Infiltration Basin
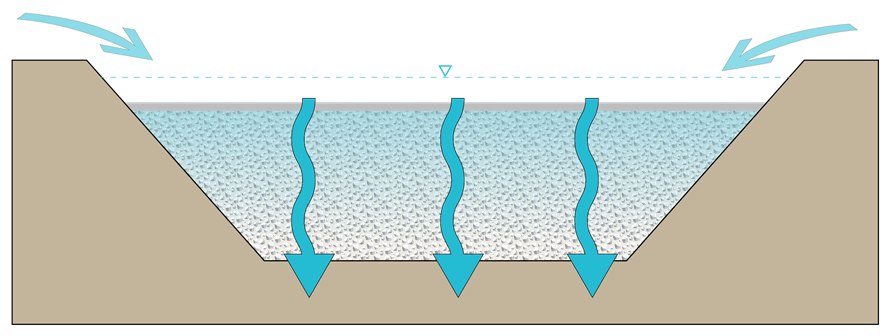 |
A natural or constructed impoundment that captures, temporarily stores and infiltrates the design volume of water into the surrounding naturally permeable soil over several days. In the case of a constructed basin, the impoundment is created by excavation or embankment. |
5 to 50 acres |
Sedimentation / Infiltration |
End |
TSS: High
TN: Medium/High
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High
Pathogens: High |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Limited
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: Limited |
Low $0.5‐$1.3 CF |
Simple‐Intensive |
Needed
Oil/Water Separator, Vegetated Filter, Sediment Basin, Water Quality Inlets |
Low |
Bioinfiltration Basin
 |
Often called rain gardens, bioinfiltration basins use engineered or mixed soils and plantings to capture and infiltrate runoff. Pollutants are removed using highly permeable soils that are able to draw the basin down in less than 48 hours. |
< 5 acres |
Sedimentation / Infiltration |
Beginning |
TSS: High
TN: Low/Medium
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Limited
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: Limited |
Low $0.5‐$1.3 CF |
Simple‐Intensive |
Needed
Oil/Water Separator, Vegetated Filter, Sediment Basin, Water Quality Inlets |
Medium‐High |
Infiltration Trench
Synonym: Infiltration Gallery
 |
A shallow excavated trench that is backfilled with a coarse stone aggregate allowing for the temporary storage of runoff in the void space of the material. Discharge of this stored runoff occurs through infiltration into the surrounding naturally permeable soil. |
< 5 acres |
Infiltration |
nd |
TSS: High
TN: Medium/High
