Difference between revisions of "Stormwater infiltration and contaminated soils and groundwater"
(Created page with "{{alert|Coming soon: we anticipate populating this page in November, 2015|alert-info}} ==Related pages== *Overview of stormwater infiltration *Pre-treatment considerati...") |
m (→Related pages) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
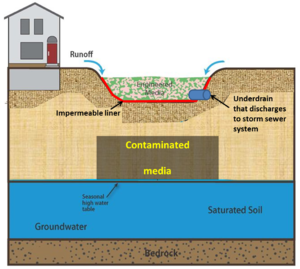
| − | {{alert| | + | [[file:Contaminated site 2.png|300px|thumb|alt=schematic of contaminated site|<font size=3>Schematic for site where infiltration is not feasible. Note impermeable liner and discharge from underdrain to storm sewer system. For a discussion of considerations at sites with on- or off-site contamination, see [[Overview of considerations for sites with on-site and off-site contamination|this page]].</font size>]] |
| + | [[File:Technical information page image.png|left|100px|alt=image]] | ||
| + | [[File:Pdf image.png|100px|thumb|left|alt=pdf image|https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php?title=File:Stormwater_infiltration_and_contaminated_soils_and_groundwater_-_Minnesota_Stormwater_Manual.pdf Download pdf]</font size>]] | ||
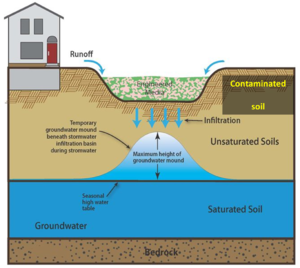
| + | [[file:Contaminated site 3.jpg|300px|thumb|alt=schematic of contaminated soil|<font size=3>Schematic for site where infiltration is feasible. Note that contaminated soils are overlain by an impermeable surface and the groundwater mound does not extend into the contamination. Source:CDM Smith.</font size>]] | ||
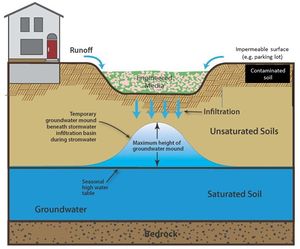
| + | [[file:Contaminated soil 1.png|300px|thumb|alt=schematic of contaminated soil|<font size=3>Schematic for site where infiltration may be feasible. Although the groundwater mound does not extend into the contamination, it needs to be determined if water will infiltrate through the contaminated soil and transport pollutants at levels of concern. Source:CDM Smith. For a discussion of considerations at sites with on- or off-site contamination, see [[Overview of considerations for sites with on-site and off-site contamination|this page]].</font size>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{alert|The Construction Stormwater General permit prohibits permittees from constructing infiltration systems where infiltrating stormwater may mobilize high levels of contaminants in soil or groundwater. Permittees must either complete the checklist ([[File:Contamination screening checklist for stormwater infiltration.xlsx]] or [[File:Contamination screening checklist for stormwater infiltration July 2018.xlsx]]) or conduct their own assessment to determine the suitability for infiltration. Permittees must retain the checklist or assessment with the SWPPP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information and to access the MPCA's "contamination screening checklist", [[Stormwater Infiltration and soil/groundwater contamination: A guide to the Construction Stormwater Permit requirements|link here]].|alert-danger}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Managing stormwater at sites with contaminated soils or groundwater is challenging because the infiltrated runoff has the potential to transport contaminants in the soil to the groundwater or mobilize contaminants in the groundwater. Stormwater at contaminated sites can be managed by surface capture and treatment, or as infiltration by avoiding contact between runoff and contaminated soils and groundwater. Surface capture includes [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Stormwater_filtration_Best_Management_Practices filtration] and [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Stormwater_sedimentation_Best_Management_Practices sedimentation] practices. When considering surface capture and treatment of runoff at contaminated sites, the surface capture treatment system will usually need an impermeable barrier to prevent infiltration and potential mobilization of contaminates in soil or groundwater. When considering [http://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Stormwater_infiltration_Best_Management_Practices stormwater infiltration] at contaminated sites, it is essential to develop management options to ensure contaminants are not mobilized. To accomplish this, a project proposer must understand site conditions (e.g. soils, hydrogeology, land use), the nature and extent of contamination (i.e. site conceptual model), and applicable regulations. The following pages provide information on these topics, including case studies and links to additional information and guidance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Contaminated sites and stormwater infiltration]] | ||
| + | *[[Stormwater Infiltration and soil/groundwater contamination: A guide to the Construction Stormwater Permit requirements]] | ||
| + | *[[Screening assessment for contamination at potential stormwater infiltration sites]] | ||
| + | *[[Stormwater infiltration guidance for sites with known or high potential for soil or groundwater contamination on or off-site]] | ||
| + | *[[Links to Minnesota Pollution Control Agency cleanup and remediation information]] | ||
| + | *[[Case studies for stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites]] | ||
| + | *[[Links to information and guidance on stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites]] | ||
| + | *[[References for stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites]] | ||
| + | |||
==Related pages== | ==Related pages== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 42: | ||
<noinclude> | <noinclude> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Level 2 - Technical and specific topic information/infiltration]] |
| + | [[Category:Level 2 - Technical and specific topic information/soils and media]] | ||
</noinclude> | </noinclude> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:17, 1 December 2022
Managing stormwater at sites with contaminated soils or groundwater is challenging because the infiltrated runoff has the potential to transport contaminants in the soil to the groundwater or mobilize contaminants in the groundwater. Stormwater at contaminated sites can be managed by surface capture and treatment, or as infiltration by avoiding contact between runoff and contaminated soils and groundwater. Surface capture includes filtration and sedimentation practices. When considering surface capture and treatment of runoff at contaminated sites, the surface capture treatment system will usually need an impermeable barrier to prevent infiltration and potential mobilization of contaminates in soil or groundwater. When considering stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites, it is essential to develop management options to ensure contaminants are not mobilized. To accomplish this, a project proposer must understand site conditions (e.g. soils, hydrogeology, land use), the nature and extent of contamination (i.e. site conceptual model), and applicable regulations. The following pages provide information on these topics, including case studies and links to additional information and guidance.
- Contaminated sites and stormwater infiltration
- Stormwater Infiltration and soil/groundwater contamination: A guide to the Construction Stormwater Permit requirements
- Screening assessment for contamination at potential stormwater infiltration sites
- Stormwater infiltration guidance for sites with known or high potential for soil or groundwater contamination on or off-site
- Links to Minnesota Pollution Control Agency cleanup and remediation information
- Case studies for stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites
- Links to information and guidance on stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites
- References for stormwater infiltration at contaminated sites
Related pages
- Overview of stormwater infiltration
- Pre-treatment considerations for stormwater infiltration
- BMPs for stormwater infiltration
- Pollutant fate and transport in stormwater infiltration systems
- Surface water and groundwater quality impacts from stormwater infiltration
- Stormwater infiltration and groundwater mounding
- Stormwater infiltration and setback (separation) distances
- Karst
- Shallow soils and shallow depth to bedrock
- Shallow groundwater
- Soils with low infiltration capacity
- Potential stormwater hotspots
- Stormwater and wellhead protection
- Stormwater infiltrations and contaminated soils and groundwater
- Decision tools for stormwater infiltration
- Stormwater infiltration research needs
- References for stormwater infiltration
This page was last edited on 1 December 2022, at 01:17.