollutant barrier between the land surface and groundwater
- Increase groundwater recharge
- Preserve baseflow in streams
- Reduce thermal impacts of stormwater runoff
Typically, stormwater from disconnected impervious surfaces is routed to a stormwater BMP. Infiltration BMPs achieve the above objectives by capturing, retaining, and infiltrating stormwater. Infiltration BMPs include
- infiltration basins,
- infiltration trenches,
- bioretention-bioinfiltration (most often a rain garden),
- permeable pavements, and
- tree trenches/tree boxes (a form of bioretention).
Small and medium sized infiltration BMPs are often located at the beginning of a stormwater treatment train, while larger BMP are often placed at the end of the train. These BMPs can also be installed as off-line treatment systems. Infiltration BMPs are most suitable in sites with permeable soils and sufficient separation from the seasonally high groundwater table, bedrock, and polluted sites. While infiltration practices can remove some types of physical and chemical pollutants, careful consideration should be given to implementing stormwater infiltration practices in potential stormwater hotspots (PSH) or at sites with known pollution issues such as brownfields. For a discussion of constraints on use of stormwater infiltration practices, see Constraints on the stormwater infiltration page.
Factors affecting stormwater infiltration
Several interrelated factors that control the infiltration of stormwater into the soil/subsurface are described below. It is important to clarify the terms soil, subsurface, and engineered media. In general, the soil or subsurface is the native material at a site. These terms may be used interchangeably when discussing a BMP, although subsoil typically refers to soil at depth. Engineered media is a material created for a site to enhance infiltration, plant growth, pollutant removal, and so on. Engineered media range from coarse-textured aggregate beneath permeable pavement systems to high organic materials used in bioretention systems. When an engineered media is used, the soil or subsurface refers to the material underneath the engineered media.
- Infiltration rate: The infiltration rate (IR) is one of the main factors affecting the performance of an infiltration BMP. While design rates exist based on soil type, it is HIGHLY RECOMMENDED that the rates be measured in-situ. Information on how to find the IR in the field can be found here. Designers should test soil at fully saturated conditions (saturated hydraulic conductivity or Ksat) to obtain the most conservative rate. All design and credit information contained in the MPCA’s stormwater manual is based on the assumption of saturated soil.
- Evapotranspiration rate: The evapotranspiration (ET) rate is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration. It is an important function when the infiltration BMP relies at least in part on vegetation for its stormwater management. The average ET rate in Minneapolis and St. Paul from 2001 to 2010 was 0.16 inches per day during the growing season. This is a general value and is subject to variation due to several coarse and fine-scale conditions. Detailed records for certain areas of Minnesota are available on the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Climate Summaries and Publications web site. It should be noted that in calculating credits for stormwater volume, differentiating between ET and infiltration may be unimportant. But actively transpiring vegetation in an infiltration system can significantly reduce the actual volume that infiltrates.
- Storm intensity: When the intensity of the storm is greater than the IR of the soil, runoff may occur (WEF, 2012). This is due to the fact that as storm intensity increases, the storage on the surface and in the subsurface macropores is more quickly exhausted and the soils rapidly reach saturation.
- Antecedent soil moisture condition: The antecedent moisture condition, or the moisture condition of the soil prior to the storm event, will affect the space available in the subsurface for infiltration. High antecedent moisture conditions reduce the amount of pore space available for infiltration, which in turn decreases the amount of runoff water entering the soil.
- Soil characteristics: While infiltration is more rapid in coarser soils (e.g., medium to coarse sands or gravels) than in fine grained soils (e.g. silts and clays), other soil properties also affect infiltration. Examples include the following.
- Bulk density of the soil: As the bulk density of the soil increases, the IR generally decreases. The average bulk density of different soils can be found here.
- Soil layering: Infiltration rates into a soil are typically controlled by the lowest infiltration layer in the soil, particularly when low infiltration layers are thick and located near the surface.
- Temperature: Infiltration rates tend to decrease as temperature decreases. This is due to the increase in viscosity of the stormwater at lower temperatures (Lin et al., 2003; Braga et al., 2007; Emerson and Traver, 2008).
Limitations and disadvantages of stormwater infiltration
The following general limitations should be recognized when considering infiltration BMPs.
- Failure can occur due to improper design and/or siting.
- Infiltration BMPs may not be appropriate for sites with soils having a low infiltration capacity.
- Infiltration BMPs may not be appropriate for areas with steep slopes.
- Infiltration BMPs are susceptible to clogging by sediment and other debris, and may require a greater amount of maintenance compared to other BMPs.
- Algae growth within the BMP can block the infiltration of runoff into the subsurface (WEF, 2012).
- Infiltration BMPs are not ideal for stormwater runoff from land uses or activities with the potential for high loads of certain pollutants. The Minnesota Construction General Permit prohibits infiltration of runoff from vehicle fueling areas and certain industrial practices.
- Infiltration BMPs may increase the risk of groundwater contamination depending on subsurface conditions, pollution concentrations in the runoff, and aquifer susceptibility.
- Wide-scale implementation is required to significantly reduce the rate and volume of discharge to downstream surface waters, especially in areas with a high density of impervious surfaces (WEF, 2012).
Pollutant fate and transport for stormwater infiltration
As stormwater travels across the land surface into infiltration BMPs, it can pick up various water quality pollutants and deliver them to the subsurface. There is concern that these pollutants have the ability to travel through the vadose zone and ultimately impact the groundwater. Whether or not this will occur depends on the type and amount of pollutant present, the volume of infiltration, the type of infiltration BMP, and subsurface conditions.
Detailed information on this topic can be found on the page addressing water quality effects of stormwater infiltration.