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High
Pathogens: High |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Yes
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: Yes |
Low $1‐$4 CF |
Medium |
Needed
Oil/Water Separator, Vegetated Filter, Sediment Basin, Water Quality Inlets |
None |
Dry Well
Synonym: Infiltration Tube, French Drain, Soak‐Away Pits, Soak Holes
 |
A smaller variation of an infiltration trench. It is a subsurface storage facility (a structural chamber or an excavated pit backfilled with a coarse stone aggregate) that receives and temporarily stores stormwater runoff. Discharge of this stored runoff occurs through infiltration into the surrounding naturally permeable soil. Due to their size, dry wells are typically designed to handle stormwater runoff from smaller drainage areas. |
< 1 acres |
Infiltration |
Throughout |
TSS: High
TN: Medium/High
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High
Pathogens: High |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Yes
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: No |
Low $1‐$4 CF |
Medium |
Needed
Oil/Water Separator, Vegetated Filter, Water Quality Inlets |
None |
Underground Infiltration
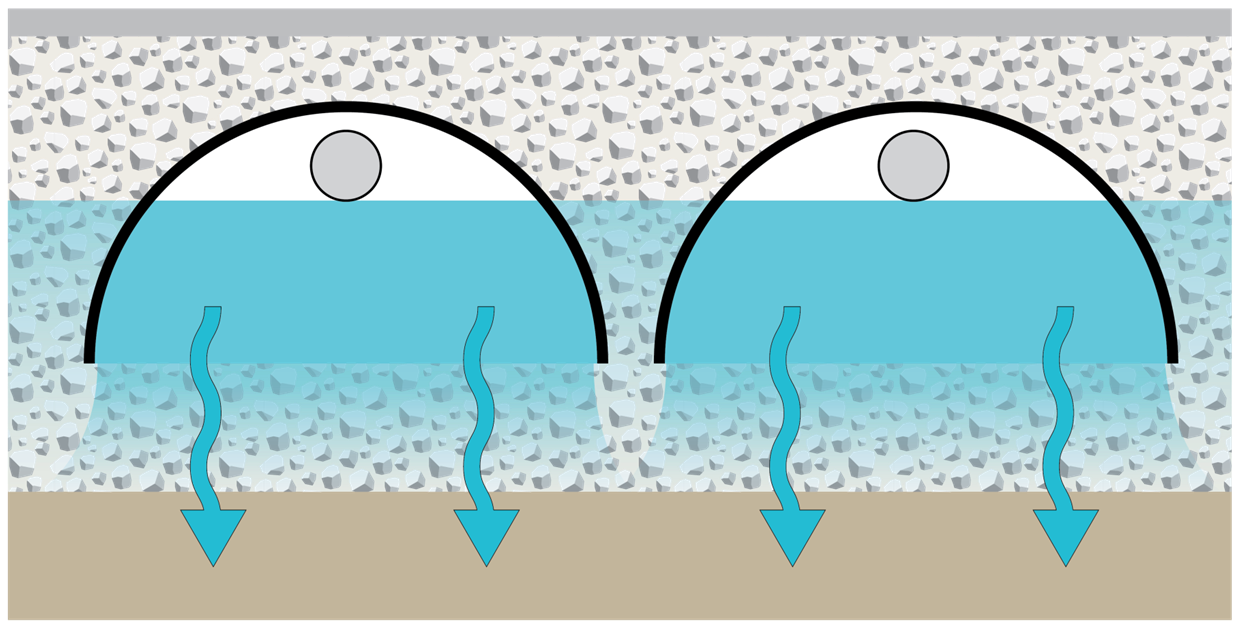 |
Several underground infiltration systems, including pre‐manufactured pipes, vaults, and modular structures, have been developed as alternatives to infiltration basins and trenches for space‐limited sites and stormwater retrofit applications. These systems are similar to infiltration basins and trenches in that they are designed to capture, temporarily store and infiltrate the design volume of stormwater over several days. Discharge of this stored runoff occurs through infiltration into the surrounding naturally permeable soil. |
