Difference between revisions of "Stormwater infiltration"
m |
m |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
*Maintenance and long-term infiltration (design phase maintenance) | *Maintenance and long-term infiltration (design phase maintenance) | ||
*Pretreatment's role in infiltration | *Pretreatment's role in infiltration | ||
| + | *Potential groundwater impacts from infiltration in soils with limited organic matter and high infiltration rates, such as underground practices | ||
[[Category:Level 2 - Technical and specific topic information/infiltration]] | [[Category:Level 2 - Technical and specific topic information/infiltration]] | ||
Revision as of 18:25, 18 January 2023
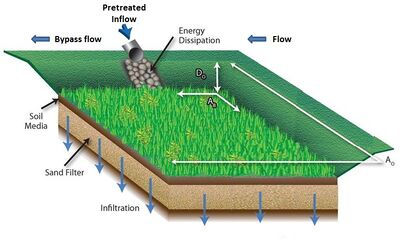
Schematic showing an infiltration basin, which is one of several stormwater control practices designed to infiltrate stormwater runoff. Infiltration practices capture stormwater runoff and allow it to infiltrate into the underlying soil. Pollutant removal occurs through a variety of mechanisms, including adsorption, absorption, plant uptake, and degradation. Note that inflow into the practice has undergone pretreatment and that once the practice is filled, runoff bypasses the practice rather than entering it.
This page contains links to several pages that address infiltration of stormwater runoff. Link to portal for Infiltration Practices.
- Overview
- Pretreatment considerations for stormwater infiltration
- Best Management Practices (BMPs)
- Water quality
- Water quantity
- Separation distances
- Constraints
- When infiltration is not authorized under a stormwater permit
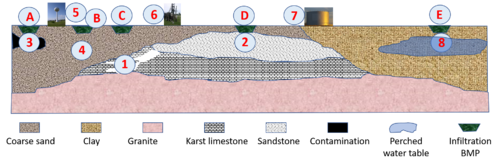
- Karst
- Shallow soils and shallow depth to bedrock
- Shallow groundwater
- Soils with low infiltration capacity
- Potential stormwater hotspots
- Wellhead protection
- Contaminated soils and groundwater
- Procedures for investigating sites with potential constraints
- Guidance for amending soils with rapid or high infiltration rates
- Decision tools
- Determining soil infiltration
- Information on soil
- Chloride and groundwater
- Impacts of stormwater infiltration on chloride in Minnesota groundwater - White paper produced for the Minnesota Groundwater Association
- Calculator for estimating chloride loading to groundwater
- Guidance for calculator to estimate chloride loading to groundwater from infiltration
- References for stormwater infiltration
- Supporting material for infiltration
Potential research topics or better guidance (for January 19 webinar)
- Long-term effects of perennial vegetation and soil biology on infiltration in stormwater practices
- Dynamic infiltration (Villanova)
- Road salt and effects of chloride (groundwater) and sodium (soil structure)
- Maintenance and long-term infiltration (design phase maintenance)
- Pretreatment's role in infiltration
- Potential groundwater impacts from infiltration in soils with limited organic matter and high infiltration rates, such as underground practices