< 10 acres |
Sedimentation / Infiltration / Flotation/Skimming |
End |
TSS: High
TN: Medium/High
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High
Pathogens: High |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Yes
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: Limited |
High 14 CF |
Medium |
Needed
Oil/Water Separator, Water Quality Inlets |
None |
Dry Swale with Check Dams
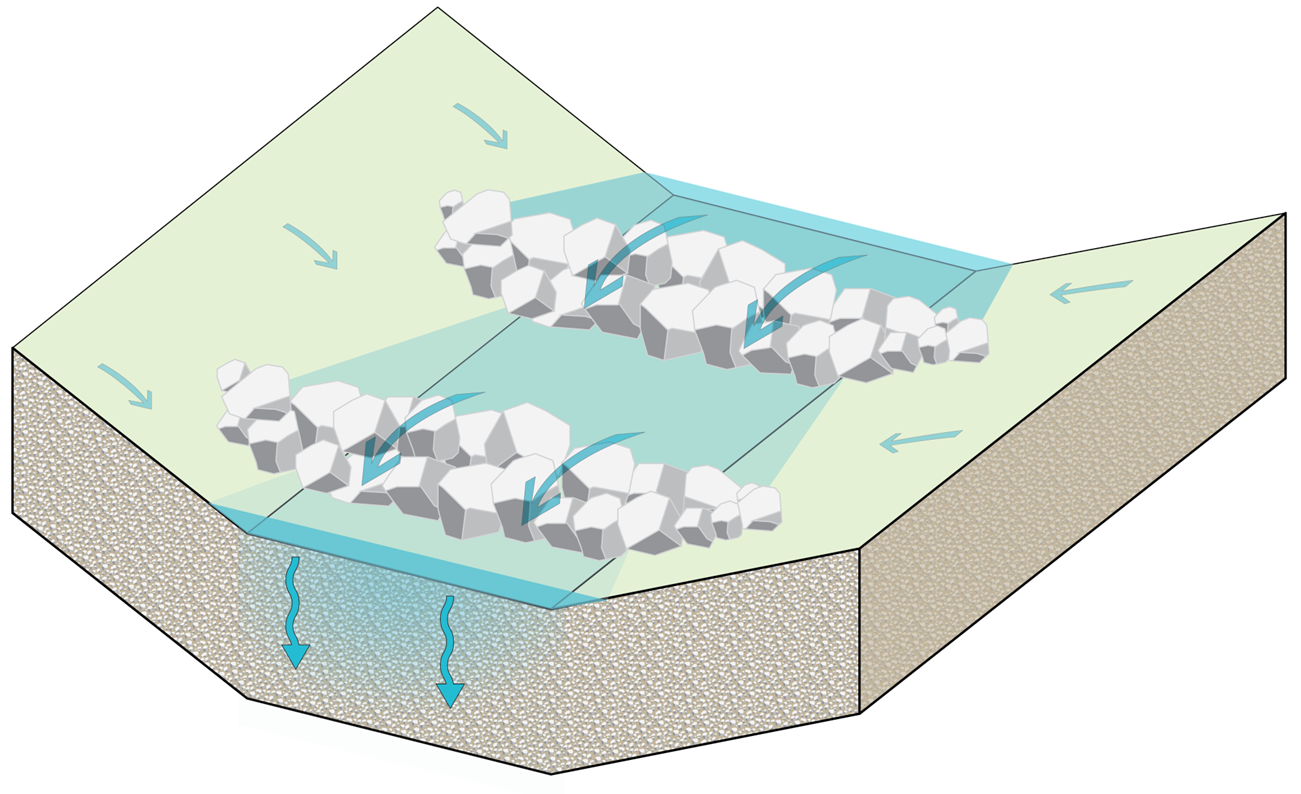 |
Similar to vegetated swales designed for stormwater conveyance, dry swales with check dams are designed as linear, multi‐celled stormwater infiltration BMPs. By incorporating earthen, structural or rock check dams, runoff is retained and infiltrated along a series of narrow, shallow basins or cells. Coarse vegetation such as decorative plantings or even turf grass slow runoff movement. This system is designed to move, store, and infiltrate runoff from impervious surfaces such as linear roadways or parking lots. |
< 1 acres |
Sedimentation / Infiltration |
Throughout |
TSS: High
TN: Low/Medium
TP: Low/Medium
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High
Pathogens: Medium |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Limited
Industrial: Yes
Retrofit: Limited
Highway/Road: Yes |
Low $.5‐$1.3 CF |
Simple‐Medium |
Needed
Vegetated Filter, Water Quality Inlets |
Low‐Medium |
Permeable Pavement
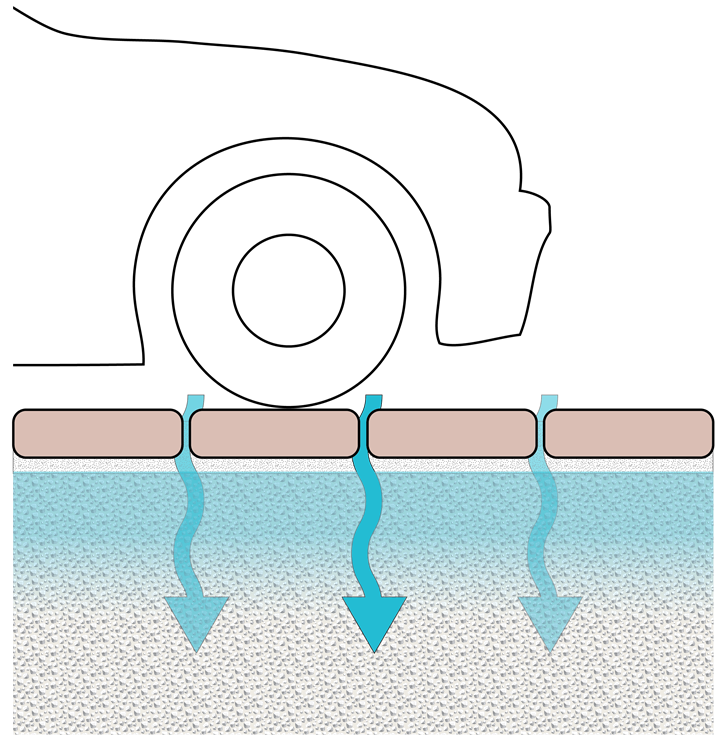 |
Permeable pavements are paving surfaces that allow stormwater runoff to filter through surface voids into an underlying stone reservoir for infiltration and/or storage. The most commonly used permeable pavement surfaces are pervious concrete, porous asphalt, and permeable interlocking concrete pavers (PICP). all permeable pavements have a similar structure, consisting of a surface pavement layer, an underlying stone aggregate reservoir layer, optional underdrains and geotextile over uncompacted soil subgrade. Discharge of this stored runoff occurs through infiltration into the surrounding naturally permeable soil. |
not to exceed twice the surface area of the permeable pavement |
Infiltration |
Beginning |
TSS: High
TN: Medium/High
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High |
Residential: Yes
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Yes
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: Limited |
Medium 3‐10 CF |
Medium |
No Pretreatment Required |
None |
Tree Trench/Tree Box
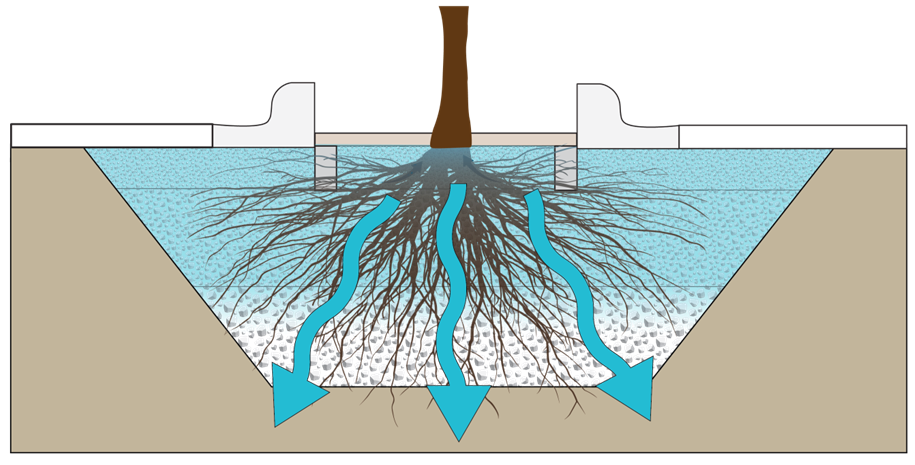 |
A system of trees that are connected by an underground infiltration structure. The system consists of a trench lined with geotextile fabric with structural stone, gravel or soil boxes in which the trees are placed. Tree systems consist of an engineered soil layer designed to treat stormwater runoff via filtration through plant and soil media, and through evapotranspiration from trees. Discharge of this stored runoff occurs through infiltration into the surrounding naturally permeable soil. |
< 5 acres |
Infiltration, Transpiration |
Throughout |
TSS: High
TN: Medium/High
TP: Medium/High
Chloride: Low
Metals: High
Oils and Grease: High
Pathogens: High |
Residential: Limited
Commercial: Yes Ultra
Urban: Yes
Industrial: Limited
Retrofit: Yes
Highway/Road: Limited |
High
$1.80 ‐ $12.70 CF based on recommended soil volume
of 1,414 CF per tree
|
Intensive |
Needed
Oil/Water Separator, Water Quality Inlets |
Medium |